Beginning of Life
advertisement

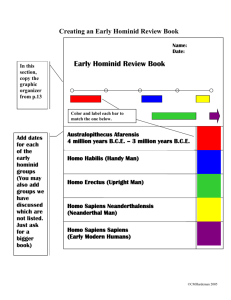
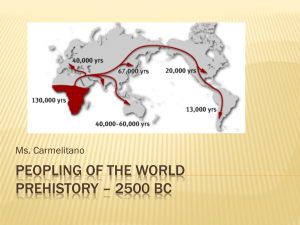
Beginning of Life Composition of early atmosphere Methane, ammonia, hydrogen; no oxygen; no life Miller/Urey Experiment Sent electrical sparks through a mixture of gases present in early atmosphere Created amino acids and sugars-molecules needed for life Evolution of Life Evolution of life forms Pre-cells- molecules organized and surrounded by fats; molecules pass through fatty membrane First living cells-Bacteria Pre-cells take in energy and reproduce Staphylococcus Bacteria Evolution of Life Heterotrophs Need energy from outside source Autotrophs Chlorophyll; use sun’s energy in photosynthesis Eukaryotes Evolve Oxygen increases in atmosphere; complex organisms evolve Algae Hallucigenia Ozone Layer Forms •Lightning converts O2 to O3 (15 miles above us) •Blocks UV light •Explosion of life Classification for Humans Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Primates Family: Pongidae (Great Apes) Genus: Homo Species: Sapiens Homo sapian The Primate Family Tree 2 Suborders of Primates Prosimians : “Before monkeys” Tree Dwelling Primates Lemurs & Tarsiers Retain claws, long snout Found in Madagascar Tarsier Lemur The Primate Family Tree 2 Suborders of Primates Anthropoids New World Monkeys (Capuchins, Howler’s) Old World Monkeys (Macaques) Humans & Apes (Gorillas, Orangutans) Trends in Primate Evolution Dexterity of Hands Opposable thumb for grasping Upright Posture Keeps hands free; plant harvesting Vision Stereoscopic; allows for Depth perception; food ID Brain -> Large Brain; Used to obtain food; get mates Infant Care Large investment = greater success Teeth Multiple Teeth types Appearance of Homo Sapiens Humans and Chimpanzee lineages split 6 million years ago Proconsul Fossil- 18mya-6mya Proconsul- 18mya-6mya Australopithecus Afarensis “Lucy” 3-4.5 million years ago A. afarensis walked on 2 feet (bipedalism) Small Brain (like a chimp) Likely vegetarians More than 1 species of Australopithecines found. Most species die out about 1-2 million years ago Homo habilis 1. 2. 3. 4. 2 million years ago Slightly Larger Brain. Some speech Simple Tools Ate plants and butchered Animals Homo erectus (upright) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1 million years ago complex tools (hand ax) Large brain (abstract thought; self consciousness) Spreads around the world Uses fire Neanderthals (230,000-29,000 years ago) •Early group of Homo sapiens? •Found in Middle east, Africa, Asia •Social Hunters (cooperative groups of 30-40) •Stone Tools (points, borers) •Cared for sick, wounded, and dead •Capable of language Homo sapians Early modern humans called Cro-Magnons • 200,000 years ago to present • Hey, that’s me! Other Hominid Fossils Ar. ramadus A. boisei A. robustus Characteristics of Humans •Bipedalism Walking on 2 feet •Shorter toes for standing upright •Enlarged Brain devoted toward complex speech •Smaller Pelvis than other hominids How and When did our species supplant H. Erectus? Multiregional v. Single Origin Theory Comparisons Among Hominids Hominid Pelvis Shallow and rounded Femurs tilt inward Body weigh transferred down through knees Bipedalism Hominid Spine Curved like an “S” Thoracic cage flattened Transmits weight to the legs Balanced center of gravity Hominid Brain Enlarged Areas devoted to complex speech and communication