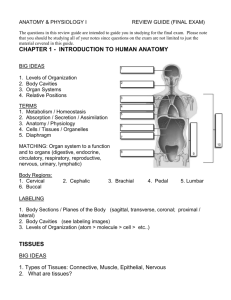
BIO 42 HUMAN BIOLOGY LECTURE MANUAL Section 1125, Spring 2016
advertisement

BIO 42 HUMAN BIOLOGY LECTURE MANUAL Section 1125, Spring 2016 Instructor- Dr. Jeffery R. Hughey Hartnell College TABLE OF CONTENTS Course Syllabus ......................................................................................... 03 Humans in the World of Biology- Chapter 1.............................................................................07 ‘Journey of Man’, Movie ......................................................................................... 09 Body Organization and the Skin- Chapter 4 ............................................................................ 11 Skeletal System and Joints- Chapter 5 ........................................................................................ 16 Muscular System- Chapter 6 ........................................................................................ 20 Respiratory System- Chapter 14 ........................................................................................ 24 Digestive System- Chapter 15 ....................................................................................... Study Guide Midterm Examination ........................................................................................ 29 26 Blood and the Circulatory System- Chapters 11, 12................................................................... 39 Nervous System- Chapters 7, 8 ........................................................................................ 44 Drugs; Senses- Chapters 8a, 9 ......................................................................................... 49 Endocrine System- Chapter 10 ......................................................................................... 54 Urinary and Reproductive Systems- Chapters 16, 17................................................................ 58 STDs, AIDS, Cancer- Chapters 17a, 21a....................................................................................... 62 Chromosomes and Inheritance- Chapters 19, 20........................................................................ 65 Study Guide Final Examination ......................................................................................... 68 2 Human Biology- Biology 42 Lecture Schedule Dr. Jeffery R. Hughey Monday 6:00-9:05 pm Date Lecture Topic Spring 2016, Hartnell College Location- N1, Section 1125 Reading January 25 Humans in the World of Biology Chapter 1 February 1 ‘Journey of Man’ Video Chapter 22 February 8 Body Organization and the Skin Chapter 4 February 15 Washington’s Day, College Closed --- February 22 Skeletal System and Joints Chapter 5 February 29 Muscular System Chapter 6 March 7 Respiratory System Chapter 14 March 14 Digestive System Chapter 15 March 21 MIDTERM EXAMINATION Study Guide Midterm Examination Due March 28- April 1 Spring Recess, College Closed --- April 4 Blood and the Circulatory System Chapters 11, 12 April 11 Nervous System Chapters 7, 8 April 18 Drugs; Senses Chapters 8a, 9 April 25 Endocrine System Chapter 10 May 2 Urinary and Reproductive Systems Chapters 16, 17 May 9 STDs, AIDS, Cancer Chapters 17a, 21a May 16 Chromosomes and Inheritance Pathology Report Due Chapters 19, 20 May 23 COMPREHENSIVE FINAL EXAMINATION (6:00-9:05 PM) Study Guide Comprehensive Final Examination Due 3 COURSE DESCRIPTION Introduction to human biology, including biochemistry, cytology, histology, organ systems, and genetics. Behaviors related to health and diseases are presented, as well as advances in biotechnology and the impact of humans on the environment. Will benefit non-majors as well as students interested in health careers. STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES 1) Given a human organ system, students will be able to list the major organs, describe their functions, and common diseases. 2) Given the human species, students will be able to describe its molecules, cells, genetics, evolution, and impact on the environment. COURSE OBJECTIVES The student will: 1. analyze how structure relates to function in biological systems, from the level of atoms and molecules up to the level of the entire organism. 2. analyze human health and disease in the context of homeostasis. 3. relate the concepts of atomic structure, chemical bonding, pH, and the properties of water. 4. compare and contrast the structures and functions of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. 5. describe the structure, function, and interactions of cellular organelles. 6. categorize the components of the plasma membrane in terms of their functions as barriers, receptors, channel proteins, and their roles in the processes of exo- and endocytosis. 7. contrast the energy yield, requirements, and end-products of aerobic vs. anaerobic cellular respiration. 8. describe and compare the glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and electron transport system pathways of cellular aerobic respiration. 9. relate the four major tissue types of the body to their structure and functions. 10. compare the organ systems of the human body in terms of their functions, locations, and major organs. 11. diagram and contrast the processes of mitosis vs. meiosis. 12. discuss the chromosomal theory of inheritance and use it to explain the principles of Mendelian and modern genetics. 13. relate transcription and translation to the overall process of gene expression. 14. evaluate modern molecular genetic techniques, their applications, and the ethical issues related to their implementation. 15. examine and analyze the effects of beneficial and disease-causing behaviors on each of the body’s organ systems. 16. outline the cellular mechanisms that lead to cancer. 17. describe and contrast the advantages and drawbacks of different types of cancer treatments. 18. list the major ways humans impact natural ecosystems. 19. propose and defend solutions to current ecological problems such as overpopulation, global warming, pollution, and scarcity/unequal distribution of vital resources. 4 INSTRUCTOR INFORMATION Instructor- Dr. Jeffery R. Hughey Office- N26C Office Telephone- (831) 770-7054 Email- jhughey@hartnell.edu Web Address- http://www.hartnell.edu/dr-jeffery-hughey-biology-instructor Office Hours- Monday 1:00-2:00 PM, Tuesday 1:00-2:00 PM, Wednesday 5:00-6:00 PM REQUIRED TEXTBOOKS • Biology of Humans: Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Goodenough, J & Mcguire, B. 2014. 5th ed. Pearson, ISBN 10: 0-321-82171-8. • Hughey, J. Biology 42 Human Biology Lecture Manual: Section 1125. Spring 2016. GRADE DETERMINATION Pathology Report Completion of 2 Study Guides Midterm Examination Comprehensive Final Examination Total GRADE A B C D F 100 pts. 100 pts. 100 pts. 100 pts. 400 pts. Total Points Earned (Percentage) 360-400 pts. (90-100%) 320-359 pts. (80-89%) 280-319 pts. (70-79%) 240-279 pts. (60-69%) 239 or fewer (59% or less) Definition Grade Points Excellent 4 Good 3 Satisfactory 2 Barely passing 1 Failing 0 EXAMINATIONS Lecture examinations will consist of a combination of multiple choice, true or false, matching, short answer, and essay questions. Questions will come from lecture material, but may also be derived from assigned readings. Supply your own Scantron 882-E form and a number 2 pencil for all examinations. PATHOLOGY REPORT Select one of the human systems and write a 2-3 page report on the common diseases of that system. The report should include the following paragraphs: normal anatomy, normal physiology, common diseases, and standard treatments for the diseases. Reports are to be submitted in single space format using "Times New Roman" font size 11. They should be written at a level that is comprehensible to your peers taking Biology 42. You may include tables and figures if you feel this will help the reader understand your system. Reports are to be handed directly in print form to Dr. Hughey at the beginning of the class on May 16, 2016, no exceptions. If you fail to submit the report on time, you will receive a zero. MAKE UP EXAMINATION POLICY If you are unable to attend an examination please notify me by telephone, email, or in person prior to the test. If you fail to contact me in advance and you miss the examination, submit a written letter signed by the authority involved (doctor, policeman) that includes their phone number and an explanation. If you have a valid excuse, I will schedule an intellectually comparable make up oral or essay examination. No make ups will be granted for the final examination without prior approval from Dr. Hughey. 5 ATTENDANCE POLICY Regular attendance and consistent study are your responsibility and the two factors that contribute most to a successful college experience. I expect you to attend all class sessions. Absences in excess of two weeks (consecutive or non-consecutive) will result in dismissal. What does that mean? IF YOU MISS 3 CLASSES, YOU WILL BE DROPPED FROM THE COURSE. DROPPING THE COURSE It is your responsibility to drop the course. Do not assume that I will submit the drop for you if you decide to stop coming to class. Students that do not officially drop the course by April 29, 2016 will receive a letter grade based on their total earned points. CLASSROOM VISITORS No one is permitted to attend this class unless he or she is a registered student. CONDUCT Please show respect for your peers and your instructor. If I observe any student performing or aiding in any of the types of misconduct listed under “Codes of Student Conduct” on page 31 of the Hartnell Catalog, that student will be dropped from the course. Disruptive behavior will not be tolerated (this includes text messaging during class). INSTRUCTIONAL SUGGESTIONS Course suggestions that will improve comprehension, retention, and cognition are warmly welcomed. Requests for less information, postponement of examinations, or easier examinations are not welcomed. SUGGESTIONS FOR EARNING A GOOD GRADE IN BIOLOGY 42 1) Review your lecture notes before coming to class 2) Study for examinations with a partner or in a group 3) Attend class and take complete notes 4) Outside of class study at least 9 hours per week 5) Study the practice questions EMERGENCY NOTIFICATIONS: In the event of a life threatening emergency call 911. • • • To report a non-life threatening incident, safety hazard, or a suspicious activity please contact campus security at 755-6888 To obtain campus status information, call the campus safety and facilities emergency status bulletin telephone number: 831-796-6222. From a campus line, simply dial 6222 AlertU subscribers can be alerted in real-time about important security information. Alert U is a SMS based emergency notification system that works on mobile phones. To sign up for AlertU, simply use the subscription tool that says "Emergency Alerts" at http://www.hartnell.edu/safety/ EVACUATION: Please note the exit(s) in the room. For evacuation, immediately heed their directions by proceeding calmly and quickly to an exterior assembly area as indicated by trained staff. Please stay back at least 200 feet from any building until the “all clear” command is issued. EMERGENCY PREPAREDNESS: The first 72 hours of a disaster are often the most difficult, but this period can be less stressful if everyone has extra supplies on hand. The college has a limited amount of emergency supplies, so students and staff should have on campus their own portable emergency kit including snacks, water, and prescription medication; this is especially important for those who may need to shelter on campus. For more information go to http://72hours.org/ and http://www.hartnell.edu/emergency/ 6 Humans in the World of Biology-Chapter 1 Science and Society The Scientific Method •A procedure used to ____________ ____________ or ______________ _______________. •A way of thinking and looking at the ______________. •A technique used to gather information and reach _____________________. Steps to the Scientific Method Scientific Method continued •Reproducibility- ____________________ experiments. •Publication- publish experiments in a ____________________ ____________________ journal. •Scientific Theory- a _______________-_____________________ explanation for some aspect of the universe that has been _____________________ confirmed through _____________________ testing. Scientific Method and Research •Clinical trials- ____________________ ____________________ on humans. Required tests before the FDA approves drugs for use by humans. 1) _______________________________ 2) _______________________________ Phase 1- _____________________________________________________________ Phase II- _____________________________________________________________ Phase III- ____________________________________________________________ All Living Things _______________ Basic _________________________ Living things contain _______________________, proteins, carbohydrates, and _________________ Living things are composed of ____________________ 7 Living things ___________________________ Living things ___________________________ Living things ___________________________ Living things maintain ___________________________ Populations of living things ___________________________and have adaptive traits Levels of Organization ________ Tissue Level ________ Ecosystem Level ________ Molecular Level ________ Individual Level ________ Biosphere Level ________ Organ System Level ________ Cellular Level ________ Community Level ________ Population Level ________ Organ Level Matching. Match the level of organization on the left to its definition on the left. ______ Molecule a. all the species in an ecosystem that can interact ______ Cell b. a single organism ______ Organ c. a community and its physical environment ______ Organ System d. group of related organs that have a common function ______ Individual e. all individuals of the same species that occupy a given area ______ Population f. two or more different tissues that perform a common function ______ Community g. the basic unit of life ______ Ecosystem h. the part of the earth that supports life ______ Biosphere i. group of similar cells that perform a common function ______ Tissue j. the chemical components of cells Classification of Humans- Homo sapiens L. 1758 Animalia Chordata Vertebrata Mammalia Primates Hominidae Homo sapiens 8 Questions for the “Journey of Man” Video 1) What is the source for Luca Cavalli-Sforza’s genetic time machine? 2) What population represents the oldest lineage of people living today? What country in Africa are they from? 3) How long ago did a small group of humans leave Africa? 4) What kind of material did the San Bushmen construct their spear tips from? 5) What is a genetic marker? 6) Why did early humans migrate out of Africa? What caused them to ‘suddenly vanish’? 7) Where did the first archaeological human remains outside of Africa show up? 8) How did the descendants of the Bushmen get to Australia? 9) How many primate species are found on Australia? 10) Where did the very first people settle in Australia? How long ago did they settle? 11) Do Aborigine’s have any evidence in their ‘Song Lines’ of a journey from Africa? 12) Do the Aborigine rock paintings from Queensland show any evidence of a journey? 13) What route did early humans take to get to Australia? 14) Why did Dr. Wells choose to analyze Y-chromosomal DNA? 15) Did Spencer find evidence for a human migration through India en route to Australia? 16) Where did the second group out of Africa migrate to? How long ago? 9 17) This second wave of people branched and went in two different directions. Where did they go? 18) How long did it take humans to get from the Middle East to Europe? Why? 19) What was the name of the hominids that arrived in Europe and lived in caves in France? 20) What route did humans take to Europe? 21) What is so interesting about Niyazov’s DNA? 22) What country is Niyazov from? Where is this country located? 23) Who are the Chukchi? Where do they live? 24) Where did the Chukchi’s ancestors come from? 25) What is an ancestor? 26) What is a descendant? 27) How long ago did people in Siberia migrate across Beringia? 28) What are Bergman’s and Allen’s rules? 29) What do the reindeer eat? What do the Chukchi eat? 30) What do the Chukchi live in? Are they nomadic? 31) What route did the ancestors of native N. and South Americans take? How many made the journey? 32) How many years did it take for humans to populate North and South America? 33) Who did the Navajo descend from? Who are the ancestors of hispanics? 10 Body Organization and Homeostasis-Chapter 4 Levels of Organization Tissue- a group of ____________________ cells that perform a common _________________. •4 Types of Tissues –___________________________ Tissue –___________________________ Tissue ___________________________ Tissue ___________________________ Tissue Epithelial Tissue •Functions- ____________________, _______________________, and _________________________. •______________________ and _____________________ epithelium –Epidermis of skin. –Lining of blood vessels, respiratory, reproductive, urinary, and GI tract. •_____________________________ epithelium –Thyroid, adrenal, sweat glands. Connective Tissue •Functions- _____________ ______________ together, provides ___________________ and protection, fills spaces, ___________________ _________________ cells, and _______________ _____________. •Composed of _____________ basic elements –____________________________ –Extracellular ______________________ •Mature Connective Tissue –_____________________ connective tissue _____________________ Tissue –_____________________ connective tissue _____________________ Tissue –_____________________ _____________________ Muscle Tissue •Functions- generate force and produce __________________________. •Composed of ___________________ ___________________ cells. •There are 3 types of muscle tissue. –___________________ , ___________________ , ___________________ Nervous Tissue •Function- convert stimuli into nerve impulses. •Composed of two types of cells. –___________________________ •Cell Body, dendrites, Axon –___________________________ Principal Systems of the Human Body •System- ____________________________________________________ that have a common function. 