Study Guide
advertisement
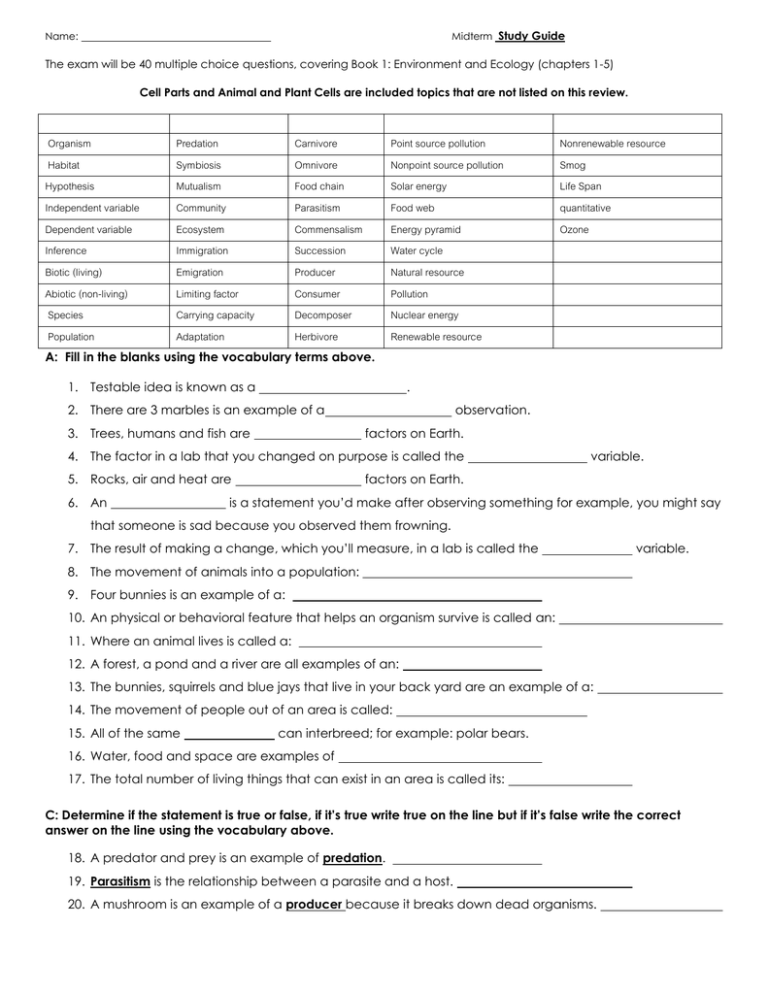
Midterm Study Guide Name: The exam will be 40 multiple choice questions, covering Book 1: Environment and Ecology (chapters 1-5) Cell Parts and Animal and Plant Cells are included topics that are not listed on this review. Organism Habitat Hypothesis Independent variable Dependent variable Inference Biotic (living) Abiotic (non-living) Species Population Predation Symbiosis Mutualism Community Ecosystem Immigration Emigration Limiting factor Carrying capacity Adaptation Carnivore Omnivore Food chain Parasitism Commensalism Succession Producer Consumer Decomposer Herbivore Point source pollution Nonpoint source pollution Solar energy Food web Energy pyramid Water cycle Natural resource Pollution Nuclear energy Renewable resource Nonrenewable resource Smog Life Span quantitative Ozone A: Fill in the blanks using the vocabulary terms above. 1. Testable idea is known as a . 2. There are 3 marbles is an example of a 3. Trees, humans and fish are observation. factors on Earth. 4. The factor in a lab that you changed on purpose is called the 5. Rocks, air and heat are 6. An variable. factors on Earth. is a statement you’d make after observing something for example, you might say that someone is sad because you observed them frowning. 7. The result of making a change, which you’ll measure, in a lab is called the variable. 8. The movement of animals into a population: 9. Four bunnies is an example of a: 10. An physical or behavioral feature that helps an organism survive is called an: 11. Where an animal lives is called a: 12. A forest, a pond and a river are all examples of an: 13. The bunnies, squirrels and blue jays that live in your back yard are an example of a: 14. The movement of people out of an area is called: 15. All of the same can interbreed; for example: polar bears. 16. Water, food and space are examples of 17. The total number of living things that can exist in an area is called its: C: Determine if the statement is true or false, if it’s true write true on the line but if it’s false write the correct answer on the line using the vocabulary above. 18. A predator and prey is an example of predation. 19. Parasitism is the relationship between a parasite and a host. 20. A mushroom is an example of a producer because it breaks down dead organisms. 21. Plants and algae are consumers. 22. A change in an area over time is homozygous 23. A relationship where both organisms benefit is called inherited. 24. Omnivores are organisms like rabbits, insects and cows which eat only plant material. D: Match the term to the example, description or definition. 25. Wolves and hawks that eat meat and plants are . 26. The energy flow of all the organisms is an ecosystem can be shown by a . 27. The flow of energy from a producer, to a herbivore to a carnivore is shown by a . 28. 90% if energy is lost as heat; a represents this energy loss. 29. The parts of an environment like metals, water and trees are 30. Organisms which eat meat are called . . 31. Evaporation, condensation and precipitation are steps of the . 32. The part of a chromosome, that is made of DNA, that tells us how to look is called a E: Determine if the statement is true or false, if it’s true write true on the line but if it’s false write the correct answer on the line using the vocabulary above. 33. When the location of pollution can be identified it is described as non-point pollution. 34. Solar energy is a renewable energy source. 35. Coal is an example of a renewable resource. 36. The use of fossil fuels can cause radioactive waste. 37. A chimney releasing smoke is an example of non-point source pollution. 38. Air pollution that cause the air to be thick and grey is called ozone. 39. The release of CFCs decreases the thickness of the ozone layer. 40. An organism’s birth rate is how long it is expected to live ___________________ .






