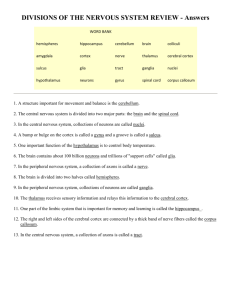
Document 14194734
advertisement

What we will learn: • Facts about the brain • Ways to help your own learning • Ways to help your own brain development Modern Myths… (We will explore) • • • • People only use 10% of their brain People are either right-brained or leftbrained which explains their natural abilities Everything people have ever experienced is stored somewhere in their brain At birth people have all the neurons that they will ever have Adapted from Pat Wolfe, 2001 Brain Research • Describes the human brain and how it works • Uses science and scientific research to help learning Become a Researcher… • Now it’s time to conduct some brain research. • Please go to my teacher website • Click on Brain Research • I will provide you with the • directions Let’s Check Our Answer… • 2 major parts of the nervous system – Central – Peripheral • Another name for “nerve cell” – Neuron • 2 structures of Central Nervous System – Brain and spinal code Let’s Check Our Answers • How much does the brain weight? – 3 pounds • About how many nerve cells are in the brain? – 100 billion • The bump in the cortex is called – gyrus • The grove in the cortex is called – sulcus Let’s Check Our Answers • The area of the brain responsible for learning is the – hippocampus Cerebral cortex Corpus callosum midbrain cerebellum thalamus pons Spinal cord medulla Let’s Check Our Answers • The four lobes – – – – Frontal Parietal Temporal occipital • 2 functions of left side of the brain; – Language and math Let’s Check Our Answers • 2 functions of left side of the brain – music and facial recognition • The structure that connects right and left hemispheres – Corpus callosum • The left side of the brain controls language Let’s Check Our Answers • • • • Famous left-handers http://www.indiana.edu/~primate/left.html Health tips: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/brainf it.html Day 2 Let’s start with a review… Human Brain • About 3 pounds • 78% water, 10% fat, 8% protein • Less than 2.5% of body’s weight • Uses 20% of body’s energy “The nerve cell, or neuron resembles a miniature tree…” (p. 21) Diamond & Hopson, 1998 Brain is changed by environment • Dendrites can grow at any age • Synaptic connections occur at any age; but easiest when you are young • Brain is adaptable Plasticity ‘Use it or Lose it’ Synaptic Density 6 year old 2 year old Diamond & Hopson, 1998 Memory Processes Sensory Holds information for a fraction of a second Perception and attention Short Term Long Term Information remains Retrieval: for about 15-20 seconds More frequent activation of neuron Cocktail Party Effect patterns leads to more efficiency Chunking Rehearsal: Rote and Elaborative Putting the Brain to Work Attention The brain is much more like a sieve than a sponge… (Sousa, 1995) Approximately 99% of all information entering through the senses is dropped (Wolfe, 2001) Things that get the brain’s attention are meaning and emotion Brain Based Brain parts Function Cerebral cortex Thinking, planning, decision making Cerebellum Balance coordination Brain stem Controls breathing and heart rate Hippocampus Learning and memory Amygdala Emotions, mood, energy Examples http://reconstructors.rice.edu/recon2/lessons/reconII_TM1_19.pdf PET Brain Scan (left side of brain) Day 3 Let’s start with a review…