11 Integumentary System •Functions- _________________________, cutaneous ______________________, regulation of body temperature, ______________________, synthesis of _____________________ D. Cell types of the Epidermis •______________________- _________% –Produce keratin (protein) •______________________- _________% –Produce melanin (pigment) •______________________- _________% –Provide immunity •______________________- _________% –Form touch receptor with sensory neuron (cutaneous sensations) Keratinization and Epidermal Growth •As cells in the stratum spinosum are pushed up towards the surface they fill with keratin. •Psoriasis –Cells shed in _______ to ______ days as flaky, silvery scales. –Abnormal keratin produced. •Treatment- ointments and UV phototherapy. Skin Cancer •1 _________________________ cases diagnosed per year. •3 most common forms of skin cancer –_____________________________ carcinoma (rarely metastasize). –_____________________________ carcinoma (may metastasize). –_____________________________________ (metastasize rapidly). •Occurrence- most common cancer in young women. •Origin- arises from melanocytes, ____________ ______________________. •Key to treatment- early detection. •Risks factors- skin color, sun exposure, family history, age, and immunological status. Dermis Papillary Region •Papillary region –Top ___________% of dermis. –______________________ epidermis to dermis. –Dermal papillae. Reticular Region •Reticular region –Bottom __________% of dermis. –Provides strength, _________________________, & _____________________________. 12 Lines of Cleavage •Lines of cleavage- orientation of _______________________ ________________________. •__________________ _ _______________ form in fetus as epidermis conforms to dermal papillae. –Increase grip of hand. –___________________________ are left by sweat glands that open on tops of ridges. Pigmentation- skin color •Melanin –_____________ _____________ of melanocytes in everyone, but differing amounts of pigment •UV in sunlight increases melanin production • Carotene –__________________-_________________ pigment –Found in stratum corneum & dermis • Hemoglobin –_________________ colored, oxygen-carrying pigment in blood cells –If other pigments are not present, epidermis is translucent, causes pinkness Clinical Observations •Freckles and age spots- melanocytes in a _________________________. •Albinism- lack of tyrosinase, __________________ to produce melanin. •Vitiligo- ________________________________________ in areas of the skin, produces white patches. Accessory Structures of Skin •Epidermal derivatives –Hair, Skin Glands, Nails Hair (pili) Structure • ____________________ –Projects from the surface –Medulla, cortex, & cuticle •____________________ –Medulla, cortex, & cuticle •____________________ ____________________ –Surrounds the root with external and internal root sheaths –Bulb- base of the follicle •Papilla of the hair •Matrix Skin Glands •_______________________ gland- a gland that secretes substances into ducts that empty 1) directly onto a free surface, or at 2) covering or lining epithelium. –Sebaceous (__________) glands. Ceruminous (______________) glands. –Sudoriferous (__________________) glands. Mammary (______________) glands. 13 Sebaceous Glands •Secretory portion- dermis. •Most open onto hair shafts. •All regions of body, except palms and soles. •___________________- oily substance. –Combination of cholesterol, proteins, fats, and salts. –Keeps hair and skin ___________________ and ___________________. –___________________ growth of bacteria and fungi. Acne •Acne- ___________________ ___________________ of oil glands. –___________________ at puberty stimulate extra sebum. –___________________. –Bacterial inflammation of oil glands. Sudoriferous Glands • ___________________ glands –Most areas of skin. –Secretory portion in dermis with a duct to surface of the epidermis. –Regulate body temperature with perspiration. • ___________________ glands –Armpit and pubic regions. –Secretory portion mostly in subcutaneous layer with duct that opens onto hair follicle. –Secretions are more viscous. Ceruminous Glands •Line the external auditory meatus. •Location- _____________. •Substance- wax and fats. •Purpose- _______________ ________________ from desiccation and irritation. Epidermal Wound Healing •Basal cells _________________________ across the wound. •______________________ between basal cells stops cell migration. •Epidermal growth factor stimulates ____________ __________________________. •Full thickness of epidermis results from __________________________ cell division. Deep Wound Healing •If an injury reaches dermis, healing occurs in 4 phases –_________________phase- clot unites wound edges and WBCs. –_________________phase- re-growth of epithelial cells and the formation of scar tissue begins. –_________________phase- completion of tissue formation. –_________________phase- the scab fall off. 14 Types of Burns •First-degree –Epidermis only (________________________). •Second-degree –Destroys entire ___________________ and _____________ ______ dermis. –Fluid-filled ______________________ separate epidermis and dermis. –Epidermal derivatives are not damaged. –________________ without grafting in _____________________________ and may scar. •Third-degree –______________________ epidermis, dermis, and epidermal derivatives. –Damaged area is _________________ due to loss of sensory nerves. 15 The Skeletal System-Chapter 5 Bone Functions •Support •Protection •Assistance in movement •Mineral storage and release •Blood cell production •Triglyceride storage Bone Chemistry •________________ (25%) •________________ ________________ (~25%) –________________. •A fibrous protein that provide flexibility. •________________ ________________ (~50%) –________________ phosphate and ________________ carbonate. •Mineral salts that provide hardness. Compact bone- __________________________________________________________________. Spongy bone- ___________________________________________________________________. Bone Cell Types •________________ ________________ - stem cells. •________________________ ________ - bone building cells, secrete matrix & collagen fibers. •________________________ ________ - mature bone cells that no longer secrete matrix. •________________________ ________ - bone digestion. Histology of Compact Bone •________________ _______________- calcified matrix surrounding a vertically oriented blood vessel. •________________ - a small hollow space, contains osteocytes. •________________ - a small channel filled with extracellular fluid that connects lacunae to each other, and to the central canal. •________________ ________- a circular channel that contains blood and lymphatic vessels, and nerves. Spongy Bone •_______________________- latticework of thin plates of bone. •Spaces in between the lattice are filled with ___________, which is where blood cells and platelets form. •Location- found near ends of long bones and inside flat bones. i.e. ______________________________. Anatomy of a Long Bone Bone Growth in Width 1) _________________________________________ 3) _________________________________________ 2) ___________________________________ 4) ___________________________________ 16 Bone Growth in Length •____________________________________ –Cartilage cells in this plate divide rapidly. –Zone of proliferating cartilage. •Between ages _______-___________, the epiphyseal plates _____________. –Cartilage cells in the plate stop dividing and bone replaces the cartilage. •Growth in length stops at age 25. Factors Affecting Bone Growth 1 •__________________________ –Adequate levels of vitamins and minerals. •____________________ and ____________________ for bone growth. •Vitamin _____ for collagen formation. •Vitamins _____ and ________ for protein synthesis. Factors Affecting Bone Growth 2 •_____________________________ –During childhood growth factors stimulate cell division. •Human growth hormone (______________) •Thyroid hormones •Insulin –Sex steroids at puberty promote _____________ and _________________________________. Hormonal Abnormalities •Oversecretion of hGH during childhood produces _________________________. •Undersecretion of hGH or the thyroid hormones during childhood produces ______________________. –The _______________________________________ before normal height is reached. •_____________________________ is responsible for closing the growth plate. –Both men and women that lack estrogen receptors on cells grow taller than normal. Bone Remodeling •_______________________ ________- the ongoing replacement of old bone tissue by new bone tissue. •_______________________ and _______________________ –___________________________- removal of minerals and collagen. •4% per year in compact bone. •20% per year in spongy bone. –___________________________- deposition of minerals and collagen. Aging and Bone Tissue •_____________________________- loss of minerals. –Very rapid in women 40-45 as estrogen levels decrease. –In males, begins after age 60, but is gradual. •Decrease in protein synthesis –Decrease in growth hormone. –________________________________________________, which gives bone its tensile strength, this causes bone to become brittle and susceptible to ________________________. 17 •Cold spots indicate –Decreased metabolism of decalcified bone, __________________, and ___________________. Osteoporosis •Decreased bone mass resulting in porous bones. •Those at risk –White, thin, menopausal, smoking, drinking females with a family history. –Athletes who are not menstruating due to reduced body fat and _____________ estrogen levels. –People allergic to milk or with eating disorders whose _________ of _____________________. •Prevention or decrease in severity of osteoporosis. –Adequate _______________, ___________________________, and ________________________________________________ (for menopausal women). –Behavior when young may be most important factor. Exercise and Bone Tissue •___________________________________- the pull on bone by skeletal muscle and gravity. •Mechanical stress increases deposition of mineral ___________ and ___________________ production. Fracture- any break in a bone. •Named for shape or position of fracture line. •Common fracture types: –_________________________- skin broken. –_________________________- broken ends of bones are fragmented. –_________________________- partial fracture. –_________________________- one side of fracture driven into the interior of other side. –_________________________- distal fibular fracture. –_________________________- distal radial fracture. –_________________________- microscopic fissures from repeated strenuous activities. Developmental Anatomy Endochondral ossification begins- week _____________. Soft spots- _________________________________________________________________________. Sacrum and Coccyx Joints •Joint- _____________________________________ –_____________________________________ –_____________________________________ –_____________________________________ •Joint= articulation=arthrosis. •_________________________- the scientific study of joints. •_____________________________________- the space between articulating bones. 18 Classification of Joints •_____________________________________classification based upon: –1) Type of connective tissue holding bones together. –2) Presence or absence of space between bones. •__________________ joint- collagen fibers, no space. •__________________ joint- cartilage, no space. •__________________ joint- dense irregular connective tissue, space. •_____________________________________classification based upon movement: –__________________ - immovable. –__________________ - slightly movable. –__________________ - freely movable. Synovial Joints •Synovial cavity separates articulating bones. •Freely movable (diarthroses). •____________________________________ –Reduces friction. –Absorbs shock. •____________________________________ –Surrounds joint. –Thickenings in fibrous capsule called ligaments. •____________________________________ –Inner lining of capsule. –Secretes synovial fluid containing hyaluronic acid (__________________________). Hinge Joint •Convex surface of one bone fits into concave surface of 2nd bone. •____________________________________, like a __________________ hinge. •Movements–__________________ - decreasing the joint angle. –__________________ - increasing the angle. –__________________ - opening the joint beyond the anatomical position. •Examples –__________________, __________________, __________________, interphalangeal joints. Ball and Socket Joint •__________________ fitting into a __________________ depression. •__________________ movement. •Movement- occurs around __________________. •Examples –____________________ joint and _______________ joint 19 Muscular System-Chapter 6 Muscle Tissue Functions • • • ___________________________________________ • ___________________________________________ – Blood, lymph, urine, air, food and fluids, sperm. • ___________________________________________ – Voluntary and involuntary (shivering) contractions of skeletal muscle. ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ – Bands of smooth muscle called sphincters. Properties of Muscle Tissue • ____________________ ________________________ – Ability of skeletal muscles to respond to stimulus. Skeletal muscle contracts as a result of stimulation by nerves. • ________________________ – Ability to __________________ (shorten and generate force). • ________________________ – Ability to be ___________________ without damaging tissue. • ________________________ – Ability to ______________ to _____________ ______________ after being stretched. Smooth Muscle Tissue • Histology- spindle-shaped, nonstriated fibers with one centrally located nucleus. • Location- walls of hollow internal structures such as __________________ __________________, • • • airways to _______________, stomach, __________________, _______________________. Speed of Contraction- ____________________. Function- motion. Nervous Control- ________________________; autorhythmic. Cardiac Muscle Tissue • Histology- branched, striated fibers, with one or two centrally located nuclei and intercalated discs. • Location- ___________________________. • Speed of Contraction- _______________________. • Function- pumps blood. • Nervous Control- ________________________; autorhythmic. Anatomy of Cardiac Muscle Skeletal Muscle Tissue • Histology- long, cylindrical, striated fibers with many peripherally located nuclei. • Location- ___________________ primarily to ________________ by tendons. • Speed of Contraction- ___________________. • Function- motion, posture, heat production. • Nervous Control- ___________________; no autorhythmicity. 20 • Fascicle- __________________________________________________________________. Muscle Terminology _______________________- stable attachment of muscle to skeleton. _______________________- moveable attachment of muscle to skeleton. _______________________- decreases joint angle. _______________________- increase joint angle. _______________________- moves bone closer to midline. _______________________- moves bone away from midline. _______________________- raises a body part. _______________________- lowers a body part. • • • • • • • • Anatomy of Skeletal Muscles- Fascia Connective Tissue and Skeletal Muscles • __________________________- a sheet or broad band of fibrous connective tissue that supports and surrounds organs of the body. – _______________________- loose connective and adipose tissue that separates muscle from skin. – _______________________- dense, irregular connective tissue that lines the body wall and limbs, it also holds muscles together. Deep Fascia • 3 Layers of deep fascia – Epimysium- surrounds _________________________________________________. – Perimysium- surrounds ________________________________________________. – Endomysium- surrounds _______________________________________________. __________________________- the fleshy portion of the muscle between the tendons. • • __________________________- cord of dense, regular connective tissue that attaches a muscle to the periosteum of a bone. Muscle Fiber- ______________________________________________________________. • _______________________ - contractile elements of skeletal muscle. • _______________________- smaller structures inside the myofibrils. – _____________ (actin) filaments (_____ nanometers in diameter). – _____________ (myosin) filaments (_____ nanometers in diameter). Filaments and Sarcomeres • _________ (myosin) and _____ (actin) filaments overlap each other in a pattern that creates striations. • Sarcomeres – __________________ ___________ in skeletal and cardiac muscle fibers. – Extend from one _________ disc to another _________ disc. Sliding Filament Theory 21 Skeletal Muscle Fiber Contraction • • Motor neurons make contact with about _________________________________. _____________ _____________- a motor neuron, and all of the muscle fibers that it innervates. Neuromuscular Junction _______________ ________________ • Rigor mortis is a state of muscular rigidity that begins __-__ hours after death and lasts about __ hours. • After death, ____ ions leak out of the sarcoplasmic reticulum and allow myosin heads to bind to actin. • Since __________ synthesis has ceased, _________________ cannot detach from ____________ until proteolytic enzymes begin to digest the decomposing cells. Energy for Muscle Contraction • __________ (___________________________)- energy. – _________________________________ (anaerobic). – _________________________________ (anaerobic). – _________________________________ (aerobic). Creatine Phosphate • Creatine phosphate is _______-______X more plentiful than ATP within muscles. • Its quick breakdown provides the phosphate for creation of __________. • Sustains maximal contraction for __________ (used for ________________________). • Creatine supplementation – Gain muscle mass but ____________________________________________. Anaerobic Cellular Respiration • ATP produced from the breakdown of glucose into pyruvic acid during glycolysis. – If still anaerobic, pyruvic acid is converted to _______________ ______________. • Glycolysis can continue anaerobically to provide ATP for __________________ seconds of maximal activity (______________________________). Aerobic Cellular Respiration • ATP for any activity ________________________ _____________ 30 seconds. – If sufficient _________________ is available, pyruvic acid enters the ______________ to generate _____________, water, and heat. – Fatty acids and amino acids can also be used by the mitochondria. • Provides _______% of ___________ energy if activity lasts _____ than __________________. Athletics and Muscle Contraction • ____________________- _______________ in muscle size. – The result of forceful muscular activity over a prolonged period of time. – Results in an increase in the number of _________________ within a muscle ________________. 