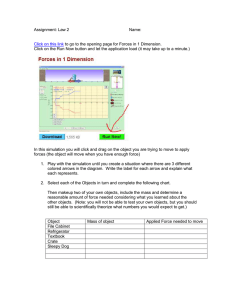
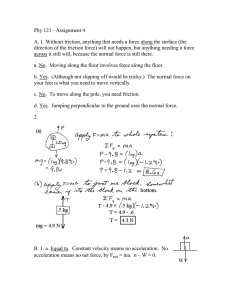
Chapter 4 - Part II Newton’s Second Law
advertisement

Chapter 4 - Part II Newton’s Second Law Mass and Weight • Mass is the amount of material in an object. • Weight is the force on a mass resulting from gravity. • Mass and weight are directly proportional to one another. • What net force does a sliding crate experience when you exert a force of 110N and friction between the crate and floor is 100 N? Mass Resists Acceleration • How much force is needed to shake a brick in space compared to the Earth? • What is Overdrive in an automatic car? • Would it be easier to push an elephant on a skateboard or a dog on roller skates? Newton’s Second Law • “The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object, is in the direction of the net force, and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object.” • acceleration = Net Force/mass • Forces are vectors - they have magnitude and direction. Free Fall • In a vacuum objects fall at the same speed independent of their masses or shapes. • For real world simulations this is not true. Non-Free Fall • When drag force is less then weight force free fall occurs. • Air drag force depends on: • Surface area that air must plow through • Speed of the object • Terminal Velocity happens when the drag force = the falling force. Mathematics of Drag • Acceleration = F/m = DV/Dt • When falling in air: a = Fnet/m = (mg - R)/m • R is a number with force units based on the geometry and velocity of the object. Brain Teasers for Thursday • If one bullet is fired parallel to the ground and a second is dropped at the same time from the same height, which will hit the ground first? Definitions • Mass - The quantity of material in an object. • Weight - The force due to gravity on an object • Force - Any influence that can cause an object to accelerate. • Friction - the resistive force that opposes the motion or attempted motion of an object. Definitions • Free Fall - Motion under the influence of gravitational pull only. • Terminal velocity - the speed at which the acceleration of a falling object is balanced by air resistance. Forces and Acceleration • F = m*a • SF is a powerful tool in statics and dynamics. • Forces that detract from a system are called non-conservative forces. Friction • Occurs when two materials come into contact. • Friction is the result of imperfections material surfaces. • Friction always opposes motion. SF and Friction • Friction is always opposite the path of motion. • The friction force is based on the normal or support force. • Static friction is greater then dynamic friction. Drag • Fluid friction is called drag. • Drag is dependant on speed and contact area. • Drag in air is approximately velocity2.