Rock Cycle
advertisement
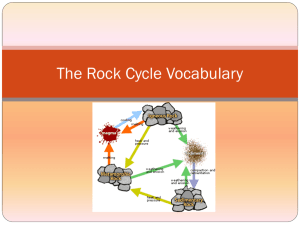
Rock Cycle Do Now 1) Move to each station that is set up with rocks. Spend two minutes at each station and list at least 4 characteristics of the rocks that you see. 2) Write down the definition for a mineral. 3) What is the difference between a rock and a mineral? Rock Definitions Igneous Rock: – Magma and Lava cools and hardens to form Sedimentary Rock: – The accumulation of various types of sediments compacted together Metamorphic Rock: – Heat and pressure cause existing rocks to change their minerals and/or shape Intermediate States: Lava & Magama Magma is still below earth. Lava is expelled from earth. Intermediate States: Sediment Broken rock fragments from the process of Weathering. Processes (There are 3!) 1. Melting and Cooling (Hardening) 2. Heat/pressure (Below Earth) Processes 3. Weathering, Eroding, Depositing, Compaction, Cementation (WEDCC) – Breaking apart of rocks into sediment fragments, and then transporting them to another location, where they settle. – Compaction: weight of overlying sediments causes pressure pushing sediments together – Cementation: minerals dissolved in water are transported and left behind to cement sediments together Do Now! Count off by 8 and get into groups. Try to arrange the rock cycle with the pieces given. Questions to ponder… What does the rock cycle that you created tell us about the fate of rocks? How are rocks classified? How does this different from the classification of minerals? Can you figure out which station held which of the three types of rock?