22 • ____________________- _______________ in muscle size. – The result of muscles not being used or only being used in weak contractions. – Causes muscle fibers to progressively shorten, leaving body parts contracted and in contorted positions. Classification of Muscle Fibers • _______________-twitch fibers – Designed for _____________________ – Contract _____________________ – Strong, _____________________contractions – _____________________in color (lots of mitochondria, myoglobin, & blood vessels) – Muscles of abdomen and back (_____________________) • _______________-twitch fibers – Designed for _____________________, powerful response – Contract _____________________ – _____________________, powerful contractions – _____________________in color (few mitochondria, myoglobin, & blood vessels) – Muscles of the _____________________ and _____________________ As we grow older... • • Skeletal muscle starts to be replaced by fibrous connective tissue and _______ beginning at age ____. _______ in fiber type from _______ to _______. Muscle Disease • _________________ ____________________- a broad term applied to a group of inherited muscular disorders characterized by progressive muscle degeneration and weakening. • Frequency- 1 in _______________ males. • Genetics- males XY, females XX. • Treatment- ______________. Mutation in DMD gene. DMD codes for dystrophin, a protein that protects muscle fibers. Abnormal Contractions • _______________- involuntary contraction of a single muscle. – ____________- a painful spasm. – ____________- multiple spasms of a skeletal muscle. • ________________- involuntary twitching of muscles normally under voluntary control. • ________________- rhythmic, involuntary contraction of opposing muscle groups. • ________________- involuntary, brief twitch of a motor unit visible under the skin. • ________________- spontaneous contraction of a single muscle fiber that is not visible under the skin. 23 The Respiratory System-Chapter 14 Functions of the Respiratory System •Gas ______________________. •Site for sense of ______________________ ______________________. •______________________ inspired air. •Aides in ______________________ ______________________. •Regulate blood ___________. Respiratory Structures •Upper respiratory tract •______________________ •______________________ ______________________ •______________________ - throat •______________________ - voice box •Lower respiratory tract •______________________ - windpipe •______________________ _____________- airways •______________________ The Nose and Sinuses •Anatomy –Nose •______________ cavities. –Composed of ______________________ and ______________________. –Sinuses •Four air-filled _____________________- in the skull. •Functions of the Nasal Cavity –______________________; filter, warm and ______________________ _______________. •Functions of the Paranasal Sinuses –Lighten skull, resonate voice, warm and moisten air. Sinuses The Pharynx- throat The Larynx- ______________________ ___________ •Passageway for air. –When food is swallowed, the ________________ moves against the ______________________ preventing food from passing into it. •The larynx contains the ______________ ____________, which are stretched across the rima glottidus. Cartilage of the Larynx Movement of Vocal Cords • Vocal folds are ______________ during breathing and ________________ during speech. 24 Trachea- windpipe •Size- 5 inches long and 1 inch in diameter. •Position- anterior to the esophagus. •Tracheal cartilage- 16 to 20 incomplete rings. •Open side faces esophagus. •Mucosa- epithelium with cilia and goblet cells. •Each bronchiole leads to an elongated space (______________________) that is enclosed by alveoli. •Alveoli- _____________ for gas exchange, _______ million in each lung, surface area of a tennis court. –A thin-walled, ________________ chamber, surrounded by a vast network of ______________. –Gases diffuse from alveoli _______________ ________________ in the capillaries. •______________________ Inhalation, air is conducted toward the lungs. •______________________ Exhalation, air is conducted away from the lungs. Inspiration Versus Expiration The Lungs •Position- lie on both sides of the heart within the _____________________ cavity; lined by pleura. –Right lung has ____ lobes –Left lung has ______ lobes •Each lobe is divided into lobules. 2 Circuits of Gas Exchange •______________________ Circuit- circulates blood through the lungs. •______________________ Circuit- circulates blood through the rest of the body. Respiration and Health ______ Sinusitus ______ Tonsillitis ______ Rhinitis ______ Laryngitis ______ Bronchitis ______ Pneumonia ______ Tuberculosis (TB) a. infection of larynx with hoarseness and inability to talk. b. infection of primary and secondary bronchi. c. inflammation and enlargement of tonsils. d. an infectious communicable disease caused by a bacterium that damages the lungs and the pleurae. e. infection of the cranial sinuses. f. acute viral or bacterial infection or inflammation of the alveoli. g. chronic or acute inflammation of the mucus membrane of the nose. Smoking and Disease •Smoking- leading cause of death in the U.S. •One cigarette- ___-____ minutes off your life, _________ years total on average. •Smoke- _________________ substances. –_____ radioactive substances. –______ carcinogens. –Poisons- hydrogen cyanide, carbon monoxide, and _________________. 25 The Digestive System-Chapter 15 Functions of the Digestive System ____ Ingestion, ____ Secretion, ____ Mixing and propulsion, ____ Digestion, ____ Absorption, ____ Defecation a. the release of water, acid, buffers, and enzymes by cells and accessory organs into the lumen. b. elimination of indigestible substances, bacteria, cells, and digested materials through the anus. c. the process of taking foods and liquid into the mouth. d. uptake of fluids, small molecules, and ions by epithelial cells lining the lumen. e. alternating contraction and relaxation of smooth muscle. f. mechanical and chemical break down of organic material into small molecules. The Digestive System •Long hollow tube- the gastrointestinal tract. –_________________- the hollow region that food, fluids, and waste travels through. •____________ _____ secrete substances into the GI tract (salivary glands, pancreas, liver, gallbladder). The Mouth •Anatomy- entrance to digestive system. •Functions ____Determine quality, ____Mechanical breakdown, ____Chemical breakdown, ___Formation of a bolus a. enzymes are secreted from the salivary glands. b. teeth. c. taste buds. d. a soft and round mass of food, formed by the tongue. Taste Buds- ____________________ _____________________ •Anatomy- located along the sides of ___________________. •Function- to determine _________________ _________________. Salivary Glands- ______________________ _____________________ Tongue- ______________________ _____________________ Pharynx- ______________________ •Anatomy –__________________ ______________ (5 inches long) that hangs from the skull. •Functions –Acts as a passageway for _______________ and _______________. –Swallow •Soft palate ________________ off the nasopharynx, and the ________________ moves under the ______________________ to cover the rima glottidus. 3 regions to the pharynx- ___________________, ___________________, ___________________ The Esophagus •Anatomy 26 –A collapsible 10 inch long ______________________ _____________________. •Functions –Secrete mucus and _________________ _________________from the pharynx to the stomach. •Rhythmic waves of muscle contraction (_________________). Stomach Anatomy •_______-shaped muscular sac with 3 layers of smooth muscle and _____________ lining the inner wall. Stomach Histology •Inner lining contains millions of _________________ _________________. –__________________________- HCL and pepsinogen, ______ _______________/day. –_______________________- protects the stomach from gastric juice, alkaline in pH. Stomach Functions •3 Major Functions –______________________ of food. –______________________ of food. –______________________ of ______________________ digestion. •Smooth muscles churn and mix food and gastric juices for 3-5 hours. –______________________- a soupy mixture of food and gastric juices. Small Intestine •Functions –______________________ digestion –Nutrient ______________________ •Anatomy –______________________ (1st 10 inches). •Enzymes •Bile •Sodium Bicarbonate –______________________ (3 feet). –______________________ (6 feet). Small Intestine Histology •The inner walls contain circular _______________, villi, and ______________________ (brush border). Pancreas •Anatomy –Exocrine tissue- produce and secrete ______________________ ______________________. •Functions –______________________- chemical digestion. Location of the Pancreas 27 Liver Functions •All absorbed nutrients are sent to the liver for processing via the hepatic portal vein. •_____________ functions to the liver –Detoxifies blood. –Stores iron and fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K). –_________________ glucose as ______________________, breaks down glycogen. –Regulates blood cholesterol. Gallbladder •Anatomy- _______________-shaped sac. •Function- ______________________ ______________________, ~50 ml. •Bile –Yellow-green color. –Components: •Water and ______________________. •Na and K salts of bile acids. •Bile pigments (______________________). Gallstones Large Intestinal Anatomy •Diameter is ~3 inches, length is ~__________ feet. •Consists of 4 specialized regions –______________________ (~3 inches long) –______________________ •Ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid. –______________________ –______________________ Large Intestine Functions •______________________ water, sodium, and potassium ions from indigestible foods. •Store ______________________. •______________________ the feces from the body. •Passes material in 18-________ hours. Note: ___________ enzymes are secreted by the large intestine. Symbiotic Bacteria Reside in the Colon •Numbers- about _____________ species. •Fecal component- accounts for ______________ of the ________________ of feces. •Nourished by ____________________ ______________________. •Metabolic processes produce _____________. •Some produce vitamins B and K. •They decompose pigmented molecules, which give feces its brown color. 28 Study guide for the midterm examination 1-68. Multiple Choice. Select the single best possible answer for each question. 1. Which of the following lists the correct order to the steps of the scientific method? a. observation, hypothesis, prediction, experiment, conclusions, analyze results b. observation, prediction, experiment, hypothesis, conclusions, analyze results c. observation, hypothesis, prediction, experiment, analyze results, conclusions d. observation, hypothesis, analyze results, prediction, experiment, conclusions e. observation, hypothesis, prediction, conclusions, experiment, analyze results 2. Approval of new drugs by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) requires _________________________. a. tests on laboratory animals b. Phase I study c. Phase II study d. Phase III study e. all of the above 3. Which of the following is not characteristic of all living things? a. they reproduce b. they are autotrophic c. they metabolize d. they are composed of cells e. they respond 4. Humans are members of the kingdom ____________________. a. Fungi b. Animalia c. Plantae d. Chordata e. Eubacteria 5. Y-chromosomal DNA and Mitochondrial DNA data ____________________. a. support similar patterns of human migration b. disagree c. are both based on the male lineage d. suggest that humans first migrated out of Europe, not Africa e. none of the above 6 The digestive system can best be described as _____________________________________. a. something that puts the ‘break’ in breakdown of foods b. a system that secretes hormones c. tissues that collectively go by the name “Henry” d. a long hollow tube with accessory organs e. none of the above 7. What kind of shape does the stomach have? a. H d. J b. P e. X c. Q 8. A group of similar cells that perform a common function are _______________________. a. cells b. atoms c. organs d. tissues e. systems 9. Two or more different tissues that perform a common function is __________________________. a. an organ b. tissue c. an organ system d. an individual e. ludicrous and does not occur in humans 29 10. Humans are members of the Family ______________________. a. Chordata b. Urochordata c. Primates d. Hominidae e. Mammalia 11. From the movie, "Journey of Man", what was so interesting about Niyazov from Kazakhstan? a. he is the direct descendant to all Australians b. he is the only living member of the Cro-Magnons c. he is the direct descendant of the Neanderthals d. he is the direct descendant of a man from 40,000 years ago from which all Europeans, North and South Americans, Asians, Russians, and some Indians came from e. none of the above 12. The San Bushmen _____________________________________________. a. are from Namibia b. carve hunting spears from bone c. represent the oldest lineage of humans alive today d. are the descendents of the people that left Africa 50,000 years ago e. all of the above 13. The second wave of people to migrate out of Africa about 45,000 years ago ___________________________. a. went to Australia via a coastal route b. migrated directly to Europe c. migrated directly to Iberia (Spain and Portugal) d. migrated to the Middle East e. none of the above 14. According to DNA data, about 18,000 years ago the ancestors of native North and South Americans migrated from _____________________________. a. Australia b. Europe c. outer space d. Siberia e. Hawaii 15. Europeans, Asians, and Americans descended from people living in ______________________________. a. northern Europe about 35,000 years ago b. central Asia about 20,000 years ago c. east Asia about 40,000 years ago d. northern Europe about 40,000 years ago e. central Asia about 40-45,000 years ago 16. The Chukchi ______________________________. a. live in Siberia b. live in Yaranga c. are nomadic d. have ancestors in central Asia e. all of the above 17. Which of the following is not one of the four major tissue types? a. epithelial b. glandular c. connective d. muscle e. nervous 18. Epithelial tissue is classified according to ______________________________. a. shape and arrangement b. shape only c. arrangement only d. shape and size e. arrangement and size 30 19. Glands are considered ______________________ tissue. a. epithelial b. nervous c. connective d. muscle e. plant 20. Exocrine glands __________________________. a. produce mucus, sweat, oil, wax, and enzymes b. secrete products directly into the bloodstream c. produce hormones d. produce thyroxine e. all of the above 21. Which of the following is not a type of mature connective tissue? a. blood b. cartilage c. bone d. muscle e. lymph 22. Dense connective tissue ________________________. a. is thick, dense, and contains many collagen fibers b. includes tendons c. includes ligaments d. attaches bone to muscle and bone to bone e. all of the above 23. Smooth muscle tissue __________________________. a. is voluntary b. occurs in muscles attached to the skeleton c. has peripherally located nuclei d. is striated e. is spindle or s-shaped 24. Which of the following is not true of nervous tissue? a. it consists of two kinds of cells b. it consists of neurons and neuroglia c. it generates and conducts nerve impulses d. it is responsible for producing