Weather and Weather Forecasting Unit 4 Lesson 5 Notes Answer Key
advertisement

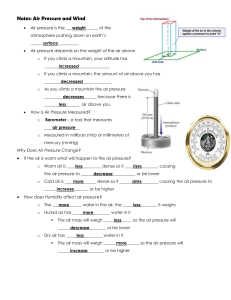
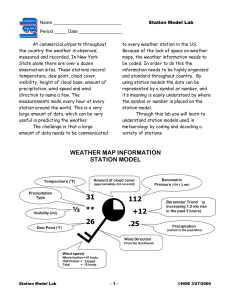
Unit 4 Lesson 5 Notes Answer Key Weather and Weather Forecasting Weather Forecasting The analysis of scientific data to predict future weather conditions Lines on the map Isobar – lines of equal pressure Isotherm – lines of equal temperature Meteorology The study of weather and Earth’s atmosphere Eight Elements of Weather 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Air temperature Humidity Wind direction Wind speed Clouds Precipitation Atmospheric pressure Visibility Ground Stations • Also called - automated surface station • Collect data from the lower atmosphere Radar • Collects data by bouncing radio waves off precipitation • The stronger the signal the heavier the precipitation • The longer it takes the signal to return the farther away the precipitation is. Balloons and Aircraft • Weather sensing instruments carried by aircraft and balloons measure weather in the upper atmosphere Satellites Orbiting weather satellites at high altitudes provide data on water vapor, cloud top temperatures and movement of weather systems. Station models A set of meteorological symbols that represent weather at a particular observing station Weather Station Model If the air pressure on the station model is 500 or more, place a 9 in front of this number then put a decimal point in front of the last number. Example: 588 = 958.8 millibars (mb) If the air pressure on the station model is less than 500 place a 10 in front of this number then put a decimal point in front of the last number. Example: 091 = 1009.1 millibars (mb) The acceptable range of pressures is 960mb to 1040mb. Station Model Practice Draw a station model for the following weather data. 1. Temperature: 18°C 999.8 mb % Cloud cover – 100% Wind direction – South wind speed - 23 knots Dew point - 18°C 2. Temperature: 29°C 1001.1 mb % Cloud cover – 10% Wind direction – west wind speed - 3-7 knots Dew point 20° Weather Maps – a map that displays pressure, temperature, front locations, etc. Upper Air Charts – used to analyze weather using instruments in the upper atmosphere like the weather balloon. Cold front - where cold air moves under warm air • Blue • Triangles in a row • In front of the cold front is heavy rain, thunderstorms • In the back of the front is cool, dry weather Warm front – where warm air moves over cold air • Red half circles • In front of the front is rain • Behind the front is warm, humid weather Stationary fronts – form when cold and warm air stop moving • Not enough wind to move the air masses • Causes many days of unchanging air Weather advisory – is issued when the expected weather conditions will not be a serious hazard. Weather watch – when severe weather conditions are possible over a large area Weather warning – is issued when weather conditions that pose a threat to life and property are happening or are about to happen