III. Metamorphic Rocks – Rocks formed by chemical change
advertisement

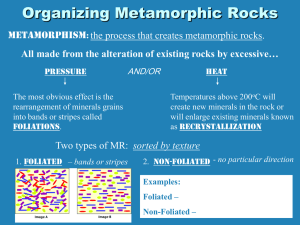
III. Metamorphic Rocks – Rocks formed by great heat (100 – 800 Celsius) and pressure causing chemical change They can be formed by one of two ways A. Contact Metamorphism – a change of an existing rock by being in close proximity to a mass of magma B. Regional Metamorphism – A change in a large area of rock due to heat and pressure from tectonic activity (movements in the earth’s crust) Metamorphic rocks are classified into two groups 1. Foliated – rocks showing bands of light and dark layers due to the arrangement of minerals. Ex. Shale (sed) Slate PhylliteSchist Ex. Granite (igneous) Gneiss 2. Non-foliated – Rocks without bands of mineral crystals Ex. Limestone (sed) Marble Ex. Sandstone (sed) Quartzite III. Metamorphic Rocks – Rocks formed by great heat and pressure causing chemical change They can be formed by one of two ways A. Contact Metamorphism – B. Regional Metamorphism – Metamorphic rocks are classified into two groups 1. Foliated – rocks showing bands of light and dark layers due to the arrangement of minerals. Ex. Ex. 2. Non-foliated – Rocks without bands of mineral crystals Ex. Ex.