hormones e. it contains neurons which have dendrites, cell bodies, and axons 25. Which of the following is not one of the three common forms of skin cancer? a. basal cell carcinoma b. squamous cell carcinoma c. merkel cell dysplasia d. malignant melanoma 26. Skin cancers can be identified using the A, B, C, D system. What does A, B, C, D stand for? a. asymmetry, brown, cyst-like, diagnose b. asymmetry, border, color, diameter c. avascular, big, callous-like, deep d. arrangement, black, cell shape, diffuse e. anything, but, cancer, dude 27. Skin consists of __________________________. a. dermis b. epidermis c. connective tissue d. epithelial tissue e. all of the above 31 28. Which of the following is not one of the four cell types found in the epidermis? a. keratinocytes b. melanocytes c. agranulocytes d. langerhan cells e. merkel cells 29. Skin color is influenced by __________________________. a. melanin b. carotene c. hemoglobin d. all of the above 30. Which of the following is not a type of skin gland? a. sebaceous b. acneceous c. sudoriferous d. ceruminous e. mammary 31. Deep wound healing does not include a ____________________ phase. a. inflammatory b. migratory c. stimulatory d. proliferative e. maturation 32. Third-degree burns _____________________________________. a. are the same as sunburns b. destroy the entire epidermis, but only part of the dermis c. can be identified by the presence of fluid-filled blisters d. heal without grafting in 3 to 4 weeks e. destroy the epidermis, dermis, and epidermal derivatives 33. Which of the following is not a type of bone cell? a. osteocyte b. osteoblast c. osteoclast d. osteoflast e. osteogenic cells 34. Which of the following is not found in compact bone tissue? a. lacunae b. central canals c. concentric lamellae d. canaliculi e. trabeculae 35. Fractures __________________________________________________________________. a. are defined as any break in a bone b. are named after the person that the break occured in, such as “Stu’s fracture” after Stu P. Idiot c. only occur in the elderly d. none of the above e. all of the above 36. Bone growth in length ________________________________________________________. a. ceases at the age of 34 in men and women b. involves periosteal ridges c. is due to division by cartilage cells in the epiphyseal growth plate d. does not require osteoblast or osteoclast activity e. none of the above 32 37. As humans age, bone tissue ____________________________________________________. a. in males very rapidly demineralizes around 40-45 years b. demineralizes and there is a decrease in protein synthesis c. increases in mass as a result of increased growth hormone d. increases collagen production which provides bones with more flexibility e. none of the above 38. Osteoporosis ________________________________________________________________. a. is due to increased bone mass and results in dense tissue b. can be prevented or decreased with diet, weight-bearing exercise, and estrogen replacement c. does not affect white, thin, menopausal, smoking, drinking females with a family history d. cannot be prevented and its symptoms cannot be decreased e. cannot be detected with a bone scan 39. Bone ______________________________________________________________________. a. is mostly composed of calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate b. is not completely solid c. consists of about 25% collagen d. consists of about 25% water e. all of the above 40. Which of the following is not a function of bone? a. protein digestion b. assistance in movement c. mineral storage and release d. blood cell production e. protection 41. Joints are points of contact between ______________________________________________. a. bone and bone b. bone and cartilage c. bone and teeth d. all of the above 42. Which of the following is a false statement about hinge joints? a. they are similar to a door hinge b. they are found at the knee, elbow, ankle c. they are responsible for flexion and extension type movements d. their movement is multiaxial e. they have concave and convex surfaces 43. Which of the following is not a function of muscle tissue? a. producing body movements b. generating heat c. regulating organ volumes d. regulating the internal environment e. moving substances within the body 44. Muscle fibers ___________________________. a. are surrounded by deep fascia b. contain myofibrils c. contain sarcomeres d. contain myosin and actin filaments e. all of the above 45. Which of the following is not true about the sliding filament theory of fiber contraction? a. thick filaments use ATP to pull thin filaments inward by means of cross bridges b. Z Discs come toward each other c. sarcomeres shorten d. thick and thin filaments do not change in length e. none of the above, they are all true 33 46. Energy for muscle contraction ______________________________. a. comes from the ATP (adenosine triphosphate) molecule b. can be acquired via creatine phosphate breakdown c. can be acquired via cellular respiration d. can be acquired via lactic acid fermentation e. all of the above 47. Starch digestion begins ____________ with the addition of salivary amylase to food particles. a. in the small intestine b. in the esophagus c. in the stomach d. in the mouth e. in the pharynx 48. In the stomach HCl in gastric juice ___________________. a. kills bacteria b. breaks down the connective tissue of meat c. activates pepsin d. all of the above e. none of the above 49. The wall of the small intestine contains circular folds with fingerlike projections called ___________ that increase surface area for absorption of nutrients. a. extensions b. flagelli c. reticuli d. villi e. milli vanilli 50. Air passing along the respiratory tract to the lungs is a. cleansed b. warmed c. moistened d. all of the above e. none of the above 51. Bronchioles terminate in elongated spaces enclosed by thin walled, spherical shaped air pockets called ______. a. glottis b. alveoli c. the larynx d. the pharynx 52. The ______________________ contains the vocal cords. a. trachea b. bronchus c. pharynx d. esophagus e. none of the above 53. Cardiac muscle tissue ____________________________________________________________________. a. is voluntary b. occurs in muscles attached to the skeleton c. lacks nuclei d. is striated and branched e. is spindle or s-shaped 54. The function(s) of the digestive system is (are) _________________________________ . a. to ingest food b. to digest food to small nutrients molecules that can pass through membranes c. to absorb nutrient molecules d. to eliminate indigestible remains e. all of the above 34 55. Food is moved through the digestive system by wave like muscular contractions by ______________________. a. peristalsis b. bolus c. chyme d. defecation e. brownian movement 56. Which of the following is not part of the large intestine? a. colon b. jejunum c. rectum d. anus e. cecum 57. Which of the following is not a major function of the respiratory system? a. gas exchange b. sound production c. filtering of inspired air d. acting as a container for olfactory receptors e. regulation of blood cholesterol 58. The nasal cavity___________________________________________________________________ . a. filters, warms, and moistens air b. produces mucus c. contains olfactory receptors d. is lined with pseudostratified epithelium e. all of the above 59. Vocal cords are___________________________________________________________________ . a. attached to cartilage b. located in the larynx c. are closed during speech d. are open during breathing e. all of the above 60. Inspiration involves the _____________________________________________________________ . a. playing of the theme song “Gonna Fly Now” from the 1976 hit movie “Rocky” b. conducting air away from the lungs c. relaxation of the diaphragm d. rib cage moving down and inward e. diaphragm contracting 61. The digestive system ______________________________________________________________ . a. consists of lymphatic vessels and accessory glands b. circulates gases and nutrients to the cells of the body c. consists of a long hollow tube termed the alimentary canal d. secretes hormones directly into the bloodstream e. filters waste and excess material from the blood 62. The small intestine _________________________________________________________________. a. regulates hormone production b. stores feces c. is the site of about 90% of nutrient absorption d. secretes pepsinogen and HCL e. none of the above 63. The mouth _______________________________________________________________________ . a. is the entrance to the digestive system b. begins digestion with mechanically breaking down food c. begins digestion with chemically breaking down food d. determines the quality of the food e. all of the above 35 64. Saliva ____________________________________________________________________________. a. is produced by salivary glands b. is slightly acidic, pH of 6.5 c. contains amylase, lipase, salts, and mucus d. is secreted on average at a rate of 1-1.5 liters per day e. all of the above 65. Which of the following is not a function of the liver? a. detoxification of blood b. storage of iron and fat-soluble vitamins c. storage of glucose as glycogen d. absorption of glycerol and fatty acids e. regulation of blood cholesterol 66. Which of the following is not true of the large intestine? a. its diameter is about 2.5 inches and its length about 5 feet b. it consists of a cecum, colon, rectum, and anus c. it absorbs water, sodium, and potassium ions from indigestible foods d. it stores the feces e. it secretes enzymes 67. The pancreas _____________________________________________________________________. a. consists of exocrine tissue only b. is about 19 inches long and about ¼ inch in width c. is directly attached by the mesocolon to the transverse, descending, and sigmoid colons d. produces insulin, glucagon, and digestive enzymes e. is the name of a new television series that stars a frog named “Fred” that likes to eat and digest pancakes 68. Which of the following is not one of the major functions of the respiratory system? a. gas exchange d. location for smell receptors b. filtration of blood e. filtration of inspired air c. sound production 69-93. True or False. Mark A for true, mark B for false. 69. The word Human comes from the latin words Humanus and Homo, which mean "man." 70. Carbohydrates are 1 of the 4 macromolecules. 71. Proteins are macromolecules with amino acid subunits. 72. The scientific method is a procedure that is used to solve problems and answer questions. 73. The scientific method is a technique that can only be applied to scientific problems. 74. A scientific theory is a broad-ranging explanation for some aspect of the universe that has been repeatedly confirmed through hypothesis testing. 75. Clinical trials involve medical studies on humans. 76. Tissues are defined as a group of similar organs that perform a common function. 77. Transitional epithelium is found in the urinary bladder. 78. Connective tissue provides support and protection, fills spaces, produces blood cells, and stores fat. 79. Cells produced in the epidermis normally shed after 28 days. 80. UV in sunlight decreases melanin production. 81. Freckles are melanocytes in a patch. 82. The skin contains sense receptors that can detect temperature, pain, touch, and pressure. 83. Bone tissue is predominantly spongy. 84. The stomach stores, liquefies, and initiates protein digestion of food. 85. The portion of a muscle that is attached to a stationary bone is its origin. 86. Each motor neuron contacts about 150 muscle fibers. 87. Atrophy is a decrease in muscle size due to a lack of or reduction in muscle usage. 88. Alveoli are thin-walled, square chambers that are surrounded by a vast network of capillaries. 89. Incomplete tracheal rings allow for the expansion of the esophagus when swallowing. 90. Laryngitis is an infection of the pharynx and causes hoarseness and inability to talk. 91. About 5,000 species of symbiotic bacteria reside in the human colon. 92. Pulling the vocal cords tight produces a lower pitch and a louder sound. 93. Vitiligo is the loss of melanocytes in areas of the skin. 36 94-103. Matching. Match the level of organization on the left to its definition on the left. 94. Molecule a. all the species in an ecosystem that can interact 95. Cell b. a single organism 96. Organ c. a community and its physical environment 97. Organ System d. group of related organs that have a common function 98. Individual e. all individuals of the same species that occupy a given area 99. Population f. two or more different tissues that perform a common function 100. Community g. the basic unit of life 101. Ecosystem h. the part of the earth that supports life 102. Biosphere i. group of similar cells that perform a common function 103. Tissue j. the chemical components of cells 104-108. Match the respiratory tract on the right to the medical term on the left. Use the tracts more than once. 104. Bronchitis a. upper respiratory tract infections 105. Tonsillitis b. lower respiratory tract infections 106. Rhinitis 107. Laryngitis 108. Pneumonia 109-113. Match the definition on the right to the digestive related medical term on the left. 109. Peptic ulcer a. inflammation of the appendix caused by an obstruction of the lumen 110. Appendicitis b. craterlike lesion caused by Helicobacter and exposure to gastric juices 111. Gallstones c. crystallization of cholesterol due to insufficient bile salts 112. Peritonitis d. inflammation of the liver caused by viruses, drugs, or chemicals 113. Hepatitis e. acute inflammation of the peritoneum 114-118. Match the definition on the right to the digestive function on the left. 114. Defecation a. alternating contraction and relaxation of smooth muscle 115. Secretion b. the release of substances by cells and accessory organs into the lumen 116. Mixing and propulsion c. elimination of indigestible substances through the anus 117. Digestion d. mechanical and chemical break down of organic material 118. Absorption e. uptake of fluids, small molecules, and ions by epithelial cells 119-123. Match the definition on the right to the term on the left. 119. Fibrous joint a. freely movable 120. Diarthrosis b. slightly movable 121. Synovial joint c. immovable 122. Synarthrosis d. collagen fibers, no space (synovial cavity absent) 123. Amphiarthrosis e. dense connective tissue, space (synovial cavity present) 124-127. Match the definition/function on the right with the epidermal cell type on the left. 124. Keratinocytes a. provide immunity 125. Melanocytes b. produce melanin 126. Merkel Cells c. produce keratin 127. Langerhan Cells d. form touch receptors with sensory neuron 128-131. Match the description on the right to the fracture type on the left. 128. Pott’s a. distal fibular fracture 129. Greenstick b. broken ends of bones are fragmented/shattered 130. Impacted c. one side of fracture is driven into the interior of the other side 131. Comminuted d. partial fracture anatomy of a long bone 132-135. Match the function on the right with the type of tissue on the left. 132. Epithelial tissue a. detects changes in conditions inside and outside of the body 133. Connective tissue b. generates the physical force needed to make body structures move 134. Muscle tissue c. covers body surfaces 135. Nervous tissue d. binds organs together, protects and supports the body and its organs 37 136. Provide an example of an everyday use of the scientific method. 137. Provide an example of the scientific method being used in science. 138. Place the following in order from largest level of classification to the smallest: Animalia, Chordata, Hominidae, Homo, Mammalia, Primates, sapiens, Vertebrata 139. How many people are diagnosed with skin cancer each year? ____________________________________ 140. ______________________ melanomas metastasize rapidly. 141. Energy (ATP) is needed for muscle contraction, how is ATP produced? 