Unit 1: The Development and Diversity of Plants
advertisement

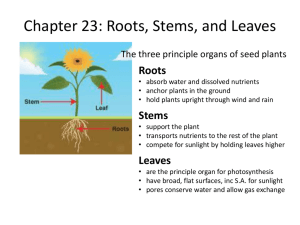
Name:___________________________ Date:_______________ Per:_______ Unit 1: The Development and Diversity of Plants 1. What makes something a plant? Characteristics of all plants: a. b. c. d. 2. What is alterations of generations? a. Alteration of generations- i. Sporophyte – ii. Gametophyte – 1. What are gametes? Characteristics of most plants: a. 3. What is photosynthesis? a. Photosynthesis- b. The general chemical formula for photosynthesis is: c. What do photosynthetic plants absorb? d. What do photosynthetic plants give off? e. What part of the plant absorbs light? f. What allows leaves to absorb light? i. Pigments – 1. Chlorophyll – 2. What colors of light does chlorophyll absorb best? 3. What colors of light does chlorophyll absorb worst? 4. Parts of photosynthesis a. What are the two parts of photosynthesis? i. Light reaction 1. What does the light reaction absorb? 2. What does the light reaction release? ii. Dark reaction – 1. What does the dark reaction absorb? 2. What does the dark reaction release? 5. Organization of plants: a. What are three levels of organization in every organism? i. Cells – ii. Tissue – iii. Organ – 6. Plant cells a. What three organelles do plant cells have that animal cells don’t? i. Vacuolesii. Chloroplasts – iii. Cell walls – 7. Plant organs a. What are the three plant organs? i. Roots – ii. Stems – 1. There are two types of stems: a. b. iii. Leaves – 8. Plant tissues a. What three tissues are in all plant organs? i. ii. iii. b. Dermal Tissue – c. Vascular Tissue – 1. Xylem – 2. Phloem – d. Ground Tissue – 9. Plant growth only happens in the roots and steams and originates from a 4 th type of tissue a. Meristem tissue – 10. Anatomy of roots a. What is the dermal tissue in roots? i. Root hairs – ii. Root hairs absorb water and nutrients from the ground using passive and active transport 1. Passive transport – a. What are some examples of passive transport? 2. Active transport – a. What are some examples of active transport? iii. How do nutrients move into roots? iv. How does water move into roots? Water in beaker 10% Water in beaker 50% Water in beaker 25% Water in root 90% Water in root 50% Water in root 75% How does water move Nutrients in beaker 90% Nutrients in root 10% How do nutrients move? How does water move Nutrients in beaker Nutrients in root How do nutrients move? 50% 50% How does water move Nutrients in beaker Nutrients in root How do nutrients move? 75% 25% b. What makes up the vascular tissue in roots? c. What is the structure and function of ground tissue in roots? i. Structure: ii. Function: 11. Anatomy of stems a. What are two types of dermal tissue in stems? i. Cork – ii. Cuticle – b. What is the function of dermal tissue in stems? c. What makes up the vascular tissue in stems? i. What are three ways water and nutrients make it from the roots through the stems to the leaves? 1. Root pressure – 2. Capillary Action – 3. Transpiration – d. What is the structure and function of ground tissue in roots? i. Structure: ii. Function: 12. Anatomy of leaves a. What is the dermal tissue on the top of the leaf? b. What is the dermal tissue on the bottom of the leaf? i. Guard cellsii. Stomata1. When the stomata are open what moves into and out of the plant? 2. What stops when the stomata are closed? 3. When would a plant: a. Close its stomata? b. Open its stomata? c. What is the structure and function of ground tissue in leaves? i. Structure: ii. Function: 13. Evolution of plants? a. What are the there ways plants are classified? i. ii. iii. b. What are the 4 main divisions of the plant kingdom? i. Mosses – ii. Fernsiii. Cone Plantsiv. Flowering Plantsc. From what organism did plants evolve? 14. Evolution of plants: Bryophytes a. Bryophytes – i. What plant organs do bryophytes lack? ii. What tissues do Bryophytes lack? iii. Why are bryophytes so small? 15. Evolution of plants: Ferns a. Ferns i. How did bryophytes evolve into ferns? ii. What do ferns and bryophytes need to reproduce? 16. Evolution of plants: Gymnosperms a. Gymnosperms – i. How did gymnosperms evolve from ferns? ii. Why are seeds more advanced than spores? iii. What are the most common gymnosperms? 1. Conifers – a. conifers produce stems made out of “soft wood” b. The resin that makes conifers smell “piney” is a adaptation that is antibacterial, antifungal, and helps stop insect attacks 17. Evolution of plants: Angiosperms a. Angiosperms – i. How did angiosperms evolve from gymnosperms? ii. What type of plant produces fruit? iii. What part of the angiosperm becomes fruit? iv. All the fruit that is consumed was produces by some type of angiosperm? v. Why don’t gymnosperms and angiosperms need water to reproduce? vi. Angiosperms have become the most diverse phyla of plants, and so botanists have developed ways of classifying them 1. Monocots vs. Dicots (based on the seed that the flowering plant produces) Monocot Flower Root Stem Leaf Dicot Flower Root Stem Leaf