Forecasting Weather Notes
advertisement

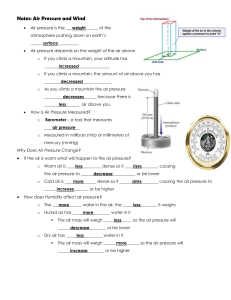
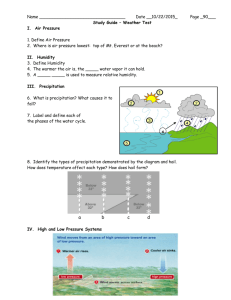
Forecasting Weather Notes Conditions measured for forecast 1. Air pressure - if rises, air mass moves over. (improving weather) -if falls, a front or low pressure is approaching, often precipitation. (a change in weather) 2. Wind direction -winds shift from southwest to northwest a cold front is located. -winds shift from east to southeast a warm front is located. 3. Clouds -cirrus to cirrostratus and altostratus is a warm front and rain for a long time. -cirrus to dark cumulonimbus is a cold front and a violent storm but not for a long time. 4. Wind speed 5. Temperature -dropping temperature is a clue to a cold front. -rising temperature is a clue to a warm front. Weather Maps – overall picture of weather across the earth. -local conditions to national weather service 8 times a day. -Station Model- group of symbols, shows weather. - measures the following from ground to make surface map. Temperature Air pressure Wind speed Wind direction Dew point Visibility Cloud cover Cloud type Precipitation Steps to produce a surface map. 1. station models printed on map 2. isobars are drawn a. circled areas that represent lowest pressure and labeled lows b. smaller circled areas that represent highest pressure and labeled highs 3. isotherms are drawn in occasionally. 4. meteorologist analyze map, mark the line for fronts and shade precipitation. Movement of weather systems- are in straight lines unless acted upon by another air mass. 1. pattern of movement shows both direction and speed of system. 2. forecast based on prediction of position of system. -forecast only accurate for about 12 hours. -long-range forecasts- very general based on seasonal averages of temperature and pressure and winds in upper troposphere. How can we find information on weather patterns? 1. ground readings 2. buoys take radio readings 3. ships report conditions 4. satellites 5. Radar 6. Doppler radar