38 Blood and The Circulatory System-Chapters 11 and 12 Oxygen enters the cardiovascular system by _____________________ from ___________________ into __________________ in the capillaries, then binding to ________________________ in red blood cells. Blood •_________________- the study of blood, blood forming tissues, and the disorders associated with them. •Blood consists of _______ components –______________ (________%) •______________________ (92%). •______________________ (8%). –______________________ (________%) •______________________ (99%)- red blood cells. •______________________ (<1%)- white blood cells. •______________________ (<1%)- fragment of cytoplasm enclosed in a cell membrane. Characteristics of Blood •1 drop of blood contains _____________________ blood cells. •Blood is __________________ than water. •Blood temperature is about _______________ °F. •ph= 7.35-7.45 •Blood is about _______% of total body weight. •Blood volume in –_____________ is 5-6 liters (1.5 gallons). –_____________ is 4-5 liters (1.2 gallons). Hemoglobin •280 million molecules of hemoglobin per red blood cell. •Hemoglobin- _____________________________________________________. –_____________ protein consists of 4 polypeptide chains. –_____________ molecules are attached to each polypeptide chain. •Each heme contains an iron ion (_________) that binds to oxygen. •Transports oxygen from the lungs to cells and also transports part of the ________ _______ to the lungs. Hematocrit and Blood Disease •Hematocrit- ________________________________________________. –Female normal range •38 - 46% (average of _________%) –Male normal range •40 - 54% (average of _________%) •Testosterone •__________________- reduced RBCs or not enough hemoglobin. •__________________- blood disease. The Heart •Anatomy –____________-shaped, the size of a closed fist. 39 –The heart has: •______ atria (upper chambers). •______ ventricles (lower chambers). •______ valves. –The heart consists mostly of ________________________ (cardiac muscle tissue). •Function –Pump blood. •About ________________ gallons pumped per day. •Beats about ___________ times per minute, over 100,000 times per day. The Heart- external The Heart- internal The Cardiac Cycle Measuring Blood Pressure •______________________________ •_____________ ________________- a measure of arterial pressure in the __________________ artery. –__________________ pressure- pressure during contraction (120 mm Hg). –__________________ pressure- pressure during relaxation (80 mm Hg). The valves prevent backflow of blood Normal Heart vs. Abnormal Heart (Mitral Valve Prolapse) Internal Conduction System •______________________ node (SA-____________________). •______________________ node (AV). •Atrioventricular bundle. •______________________ fibers. Arteries vs. Veins •Each have the _________ layers. •The middle layer of an artery has more _________________ muscle. •The lumen is ____________________ in arteries. •Veins ___________________ contain valves. •Veins are blood reservoirs, hold ______%___________________________. Capillaries are sites of exchange •Capillaries are _____________________, ______________________________. –Substances are exchanged through pores and slits in the plasma membrane of the capillary. •__________________________ of capillary 40 –Blood pressure forces fluid out of the capillary. •__________________________ of capillary –Fluid is drawn back into the capillary by osmotic pressure. •Blood pressure _____________________ in capillaries. •Blood velocity _____________________ in capillaries due to greater surface area. ___________- a pressure wave created by the ejection of blood from the left ventricle into the aorta. Drainage- the flow of blood back to the heart. •Accomplished by –____________________________________________________. –____________________________________________________. –____________________________________________________. Atherosclerosis •Atherosclerosis- the buildup of __________________________. (athero- yellow; sclerosis- hardening). •Buildup of fatty deposits (_______________), particularly ____ (bad cholesterol), obstructs blood flow. •Leading cause of ________________ ___________________ (death of heart muscle cells) and ________________ (death of brain cells). Balloon Angioplasty •A _____________ and ______________ are threaded into the coronary artery to the point of blockage. •The balloon is inserted into the blocked area and _______________________. •_____________________ is pushed to the artery walls. Coronary Bypass Surgery Lymphatic System Lymphatic Components •Lymphatic ____________________ and __________________. •_____________________- fluid. •Lymphatic Organs –Red bone ___________________________ –___________________________ –___________________________ –Lymph ___________________________ –______________________________________________________ •Tonsils, adenoids & Peyer’s patches. Function #1- ______________________________________________________________________. •About ____% of what exits the arterial end is reabsorbed by the venous end of the capillaries. •The ____% that doesn’t return is excess tissue fluid, it is absorbed by the lymphatic system. 41 Lymph is returned to the bloodstream just above the heart in the _________________ __________. Function #2- ______________________________________________________________________. Function #3- Facilitating ____________________ _____________________ by recognizing microbes or abnormal cells and killing them directly or by antibodies. White Blood Cells •Function- fight infection; defend against pathogens that invade the body. –___________________ leukocytes •__________________- phagocytosis and destruction of bacteria (pus). •__________________- destroy worms, lessen the severity of allergies. •__________________- release histamine, a chemical that attracts other white blood cells to the site of infection, causes blood vessels to dilate. –____________________ leukocytes •__________________ –T cells- attack viruses, cancer cells, and transplanted tissue cells. –B cells- develop into plasma cells that secrete antibodies. –Natural killer cells- attack microbes and tumor cells. •__________________- develop into phagocytotic macrophages. Red Bone Marrow •_________________ bone- site of red and white blood cell production. –Stem cells in the marrow give rise to all ___________________ _____________________. Lymph Node Anatomy •____________-shaped organ, up to 1 inch long (1-25 mm), located along lymphatic vessels. •Scattered throughout body but concentrated near mammary glands, axillae, and the groin. •About ____________ per human. Lymph Node Function •Lymph nodes ______________-____________ ___________________. •House _____________________ that phagocytize debris, cancer cells, viruses, and bacteria. •House _____________________ that mount attacks on pathogens. Spleen •Anatomy –5 inch long organ between stomach and diaphragm. •Function –________ bacteria and viruses. The white pulp consists of mostly lymphocytes & macrophages. –___________________ old and damaged ___________________________ and pathogens from blood. The red pulp consists of mostly lymphocytes and macrophages. __________________________ Gland •Large in infants (70 g), atrophied in adult (3 g). •2 lobed organ. •Each lobule has a __________________ and __________________. 42 •The cortex is tightly packed with lymphocytes & macrophages. •Chief Function –Aid in the _______________________ of _____-lymphocytes. __________________________ __________________________ •Lymphatic nodules- oval-shaped concentrations of lymphatic tissue. –____________________- form a ring around the throat where they protect against disease organisms that are inhaled or swallowed. –_____________’s patches- keep bacteria from breaching the wall of the ________________. 43 Nervous Tissue and the Nervous System-Chapters 7, 8 Surgical Papyrus • • • • Egyptian hieroglyphics. __________th Century B.C. Oldest known ______________________ _____________________. ____________ case histories are outlined. Organization of the Nervous System • Consists of two divisions: – ___________________________ Nervous System (CNS). • _________________ and _________________. – ___________________________ Nervous System (PNS). • All nervous tissue _________________ the CNS. Nervous System • • Neurology- (neur- gr. __________________) the scientific study of the nervous system. Nervous Tissue – ___________________ (nerve cells) and ______________________________ Neurons • • Neuron- the _______________________ ___________ of the nervous system. • Neurons consist of ________________, __________________, and ________________. Numbers – _________ billion in the brain. – _________ billion in the spinal cord. Functional Classification of Neurons • Based on the direction the neurons transmit nerve impulses. – ____________________neurons • Transmit nerve impulses ___________ receptors in the skin, sense organs, muscles, joints, and organs toward the spinal cord and brain. – ____________________ • Transmit nerve impulses from one neuron to another. – ____________________neurons • Transmit nerve impulses away from the spinal cord to __________________ or glands. Nervous System Functions • ____________________ – Detecting internal and external stimuli. • Sensory receptors and ____________________ neurons • ____________________ – Processing sensory information by analyzing, storing, and making decisions regarding appropriate 44 responses. • ____________________ • ____________________ – Responding to integration decisions. • ____________________ neurons Neuroglial Cells • • • • • ___________________________ (glia= gr. glue). • _____ types of neuroglia. Half the volume of the CNS. ____________________ than neurons. ____________ X more numerous. Functions – ____________________ and ____________________ the neurons. – Maintain ____________________ in the fluid that bathes neurons. Nervous System Structures ____________________ – 12 pairs of cranial nerves and their branches. • ________________________________________ – 31 pairs of spinal nerves and their branches. • ____________________- clusters of cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. • ________________________________________- a network of nerves in the GI tract. • ________________________________________- parts of neurons or specialized cells that monitor changes in the internal or external environment. • What is a nerve? • Nerve- a ________________________________________ outside the central nervous system. Lining the Brain & Spinal Cord= Meninges • _________________- 3 layers of ________________________ lining the brain and spinal cord. – ____________________ Mater, ____________________ Mater, ____________________ Mater • The spaces between the meninges are filled with __________________________________. Gray and White Matter • ____________________ matter- aggregations of ____________________ processes. • ____________________ matter- nerve fibers with little to no myelin. The Brain • One of the largest organs in the body, _________ lbs. • Average length- 7 inches, width- 5.5, height- 4. • Center for ____________________ ____________________, ____________________ them with one another and with ____________________ ____________________. • Center for ________________, _________________, _________________, and ________________. • Chemistry- _______ % H2O, _____ % lipids, ______ % protein, 2% other. 45 • Consists of four principal parts: – __________________, ____________________, ____________________, _________________ The Cerebrum • The cerebrum is the ____________________ portion of the human brain. – __________________ with and _________________ activities of other parts of the brain. – Divided into _________ and _________ cerebral hemispheres. – The outer layer is termed the ______________ ____________. Higher Mental Functions • Memory is the ability to hold a thought in the mind or to recall events from the past. – Short-term- ___________________________. – Long-term- __________________. – Amygdala- adds __________________ overtones to memories. Brain Stem • Functions – Acts as a _________ __________ between the cerebrum and the spinal cord and cerebellum. – _______________ center for visual, auditory, and tactile responses. Cerebellum • Functions – Acts as an ______________________ center for sensory input from the eyes, ears, joints, and muscles that relates to body position. – Sends motor impulses to skeletal muscles that maintain ____________ and ____________. Diencephalon • Consists of the hypothalamus and thalamus. • Functions – __________________ for hunger, sleep, temp, water balance. – Receiving center for all __________________ _________, except smell. – Plays a role in memory and emotions. Alzheimer’s Disease • Presence of ______________ ___________ in the brain. – ___________________ _____________ envelopes axons. – Tangled axons (neurofibrillary tangles). • _____ % of adults 65-74 years in age. ______ % of those 85 and over. • Appears to be partly ________________, APOE4. Parkinson’s Disease • Characterized by _________________ or _________________. • Due to the _______________ of ______________-releasing neurons in the brain. • The lack of dopamine results in the sending out of excess signals to effectors (muscles). • ____ % of those over the age of 60. • Treatment is with __________________. 46 Spinal Cord • Anatomy – Flattened cylinder, ___________ inches in length and 3/4 inch diameter. – In adult ends at ___________. • Functions – Provides ________________ between the _________ and the _______________ nerves. – Spinal cord ___________________. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) • _________________Nervous System (somat-body) – Neurons that conduct impulses from somatic and special sense receptors to the CNS. • _________________Nervous System (enter-intestines) – Two plexuses that extend the length of the gastrointestinal tract. • _________________Nervous System (auto-self, nomic-law) – Motor neurons that convey impulses from the CNS to smooth muscle tissue, to cardiac tissue, and to glands. Somatic vs. Autonomic • The ANS pathway is a __ _____________ ____________, while the SNS is a 1 neuron pathway. Divisions of the ANS • 2 Major Divisions – _________________ • _________________ the visceral effector. – _________________ • _________________ the visceral effector. • Most body organs receive dual innervation. • Hypothalamus regulates balance between these two divisions. Sympathetic Responses • The sympathetic system dominates during physical or emotional stress conditions. – “____ situations”- _______________, _________________, excitement, ______________. • Alarm reaction- flight or fight response. – _________________ of pupils. – _________________ of _________________ rate and blood flow to muscles. – Decrease in blood flow to nonessential organs. – Increase in blood flow to skeletal and cardiac muscles. – __________________________________ and respiratory rate increases. – Blood _________________ level _________________. – Decrease in intestinal activity and inhibition of urination. – Causes genital erection. Parasympathetic Responses • _________________-and-_________________ activities. • Mechanisms that help conserve and restore body energy during times of rest. • _________________responses 47 – _________________, Lacrimation, _________________, Digestion, _________________ • 3 “decreases”- decreased – _________________, diameter of _______________, and diameter of _______________. Development of the Nervous System • Appears around _________________ weeks. • Nervous tissue is derived from the _________________ germ layer. 48 Lecture Notes- Drugs and Senses-Chapters 8a and 9 What are drugs? •________________________ substances that affect the central nervous system, causing changes in ____________________ and often ________________________. Neuromuscular Junction (NMJ) or Synapse Communication Between Neurons Normal Communication Drugs stimulate the release of a neurotransmitter Drugs inhibit the release of a neurotransmitter Drugs can bind to receptors and stimulate a response Drugs can bind to receptors and inhibit a response Alcohol •_____________________ the Central Nervous System. •First blocks GABA (__________________________ neurotransmitter). •Then blocks Glutamate (__________________________ neurotransmitter). Marijuana •_____________ is the psychoactive ingredient in marijuana. •THC binds to __________________ ________________________ in the brain. •Anandamide brings on a feeling of “internal bliss.” Stimulants ____________________ the CNS •________________________ –Increases the ____________________ ______ neurotransmitters dopamine and norepinephrine. –Interferes with reuptake of dopamine. –__________________ –__________________ or __________________ responses _____________________________ •Synthetic •_____________________________ the neurotransmitters dopamine and norepinephrine. •Active for _____________________________. •Inhibits the action of an _________________ that normally breaks down these two neurotransmitters. _____________________________ •Blocks adenosine, an _____________________________. •Adenosine inhibits neurons from releasing neurotransmitters. 49 Hallucinogenic Drugs •Alter _____________________________ _____________________________. •Increases the neurotransmitters _____________________________, norepinephrine, and acetylcholine. •Increase ______________________ levels, _____________________, ______________________. Opiates •____________________________________________. •Bind to natural receptors that are involved in the perception of pain. –____________________________ Senses •Sense of _______________________, _______________________, _______________________, _______________________, _______________________, _______________________, Types of Sensory Receptors •__________________receptor –Chemical stimuli. •Taste, Smell –_________________________- chemicals released by damaged tissue. •__________________receptor –Light stimuli. •Vision •__________________receptor –Mechanical stimuli. •Touch, Pressure, Hearing, Equilibrium •__________________receptor –Changes in temperature. •Temperature (cold and warmth receptors) Taste Buds- chemoreceptors •Numbers- _____________________ on the tongue. •Shape- ____________________-like in morphology. •Location- along the sides of papillae. •Cell Division- replaced every ______________ days. •Structure –_____________________ ____________________. •Microvilli (=taste hairs) have receptors that generate electrical signals. –Supporting cells. •Sensitivity- respond to all ___________ basic tastes, but are more sensitive to one or two than the others. Taste Buds Olfactory receptors- chemoreceptors •Numbers- ________ _____________________ olfactory receptors. •Size and Shape- similar to a _________________ __________________. •Location- _______________ of the nasal cavity. 