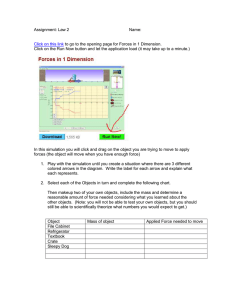
Chapter 4 Friction
advertisement

Chapter 4 Friction Definitions • Mass - The quantity of material in an object. • Weight - The force due to gravity on an object • Force - Any influence that can cause an object to accelerate. • Friction - the resistive force that opposes the motion or attempted motion of an object. Definitions • Free Fall - Motion under the influence of gravitational pull only. • Terminal velocity - the speed at which the acceleration of a falling object is balanced by air resistance. Forces and Acceleration • F = m*a • SF is a powerful tool in statics and dynamics. • Forces that detract from a system are called non-conservative forces. Friction • Occurs when two materials come into contact. • Friction is the result of imperfections material surfaces. • Friction always opposes motion. SF and Friction • Friction is always opposite the path of motion. • The friction force is based on the normal or support force. • Static friction is greater then dynamic friction. Drag • Fluid friction is called drag. • Drag is dependant on speed and contact area. • Drag in air is approximately velocity2.