50 •Cell Division- replaced every __________ days. •Structure –Olfactory receptor cells. •Olfactory _____________________ with odorant receptors. –Supporting cells. •Sensitivity- ________________ different types of receptors, each controlled by a different gene. Together able to detect ____________________ different odors. Olfactory Cell Location and Anatomy •Olfactory glands produce ________________ that dissolves odorants. Temporal Lobe and Limbic System Sense of Vision- photoreceptors •Numbers- _________ _______________________ photoreceptors. •Eye- 25 mm in diameter (_________________). •Eyes- contain ________% of all the sensory receptors in the human body. •The eyeball has three layers –________________- the white of the eye. –________________- contains melanin that absorbs light. –________________- contains photoreceptors. •The retina contains 2 types of photoreceptors. –________________- responsible for black and white vision. –________________- responsible for color vision. Iris and Pupil •Iris- _____________________________________ of light that enters the eye. –Smooth muscle fibers automatically adjust the size of the pupil. •Pupil- ________________________ at the center of the iris. Dilated vs. Constricted Pupils •Dilate- pupil becomes ________________________. •Constrict- pupil becomes ________________________. •______________ fold variation between constricted and dilated. Cornea and the Choroid •Cornea and Lens- refract (_________________) _______________ rays and focus light on the retina. Photoreceptors in the Eye Structure and Function of the Retina Abnormalities of the Eye •Distance Vision –_____________________________ •Close objects are seen clearly. •Long eyeball causes image to focus in front of the retina. 51 –_____________________________ •Distant objects are seen clearly. •Short eyeball causes image to focus behind retina. •_____________________________ •Image is blurred. •Irregular curvature of the cornea or lens causes light rays to focus unevenly. Abnormalities of the Eye #2 •Color blindness –Colors cannot be distinguished. –___________% of people have poor green perception. –8-10% of _______________, <1% _________________. •X-Linked. –A lack of or reduced number of one of the ____________________ types. Humors •_____________________________Humor –Embryonic, _____________________ replaced. –_____________________________ chamber. –Keeps the eyeball from collapsing. •_____________________________Humor –Drained and replaced every _____________ minutes. –_____________________________ chamber. –Supplies the cornea and lens with nutrients and oxygen. Glaucoma Cataracts •_____________________ _____________________ worldwide of blindness. •A lens becomes ______________________ or opaque. •Caused by –Natural ____________________. 50 or over. Drug reactions. –___________________________. –UVB damage. •At risk –_____________________________ (2X). •Treatment- surgery, removal and replacement of the lens. Injury. Sense of Hearing •Vibrating objects create __________________ •Pressure waves vary in –Amplitude- __________________. __________________ in the air or water= sound. Frequency- __________________. Anatomy of the Ear •There are 3 compartments in the _____________________________ 52 –____________________ compartment- vestibular canal. –____________________ compartment- cochlear duct. •Contains “Organ of Corti.” –____________________ compartment- tympanic canal. Sense of Equilibrium •____________________ Equilibrium –____________________ movement within the semicircular canals detects rotation and/or angular movement of the head. •____________________ Equilibrium –Movement of the ____________________ ____________________ within the utricle and saccule is detects movement of the head in vertical and horizontal planes. 53 Endocrine System-Chapter 10 Endocrine Glands •Endocrine glands are _________ glands and tissues that __________________________________. •Hormone –Hormon- gr. _______________________. –_____________________ ______________________. –Released in ________________ _______________________. –Affect __________________ __________________. General Functions of Hormones •Growth and development •______________________________ •______________________________ •______________________________ clock •______________________________ of cardiac and smooth muscle •Glandular ______________________________ Feedback mechanisms regulate the secretion of hormones •____________ feedback- the outcome of a process feeds back on the system, shutting down the process. •___________________feedback- one hormone has an opposite effect of another hormone on the system. •________ feedback- the outcome of a process feeds back on the system, further stimulating the process. Positive Feedback- Oxytocin (OCT) •Sucking by the infant stimulates ______________ _________________ in the nipple. •The resulting impulses travel along nerves to the ___________________________. •The hypothalamus signals the posterior ______________________ to release ____________. •OCT travels via the _______________________ to the mammary glands. •_____________________ is ejected from the mammary glands. Hypothalamus •Anatomy –Part of the diencephalon, inferior to the thalamus. •Functions –___________________ the internal environment through the ______________ nervous system. –Controls glandular secretions of the _______________________ ____________________. Pituitary Gland- anatomy •Anatomy –____________-shaped structure. –____________ inch in diameter. –Lies in the _____________ ________________ of the sphenoid bone. –___________ anatomically and functionally different portions. 54 Pineal Gland •Anatomy –_____________ cone shape. –In the _____________________________. –Covered by a _______________________ made of ____________ mater. •Function –Secretes _______________ that targets the brain; involved in regulating daily sleep-wake cycle. Thyroid Gland •Anatomy –Inferior to the larynx. –________ lobes, shield-shaped and deep red in color. –_______________ connects the lobes. –30g in weight (=1 oz.). •Functions –Increases ________________________ rate. –Regulates __________________ and ___________________________. The Thyroid Gland Secretes Thyroid Hormone (TH) •_____________________________- undersecretion of the thyroid hormone. –Fetus or infant- ______________________________. •Dwarfism and mental retardation. –Adult- ______________________________. •_____________________ gain. •_____________________. •Loss of _____________________. •_____________________ body temperature. •________________________________- oversecretion of thyroid hormone. –Adult- ______________________disease –_____________________ metabolic rate. –_____________________ of the thyroid gland. –_____________________ heart rate. –_____________________ blood pressure. –_____________________. –Treatment for Graves’ disease •Surgery. •Ingestion of radioactive _____________________. Parathyroid Glands •Anatomy- _____________ small masses at the ______________ of the thyroid gland. •Hormones- ________________________ hormones. •Target- bones, _____________________, intestines. •Hormone Functions 55 –_____________________ blood calcium level. –Antagonistic action between _____________________ and ____________________ hormones maintains blood calcium levels. Thymus Gland •Anatomy –Upper mediastinum. –Large in infants (70 g), atrophied in adult (3 g). –2 lobed organ. •Hormones- _____________________. •Target- _____________________ (white blood cells). •Hormone Functions –Promote _____________________ and _____________________ of T lymphocytes. Adrenal Glands •Anatomy –_____________________ -shaped, located at the tops of the kidneys. –Consists of adrenal _____________________ and adrenal _____________________. •Hormones and Functions –Adrenal Medulla •Epinephrine- _____________________. Fight or flight. •Norepinephrine- _____________________. “ .” –Adrenal Cortex •Sex Hormones. _____________________. •Mineralocorticoids. _____________________ & _____________________ balance. •Glucocorticoids. Regulate _____________________ levels. •Targets- all tissues. Pancreas •Anatomy –5-6 inches long, 1 inch thick. –Attached to the duodenum, posterior to the stomach. –Two tissue types. •_____________________ tissue- produce and secrete digestive juices. •_____________________ tissue- produce and secrete insulin + glucagon into the blood. •Target- _____________________, _____________________, _____________________ tissue. •Hormones and Functions –_____________________ - lowers blood sugar. –_____________________ - increases blood sugar. Testes •Anatomy –_____________________ of male. –2 _____________________ glands. –2 inches long, 1 inch in width. •Hormone- _____________________. 56 •Target- gonads, skin, _____________________, _____________________. •Hormone Function –Stimulate _____________________ sex characteristics. Ovaries •Anatomy –Abdomen of female –5 cm X 2.5 cm (2 X 1 inch). •Hormones –_____________________. –_____________________. •Targets –Gonads, skin, muscles, bones. •Hormone Function –Stimulate _____________________ sex characteristics. 57 Urinary and Reproductive Systems-Chapters 16, 17 •__________________- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. •__________________- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology, and pathology of the _________. Major Functions of the Urinary System •Filter waste and excess material from the blood. •Regulate blood volume and composition. •Help regulate blood pressure. •Store urine. •Discharge urine. Urinary Organs ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ The kidney consists of ~ 1 _______________________ ______________________ •Nephrons- the _______________________ _______________ of the kidney. •Nephrons form _____________________ •Nephrons consists of _______________ parts along with a surrounding capillary network. –Renal ____________________________ –Renal ____________________________ Nephron Anatomy Renal Corpuscle- part 1 of the Nephron 1) Renal Corpuscle- site where fluid (blood) is _________________. Water, glucose, amino acids, urea, uric acid, and salts move from the glomerulus through a filter to Bowman’s space. •____________________________- a cluster of capillaries. •____________________________- cuplike structure that surrounds the glomerulus. Renal Corpuscle Renal Tubules- part 2 of the Nephron 2) Renal Tubules- site of absorption and secretion. •_____________________________________ –Water, glucose, amino acids, and salts are ________________ from the proximal convoluted tubule by the peritubular capillary network. •_____________________________________ –At this site water and salts are ________________ by the peritubular capillary network. •_____________________________________ –At this site water and salts are ________________ ________________ by the peritubular convoluted tubule. 58 –Drugs and hydrogen ions, ________________ from the peritubular capillary network, are absorbed. Urinary Bladder •Anatomy –____________________ muscular organ. –Situated at the base of the pelvic cavity. –Capacity average= ________________________ ml. –Smaller in _______________ because the uterus occupies the space just superior to the bladder. –_____________________ (folds) are present. •Function- store urine. Urination •The bladder ____________________ with urine. •_________________ ____________________ are sent to the spinal cord and then the brain. •Motor nerve impulses are returned and signal the bladder to contract and the _______________ to open. Hormones ________________ water concentration in the blood. •Reabsorption of water- __________ gallons of filtrate enters Bowman’s space each day, ~________ is returned to the blood. •Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and Aldosterone cause water to be __________________ into the peritubular capillary network. Diuretics ________________ water concentration in the blood. •Diuretics- chemicals that increase the flow of urine. –________________ inhibits the secretion of ADH (antidiuretic hormone). –________________ increases glomerular filtration rate and decreases absorption of sodium. Maintaining Salt Balance •Absorption of Salt- >__________% of the sodium filtered at the glomerulus is returned to the blood. –Atrial natriuretic hormone (ANH)- a hormone secreted by the heart atria that promotes sodium ________________. –Aldosterone- a hormone secreted by the adrenal glands that promotes sodium ______________. Early Developmental Anatomy Male Reproductive System ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ Testes Epididymis Vas deferens Seminal vesicles Prostate gland Bulbourethral glands Urethra a. the male gonads, they produce sperm (spermatogenesis) and sex hormones. b. secrete alkaline fluid that activates the sperm. c. secrete clear and slippery fluid into semen. d. secrete fructose, citric acid, amino acids, and prostaglandins. e. ducts where sperm mature and some are stored. f. tubular structure that expels sperm. g. conduct and store sperm. Male Reproductive System 59 Semen and Sperm •Semen- mixture of sperm & seminal fluid (60% _______________ _________________, 25% prostate, and 15% from the bulbourethral). –Slightly alkaline (7.2-7.7ph). •Typical ejaculate is ______ to ______ ml in volume. •Normal sperm count is ______ to ______ million/ml. Erection and Ejaculation •Erection –Sexual stimulation ____________ the __________________ supplying the penis. –Blood enters the penis compressing the ______________ and _____________ the blood. •Ejaculation –Muscle contractions close sphincter at the base of the bladder and move fluids through vas deferens. –Once the semen is in the urethra, ________________ muscle contractions ______________ it. Hormonal Control of Testes Female Reproductive System ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ Ovaries Oviducts Uterus Uterine wall Endometrium Cervix Vagina Clitoris Mammary glands a. receives penis during sexual intercourse; serves as birth canal and menstrual flow exit. b. the female gonads, produce eggs (oogenesis) and sex hormones. c. lining of the uterus, built up and lost each month. d. milk production and ejection. e. receives and nourishes the embryo. f. contributes to sexual arousal. g. fallopian tubes, transport eggs (oocytes) to uterus by cilia that line the tubes. h. opening to uterus. i. muscle layer that stretches to accommodate the developing baby; contracts during childbirth. Mammary Glands •Modified ______________ ________________ that produce milk (lactation) –Amount of ___________________ determines ____________ of breast. –Milk-secreting _______________ open by lactiferous ___________ at the nipple. –________________ is pigmented area around nipple. –Suspensory ligaments suspend breast from deep fascia of pectoral muscles. Female Reproductive System 60 Lining of the Uterine Tubes Hormonal Concentrations Ovarian Cycle •Development of a vesicular follicle, ovulation, and development of corpus luteum, _______ day cycle. –Under control of ____________ and ____________. •________________ Phase- FSH promotes development of a follicle. •________________ Phase- LH promotes development of corpus luteum. Hormonal Control of Ovaries Uterine Cycle •________________ day cycle. ____ Days 1-5 a. Proliferative phase ____ Days 6-13 b. Ovulation ____ Day 14 c. Secretory phase ____ Days 15-28 d. Menstruation •Controlled by ________________ and ________________. •During menopause, usually between age ________ and ________ the uterine cycle ceases, and the ovaries no longer produce estrogen and progesterone. •FSH stimulates development of follicles. •LH surge triggers ovulation & corpus luteum formation. •Follicle cells secrete estrogen. •Estrogen & progesterone stimulate development of endometrium. •Corpus luteum in ovary secretes estrogen & progesterone. Infertility •Infertility is defined as the failure of a couple to achieve pregnancy after _____ year of regular, unprotected intercourse. –Estimated _________% of all couples. •Female causes, ________%. –________________ oviducts. –Endometriosis- presence of uterine tissue outside the uterus. •Male causes, ________%. –________ sperm count. –Sperm ________________. From Fertilization to Implantation 61 STDs and AIDS-Chapter 17a Chlamydia Gonorrhea Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Syphilis Oral and Genital Herpes Genital Warts HIV Infections Progress to AIDS •June of _____________ •HIV/AIDS is a global epidemic. –___________________ _________________ _______________________ estimates that AIDS has killed more than 25 ____________________ people. •Most HIV is transmitted through ____________________ contact, _____________________ drug use, or from a _____________________ woman to her _____________________. •HIV consists of ______________ and ____________________ encased in a __________________ coat. HIV enters the cell, rewrites its RNA as DNA, inserts DNA into the host chromosome, and replicates. An HIV infection progresses through several stages as _____________ __ ______ numbers decline. _____________________, _______________________, _________________________, __________________________, ______________________________ HIV Treatments •Treatments for HIV infection are designed to block specific steps in HIV’s replication cycle. •Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (___________________) –______________________ •Nucleoside analog reverse ________________________ inhibitors (NARTIs or NRTIs) •_______________________ inhibitors ______________________________- incidence, distribution, and control of disease in a population. Most prevalent where in the world? _______________________________ 62 Cancer-Chapter 21a Cancer •Cancer- a _______________________ tumor; the result of abnormal ___________ •Regulation of Cell Division _______________. –Tumor __________________________ Genes •Genes that ________________________ cell division. –Proto-___________________________ •Genes that ________________________ cell division. p53 Tumor Suppresor Gene DNA Repair is Successful DNA Repair is Unsuccessful Apoptosis Successful p53 Tumor Suppresor Gene p53 Gene 63 Pedigree •Pedigree- the _______________________ of an individual or family. Example of a p53 Hereditary Pedigree Match the tissue type with the cancer type on the right. 1. Carcinomas a. glandular epithelia such as liver, salivary glands, breast 2. Leukemias b. lymphatic tissue 3. Sarcomas c. muscle, bone, cartilage, connective tissue 4. Lymphomas d. bone marrow stem cells 5. Adenocarcinomas e. epithelial tissue that infiltrates and spreads Leading Sites of New Cancer Cases and Deaths Breast Cancer Prostate Cancer Colon Cancer Lung Cancer and Smoking Cancer’s Seven Warning Signs 64 Human Genetics-Chapters 19 and 20 The Human Life Cycle Involves •1) _________________________ –_________________________- a nuclear division of a parental cell that produces two daughter cells with the same chromosome number as the parental cell. (2N= _________) •2) _________________________ –_________________________- two nuclear divisions of a parental cell that produces four daughter cells with half the chromosome number as the parental cell. (N= _________) ____________________ ______________________- father of genetics Mendel’s Methods •_________________ crosses- an experimental cross between individuals that differ by a ________ trait. •First generation (__________). Mendel’s F1 Observations •One of the traits could be _____________ in the F1 generation= _________________________ •One of the traits was ______________ in the F1 generation= _________________________ Genetic Terminology #1 •_________________________- an organisms traits. •_________________________- an organisms genetic makeup. •_________________________- identical alleles for a gene. •_________________________- two different alleles for a gene. Genetic Terminology #2 •_________________________- a sequence of DNA that codes for a protein. •_________________________- the position on a chromosome occupied by a gene. •_________________________- one of ______ or more alternative forms of the same ______________. Mendel’s F2 Observations •Flower color –Purple:white 705:224 ________:__________ Mendel’s Dihybrid Cross •315:108:101:32 = 9:3:3:1 Mendel’s Work Yielded These Genetic Rules •Alternative versions of genes (different alleles) account for _________________ in inherited characters. •For each character, an organism inherits two alleles, 1 from the __________ and 1 from the __________. 65 •If two alleles differ, then one, the dominant allele is ________ _________ in the organism’s appearance. •The two alleles for each trait segregate during __________________ ______________________. •Alleles of a gene _____________________ _______________________ of the alleles of other genes. Punnett Square •Punnett square- a ___________________ used to predict the result of a genetic __________________. Cystic Fibrosis Pedigree- Black= cystic fibrosis Pink= carrier, Blue= five ancestral families Chorionic Villi Sampling and Amniocentesis Cri-du-chat Karyotyping Klinefelter Syndrome Complete Dominance •The dominant allele produces a ___________________ protein and the protein’s effects are apparent. •The recessive allele produces a ______ functional protein or _______ at all and the trait is not apparent. 66 Codominance- _______________ _______________ •Codominance- the _________________ of _________________ alleles are apparent. Incomplete Dominance •Incomplete dominance- inheritance in which the F1 is _____________ in phenotype between the parents. •_______________________ allele is dominant. Continuous Variation Continuous Variation is the result of ______________________ ____________________ •Continuous variation- a ________ in phenotype; indicates that a trait is controlled by two or more genes. 67 Study Guide for Comprehensive Final Examination- PART 1 General recommendations- study your notes, PowerPoint slides, the midterm exam, and study the questions from this and the other study guide. 1-46. Multiple Choice. Select the single best possible answer. 1. The brain stem ______________________________________________________. a. is part of the peripheral nervous system b. is the control center for balance and posture c. is the center for auditory, visual, and tactile responses d. is the integration center for sensory input from the eyes, ears, and joints e. all of the above 2. The limbic system ____________________________. a. is responsible for long-term memory b. includes the amygdala and hippocampus c. is considered a higher mental function d. adds emotional overtones to memory e. all of the above 3. Parkinson's disease ____________________________________________. a. is due to a tangling of the axons b. is due to amyloid plaque that envelopes axons c. can not be clinically treated d. is characterized by trembling and shaking e. is inherited and possibly due to a mutation in the APOE4 gene 4. The peripheral nervous system __________________________________. a. is subdivided into three systems b. includes the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions c. includes all nervous tissue outside the CNS d. includes the cranial and spinal nerves e. all of the above 5. The primary function of the cerebellum is _________________. a. consciousness b. muscle coordination c. temperature regulation d. sensory reception e. depth perception 6. Alcohol __________________________________________. a. depresses the Central Nervous System b. first blocks GABA (inhibitory neurotransmitter) c. blocks Glutamate (excitatory neurotransmitter) d. first affects the cerebral cortex e. all of the above 7. Neurons _____________________________________________________________. a. occur in the central nervous system, but not the peripheral nervous system b. are never myelinated c. are the functional units of cardiac muscle d. perform sensing, thinking, and remembering functions e. none of the above 8. The nervous system _________________________________________________________________________. a. contains white, gray, and black matter b. contains neurons, but nothing else c. innervates bones, but not muscles d. includes the brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexus, sensory receptors e. was first studied by Egyptians 500 years ago 68 9. Which of the following is not true of the human brain? a. it is the center for registering sensations and correlating sensations with one another b. it is the center for intellect, emotions, behavior, and memory c. it weighs approximately 3 lbs. d. it consists mostly of water and lipids e. it is part of the peripheral nervous system 10. The _____________________ node sends an impulse that initiates atrial systole. a. AV (atrioventricular) b. SL (slow-wave) c. SA (sinoatrial) d. IVC (interventricular) e. SUV (sports utility vehicle) 11. ______ pressure occurs when the ventricles of the heart are relaxing. a. systolic b. diastolic c. pulmonary d. ventricular e. none of the above 12. Hypertension and atherosclerosis are associated with _________. a. stroke b. heart attack c. aneurysm d. all of the above e. none of the above 13. The function(s) of blood is/are ________________. a. transport of oxygen and nutrients b. regulation of body temperature and pH c. fighting infections d. all of the above e. none of the above 14. Red blood cells ____________. a. have a nucleus b. lack hemoglobin c. fight infection d. all of the above e. none of the above 15. The liquid portion of blood is called _________. a. lymph b. plasma c. a cellular matrix d. blood cells e. sputum 16. Major lymphatic vessels enter the __________ veins just above the heart, bringing tissue fluid to systemic blood. a. cardiovascular b. venae cavae c. femoral d. subclavian e. submarine 17. The function(s) of blood is/are ____________________. a. transport of oxygen and nutrients b. regulation of body temperatures and pH c. fighting infections d. transport of carbon dioxide e. all of the above 69 18. The formed elements of blood ________________________. a. include red blood cells b. include platelets c. make up about 45% of the volume of whole blood d. include white blood cells e. all of the above 19. The heme-containing portion of hemoglobin is excreted by the liver into the ______ for excretion from the body. a. bile c. mucosa lining b. lymph d. blood 20. White blood cells _________________________________. a. have a nucleus c. fight infection b. lack hemoglobin d. all of the above 21. The most abundant type of white blood cells that are also the first to respond to an infection are __________. a. neutrophils c. basophils b. monocytes d. monocytes 22. Platelets function to ________________. a. plug blood vessel breaks b. start the clotting process c. do both A and B 23. The liquid portion of blood is called ______________________. a. lymph b. plasma c. a cellular matrix d. blood cells 24. Amphetamines ______________________________________________. a. decrease the neurotransmitters dopamine and norepinephrine b. interfere with the reuptake of dopamine c. are depressants d. include valium and LSD e. are active for hours 25. The lymphatic system _________________________________________________. a. takes up excess tissue fluid and returns it to the bloodstream b. absorbs fats in the intestinal villi and transports them to the bloodstream c. helps to defend the body against disease d. does all of the above 26. Localized swelling caused by accumulation of tissue fluid is called a(n) ______. a. edema b. aneurysm c. inflammation response d. node e. normal 27. Each nodule of a lymph node contains a sinus filled with __________. a. lymphocytes b. macrophages c. both A and B 28. The spleen's purpose is to __________. a. filter lymph of impurities b. filter blood of impurities c. both A and B 29. A spleen contains ________________________________. a. red pulp with blood cells and macrophages b. white pulp with lymphocytes c. both A and B 70 30. The circulatory system has ______ types of blood vessels. a. one b. two c. three d. four 31. ______ are small arteries that retain a few muscles fibers. a. venules b. capillaries c. veins d. arterioles 32. What important function(s) can be attributed to capillaries? a. exchange of substances takes place across capillary walls b. capillaries help maintain the constancy of tissue fluid c. capillaries regulate blood pressure d. both A and B are correct e. All of these are correct. 33. What is the function of valves in veins? a. valves increase the rate of blood flow. b. valves prevent the backward flow of blood. c. valves only occur in the heart. 34. The ______ act(s) as a blood reservoir. a. veins c. heart b. lungs d. capillaries 35. The venae cavae carry low-oxygen blood to the ______ of the heart. a. right ventricle c. left ventricle b. right atrium d. left atrium 36. The left ventricle sends oxygenated blood into the ______ to be distributed throughout the body. a. vena cava c. aorta b. pulmonary artery d. pulmonary vein 37. The alternating expansion and recoiling of an arterial wall can be felt as ______ . a. pressure b. flow c. a pulse d. a vibration 38. Blood pressure ______________________ with distance from the left ventricle. a. decreases b. increases c. stays the same d. increases, then decreases 39. The largest artery in the systemic circuit is the ______ . a. anterior vena cava b. pulmonary vein c. aorta d. femoral artery 40. The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between alveolar air and blood is governed by a. gravity b. blood pressure c. diffusion d. the senate e. none of the above 41. Blood ____________________________________________________________________________. a. contains plasma b. contains white and red blood cells c. contains platelets d. transports nutrients, gases, hormones, and waste e. all of the above 71 42. Marijuana __________________________________________________. a. contains THC that is a psychoactive ingredient b. stimulates dopamine c. contains THC that binds to anandamide receptors in the brain d. brings on a feeling of “internal bliss” e. all of the above 43. Which of the following is not true of nervous tissue? a. it consists of two kinds of cells b. it consists of neurons and neuroglia c. it generates and conducts nerve impulses d. it is responsible for producing hormones e. it contains neurons which have dendrites, cell bodies, and axons 44. Within the limbic system, the ______ is/are involved in learning and memory. a. pineal gland b. cerebrum c. corpus callosum d. hippocampus and amygdala e. spinal cord 45. The diencephalon ____________________________________. a. consists of the thalamus and hypothalamus b. plays a role in memory and emotions c. is the receiving center for all sensory input d. regulates hunger, sleep, and internal temperature e. all of the above 46. Which of the following is characteristic of the parasympathetic division of the autonomic system? a. inhibits the digestive tract b. dilates the bronchi c. accelerates the heart rate d. brings responses associated with a relaxed state e. all of the above 47-52. Describe the direction of blood flow as it enters and exits the heart. Label the anatomical structures associated with the route. 53-65. True or False. Mark A on your answer sheet if the statement is true, Mark B if it is false. ____ 53. Neuroglia maintain homeostasis in the fluid that bathes neurons. ____ 54. The portion of a muscle that is attached to a stationary bone is its origin. ____ 55. Each motor neuron contacts about 150 muscle fibers. ____ 56. Atrophy is a decrease in muscle size due to a lack of or reduction in muscle usage. ____ 57. Neurology is the scientific study of the nervous system. ____ 58. The nervous system performs sensory, integrative, and motor functions. ____ 59. Drugs increase and decrease the action of neurotransmitters. ____ 60. The right hemisphere of the brain is verbal and analytical. ____ 61. The stomach stores, liquefies, and initiates protein digestion of food. ____ 62. Compared to veins, arteries have more smooth muscle and therefore have larger lumens. ____ 63. Valves, respiratory movements, and muscle contractions help to return blood to the heart. ____ 64. Lymph nodes are bean shaped organs that filter lymph. ____ 65. Nervous tissue develops in 3-4 weeks in the fetus. 72 66-69. Labeled A, B, C, and D below are the four principal regions of the brain. Match each region to the anatomical name listed on the left. 66. Cerebellum 67. Cerebrum 68. Brain Stem Refer to PowerPoint image or your text for this illustration 69. Diencephalon 70-73. Match the lobes labeled below to their primary function listed left. 70. Sensory 71. Visual 72. Auditory Refer to PowerPoint image or your text for this illustration 73. Motor 74-77. Labeled A, B, C, and D below are four cardiovascular structures. Match the structure to its correct anatomical name. 74. Aorta 75. Right Atrium 76. Left Ventricle Refer to PowerPoint image or your text for this illustration 77. Pulmonary Veins 78-81. Identification. Match the letter on the diagram with the name of the structure. 78. Dendrites 79. Axon 80. Cell Body Refer to PowerPoint image or your text for this illustration 81. Schwann cell 82-84. Match the function on the right to the neuron on the left. 82. Sensory neurons a. transmit nerve impulses toward the spinal cord and brain. 83. Motor neurons b. carry nerve impulses from one neuron to another neuron. 84. Interneurons c. transmit nerve impulses away from the spinal cord to muscles or glands. __________________________________________________________________________________________ Study Guide for Comprehensive Final Examination- PART 2 Multiple choice and other miscellaneous practice questions. 1. Which of the following is not a human sense? a. touch b. taste c. smell d. talking e. hearing 2. Which of the following is not a type of sensory receptor found in humans? a. chemoreceptor b. photoreceptor c. mechanoreceptor d. thermoreceptor e. osmoreceptor 3. Many taste buds lie on the walls of small elevations on the tongue called _______________ . a. mumps b. bumps c. palate pieces d. epiglottis pyramids e. papillae 73 4. The eye _______________________________________________________. a. contains photoreceptors b. has three layers (sclera, choroid, retina) c. contains rods and cones d. contains about 70% of all sensory receptors in the human body e. all of the above 5. Which of the following is not an endocrine gland? a. salivary gland d. thymus gland b. thyroid gland e. adrenal gland c. pineal gland 6. The thyroid gland ____________________________. a. requires iodine for hormone synthesis b. alters the functioning of the thymus gland c. has no effect on metabolic rate d. regulates growth, but not development e. does not cause cretinism 7. Calcitonin ________________________________________. a. is produced by the thyroid gland b. lowers blood calcium levels c. stimulates absorption of calcium by bones d. stimulates the excretion of calcium in the urine e. all of the above 8. The parathyroid glands ________________________________________. a. are located on and behind the thymus gland b. are four small round masses at the back of the thyroid gland c. secrete hormones that target muscles d. increase blood sugar levels by secreting glucagon e. secrete thymosins 9. The pancreas ___________________________________________________. a. is partly responsible for maintaining a balanced blood sugar level b. secretes insulin and glucagon c. secretes hormones that target the liver, muscles, and adipose tissue d. consists of two tissue types e. all of the above 10. Which of the following is a false statement about the ovaries? a. they produce hormones that target other endocrine glands b. they secrete estrogen c. they are located in the abdomen d. they stimulate the formation of female sex characteristics e. they secrete progesterone 11. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) from the pituitary promotes the absorption of ______________________. a. calcium b. magnesium ions c. hydrogen ions d. water e. sperm 12. In ___________________, the pancreas is not producing insulin. a. type I diabetes b. type II diabetes c. type III diabetes d. diabetes insipidus e. none of the above 13. The thymus aids in the maturation of ___________________. a. blood d. B lymphocytes b. T lymphocytes e. erythrocytes c. basophils 74 14. Hormonal secretion can be controlled by __________________. a. antagonistic feedback b. positive feedback c. negative feedback d. all of the above e. none of the above 15. The iris _____________________________________. a. is never pigmented b. refracts light rays c. absorbs stray light rays d. contains photoreceptors e. regulates pupil size and light entrance 16. Adrenal glands _____________________________________. a. are almond sized and located at the tops of kidneys b. secrete adrenaline c. secrete noradrenaline d. secrete mineralocorticoids e. all of the above 17. Rods in the retina _____________________________________. a. are responsible for color vision b. do not absorb light, they reflect light off the cones c. are responsible for night vision d. contain blue, green, or red pigment molecules e. are concentrated in the fovea 18. Farsightedness _____________________________________. a. is due to an elongated eyeball b. means that distant objects are seen clearly c. means that distant objects are out of focus d. means that close objects are seen clearly e. is due to an irregular curvature of the cornea 19. Which of the following is a false statement with respect to color blindness? a. colors cannot be distinguished b. 75% of the people with color blindness have poor green perception c. it is an X-linked abnormality d. it occurs more frequently in males e. it is the result of having too many red, green, and blue rods 20. The vitreous humor _____________________________________. a. is drained and replaced every 90 minutes b. is the liquid in the anterior chamber of the eye c. supplies the cornea and lens with nutrients and oxygen d. is drained and replaced every 30 minutes e. none of the above 21. The human ear is responsible for ________________________________. a. hearing b. amplifying sound c. receiving sound d. transmitting sound e. all of the above 22. The cochlea _____________________________________. a. consists of 5 compartments b. contains the malleus, incus, and stapes c. contains the organ of corti d. is responsible for equilibrium e. none of the above 75 23. Gravitational equilibrium _______________________________________. a. involves otoliths and an otolithic membrane b. utricles and saccules c. detects movement of the head in vertical and horizontal planes d. requires hair cells for detection e. all of the above 24-41. True or False. Mark A on your answer sheet if the statement is true, Mark B if it is false. 24. Visible light is composed of particles of energy called photons. 25. Humans can see infrared and visible light, but can only absorb visible light. 26. Hair cells in the cupula detect rotational movement. 27. Nearsighted vision is the result of an elongated eyeball. 28. Astigmatism is an abnormality due to a shortened eyeball. 29. Color blindness is due to a lack of or reduced number of one of the cone types. 30. Loud noises can permanently damage stereocilia in the ear. 31. Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly onto the surface of the skin. 32. Astigmatisms are due to irregular curvature of the cornea or lens. 33. A sensory receptor is a structure that receives internal or external environmental stimuli. 34. Glaucoma is the leading cause worldwide of blindness. 35. Olfactory receptors are able to detect 100,000 different odors. 36. Diuretics are chemicals that decrease the flow of urine. 37. Nephrology is the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology, and pathology of the kidney. 38. In females, on average the urinary bladder is larger than males. 39. Oxytocin (OCT) is an example of a hormone with a negative feedback mechanism. 40. The hypothalamus regulates the internal environment through the autonomic nervous system. 41. The myometrium of the uterus is built up and lost each month. 42-46. Match the hormone on the right with the endocrine gland on the left that secretes it. 42. Testes a. oxytocin 43. Thyroid b. melatonin 44. Adrenal gland c. testosterone and estrogen 45. Posterior Pituitary gland d. calcitonin 46. Pineal gland e. testosterone 47-51. Match the definition on the right to the physiological response on the left. 47. Gene a. a sequence of DNA that codes for a protein 48. Locus b. an organisms traits 49. Allele c. the position on a chromosome occupied by a gene 50. Genotype d. one of 2 or more alternative forms of the same gene 51. Phenotype e. an organisms genetic makeup 52-56. Match the function on the right to the structure on the left. 52. Sclera a. admits light 53. Cornea b. refracts light rays 54. Pupil c. protects and supports the eyeball 55. Iris d. regulates light entrance 56. Lens e. refracts and focuses light rays 57-61. Match the receptor on the right with the sense/s they detect on the left. 57. Taste a. chemoreceptor 58. Smell b. photoreceptor 59. Vision c. mechanoreceptor 60. Touch d. thermoreceptor 61. Hearing 62. Equilibrium 76 63-67. Match the functions on the right to the appropriate hormone on the left. 63. Insulin a. increases blood sugar 64. Oxytocin b. secreted by the heart atria, promotes sodium excretion 65. Calcitonin (CT) c. lowers blood sugar 66. Atrial natriuretic hormone (ANH) d. causes contractions during childbirth and milk letdown (lactation) 67. Glucagon e. lowers blood calcium levels 67.5-71. Match the definitions on the right to the correct renal term on the left. 67.5. Loop of Henle a. receives fluid from several nephrons & drains it into the renal pelvis 68. Proximal convoluted tubule b. water and salts are reabsorbed by the capillary network at this site 69. Distal convoluted tubule c. cuplike structure that surrounds the glomerulus 70. Bowman’s capsule d. drugs and hydrogen ions are absorbed by this structure 71. Collecting duct e. majority of the water, glucose, AAs, & salts are reabsorbed here 72-76. Match the functions on the right to the appropriate reproduction related hormone on the left. 72. Progesterone a. triggers ovulation and testosterone production 73. Estrogen b. produced in the testes and is responsible for male characteristics 74. Luteinizing hormone (LH) c. stimulates spermatogenesis and oogenesis 75. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) d. produced by the corpus luteum, partly responsible for PMS 76. Testosterone e. produced by the follicle, stimulates development of the endometrium 77-120. Additional multiple choice questions. 77. Who is the fatherof genetics? a. Charles Darwin d. Gregor Mendel b. Jean Baptiste Lamarck e. John Klinefelter c. Newt Gingrich 78. The human life cycle involves _________________________________. a. mitosis d. reproduction b. meiosis e. all of the above c. growth 79. The dominant trait is ______________________. a. the trait that is hidden in the F1 generation b. the trait can be seen in the F1 generation c. the trait that is hidden in the F2 generation d. is the same as the recessive trait 80. An individual that is homozygous for a gene ________________. a. has three identical alleles for that gene b. always has two of the same recessive alleles c. has two different alleles for that gene d. has two identical alleles for that gene e. none of the above 81. A gene is _________________________________________________. a. a sequence of DNA that codes for a protein b. the term used to describe the constricted portion of the chromosome c. always homozygous d. always dominant e. all of the above 82. Which of the following is not one of Mendel’s genetic rules? a. alternative versions of genes (different alleles) account for variations in inherited characters b. if two alleles differ, then one, the dominant allele is fully apparent in the organism’s appearance c. for each character, an organism inherits three alleles, 2 from the mother and 1 from the father d. alleles of a gene segregate independently of the alleles of other genes e. the two alleles for each trait segregate during gamete production 77 83. A Punnett square is __________________________________________________________. a. the genetic term for a “mutated gene” b. used to determine if a gene is sex-linked c. used to determine if a piece of a chromosome is missing d. a person who gives opinions in an authoritative manner usually through the mass media e. a diagram used to predict the result of a genetic cross 84. Which of the following is not true about Gregor Mendel? a. he studied 7 characters (traits) b. he crossed garden peas c. he was an Austrian monk d. he proposed the cell theory e. he concluded that traits in peas can be predicted mathematically 85. Mendel learned from his F1 observations that ______________________. a. dominance in flower color does not exist in the pea b. homozygous recessive, in terms of flower color, was always purple c. one of his traits was always dominant and the other was recessive d. 50% of his flowers were the purple phenotype, 50% were the white phenotype e. none of the above 86. Assuming the freckle (F) form of the gene is dominant over the non freckle (f) form of the gene, what is the probability that a male with the genotype FF and a female with ff will produce a child with freckles? a. no freckles d. 75% of the time freckles b. 25% of the time freckles e. 100% of the time freckles c. 50% of the time freckles 87. Assuming the freckle (F) form of the gene is dominant over the non freckle (f) form of the gene, what is the probability that a heterozygous dominant male and a heterozygous dominant female will produce a child with freckles? a. no freckles d. 75% of the time freckles b. 25% of the time freckles e. 100% of the time freckles c. 50% of the time freckles 88. Assuming that the unattached earlobes (E) allele is dominant over attached earlobes (e) allele, what is the result of a cross between a heterozygous dominant male and a homozygous recessive female? a. 2 Ee, 1 EE, and 1 ee d. 2 Ee and 2 EE b. 1 Ee, 2 EE, and 1 ee e. none of the above, your crazy Hughey c. 2 Ee and 2 ee 89. Which of the following is not an example of polygenic inheritance? a. height d. weight and intelligence b. skin color e. hairline c. eye color 90. Cystic fibrosis ______________________________________________________________________. a. occurs in 1 in 100,000 infants in the United States b. is caused by a dominant allele c. causes excessive mucus production that leads to congestion and infection of the respiratory tract d. causes mucus clogs in the gall bladder and this leads to malnutrition e. all of the above 91. If a carrier of the cystic fibrosis gene (Cc) mates with a non-carrier (CC), what are the chances that the offspring will have the cystic fibrosis disorder? a. no chance d. 75% chance b. 25% chance e. 100% chance c. 50% chance 92. Chorionic villi sampling and amniocentesis are techniques used to ________________________. a. estimate the height of an individual before birth b. detect genetic disorders before birth c. screen the pregnant mother for genetic disorders d. determine paternity e. none of the above 78 93. Karyotyping __________________________________________________________. a. is the period of chromosome growth between the S phase and cytokinesis b. is a type of mutation found on the X chromosome c. involves transcription and translation d. involves determining the arrangement and number of an individual’s chromosomes e. is a technique used to determine polypeptide sequence 94. Incomplete dominance ___________________________________________________. a. is inheritance in which the F1 is intermediate in phenotype between the parents b. is responsible for the three different hair types of an individual (curly, wavy, straight) c. indicates that neither allele is dominant d. in the snapdragon leads to three different flower color types (red, pink, white) e. all of the above 95. Continuous variation ______________________________________________________. a. is a gradation in phenotype and indicates that a trait is controlled by two or more genes b. within the human population leads to discrete traits c. is best exemplified by the presence or absence of freckles d. is controlled by a single gene e. all of the above 96. Klinefelter syndrome ____________________________________. a. is due to the inheritance of an extra X chromosome b. individuals are often tall c. individuals do not develop secondary sex characteristics d. is diagnosed by karyotyping an individual e. all of the above 97. Based on epidemiological study, since 1985 medical cases of ___________________ are on the rise. a. gonorrhea b. chlamydia c. syphillis d. gravititis e. none of the above 98. Untreated, syphillis goes through the following 3 stages ______________, _______________, _____________. a. lesions, chancre, rash d. chancre, rash, lesions b. chancre, lesions, rash e. rash, lesions, chancre c. rash, chancre, lesions 99. Chlamydia and gonorrhea may cause _______________________. a. death d. ulcers b. pelvic inflammatory disease e. all of the above c. drain bamage 100. Chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphillis _____________________________________. a. can be cured with antibiotics b. can be cured with antiretroviral drugs c. can be cured with chemotherapy d. can be cured with radiation therapy e. cannot be cured 101. Genital herpes and genital warts ________________________________. a. are caused by bacteria b. are caused by viruses c. are caused by the human immunodeficiency virus d. are caused by fungi e. none of the above 102. The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) ______________________________. a. inserts its DNA into the chromosomes of the host cell b. fuses with the cell membrane of macrophages and helper T cells c. replicates itself inside the host cell d. contains an enzyme that rewrites RNA into DNA e. all of the above 79 103. Genital warts can lead to __________________________. a. cervical cancer b. penile cancer c. anal cancer d. all of the above e. none of the above 104. The herpes simplex virus ______________________________. a. can be treated, but not cured b. causes Kaposi’s sarcoma c. can be treated with the HAART cocktail d. can be treated with antibiotics e. none of the above 105. Most HIV is transmitted through ____________________________________________. a. drinking from the glass of an HIV positive individual b. shaking the hand of an HIV positive individual c. kissing your partner d. sexual contact, intravenous drug use, or from a pregnant woman to her fetus e. sitting on an unsanitary public toilet seat 106. Viruses consist of _____________________________. a. DNA and enzymes encased in a lipid coat b. RNA and enzymes encased in a lipid coat c. DNA and enzymes encased in a protein coat d. RNA and enzymes encased in a protein coat e. ZDNA and enzymes encased in a protein coat 107. Which of the following is not one of the stages that the HIV infection progresses through? a. asymptomatic stage d. gastrulation b. initial disease symptoms e. AIDS c. early immune failure 108. AIDS is an acronym for ________________________________________. a. acquired immune deficiency syndrome b. acquired immune deficiency syndrome c. acquired immune deficiency syndrome d. acquired immune deficiency syndrome e. all of the above 109. How is an HIV infection monitored? a. quantification of T cells/ml plasma b. quantification of red blood cells/ml plasma c. quantification of basophil cells/ml plasma d. quantification of B cells/ml plasma e. none of the above 110. NARTIs and protease inhibitors __________________________. a. are used to treat HIV b. are used to treat gonorrhea c. are cancer drugs d. are used to treat genital herpes e. none of the above 111. p53 __________________________________. a. is a tumor suppressor gene b. inhibits cell division c. is a DNA repair enzyme d. is also known as the ‘death star’ e. all of the above 80 112. Dysplasia _______________________________________________________. a. is a change in size, shape, and organization of cells b. is an early change in cells that leads to cancerous cells c. has been linked to the presence of the Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) d. can be detected with the Papanicolaou test (PAP smear) e. all of the above 113. Malignant tumors ________________________________________. a. metastasize b. are studied by oncologists c. are neoplasms d. enlarge rapidly and continuously e. all of the above 114. Carcinomas are ________________________________________________. a. cancers of the glandular epithelia, such as salivary glands b. cancers of the bone marrow c. cancers of the muscle d. cancers of the epithelial tissues that infiltrate and spread e. cancers of the lymph 115. Epidemiology is the branch of medical science that deals with _____________________________________. a. developing laboratory techniques for better spreading disease b. curing viral and bacterial diseases c. identifying sexually transmitted diseases d. incidence, distribution, and control of disease in a population e. the epidermis 116. Smoking increases the risk of ____________________________ cancer. a. mouth and lip d. kidneys and bladder b. laryngeal e. all of the above c. esophageal 81