Earth, Moon, and Sun Chapter 19
advertisement

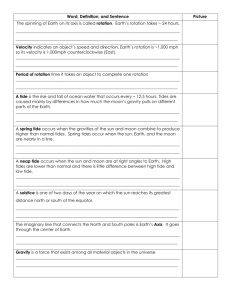
Earth, Moon, and Sun Chapter 19 Voting Questions: How many of you…… • would like to live where it is dark all the time? How many of you…… • would like to live where it is light all the time? How many of you…… • enjoy having four seasons? How many of you…… • would like to travel into space? How many of you…… • would like to go to the moon? How many of you…… • would like to live on Mars? How many of you…… • would like to live on Mars if it meant never returning to Earth and seeing your family and friends again? • Ancient Egyptians were among the first people to study the stars. • The study of the moon, stars, and other objects in space is called Astronomy. • In past times people believed the Earth to be a the center of the Universe and everything revolved around us. • The Earth rotates on its axis which is an imaginary line that runs through the North and South Poles. • This axis is tilted to 23.5 degrees (the tilt of the Earth on its axis changes from 24.5 degrees to 22.5 degrees on a 41,000 year time scale). • Earth spinning on its axis is called its rotation (this is how we have day and night). • A point on the equator rotates at about 1,600 kilometers per hour (most commercial jets don’t move this fast). • As the Earth rotates eastward, the sun appears to move westward across the sky. • The side facing the sun is daytime and the side not facing the sun is night time (no kidding Mr. J we are not stupid). DEMO • The Earth rotates on its axis about once every 24 hours. • The Earth also revolves around the sun. • The movement of one object around another is called revolution. Harvard Question • When are we closer to the SUN? Summer or Winter • One complete circle around the sun is called an orbit. • As the Earth circles around the sun it is not a perfect circle. The orbit is elliptical (this changes over time). • The elliptical orbit of the Earth around the sun changes on a 100,000 year time scale. • There are 365 days a year, but actually it takes the Earth 365.25 days to make one orbit around the sun. • So this is why we have leap year. • What would happen if we did not have leap year? Earth has seasons because its axis is tilted as it moves around the sun. • The SOLSTICE occurs in December and June. • It is when the axis of the Earth is facing towards or away from the sun. • When this occurs the sun will be directly over head at 23.5 degrees north or 23.5 degrees south Halfway between the solstices, neither hemisphere is tilted toward or away from the sun. This is known as an EQUINOX which means “equal night”. During the equinox the daytime and nightime are about the same. Vernal equinox occurs around March 21st, and the autumnal equinox occurs around September 21st. Phases, Eclipses, and Tides Moons Facts • It takes the moon 27.3 days to revolve around the Earth. • The moon has an oval orbit around the Earth. • The moon rotates on it’s axis once every 27.3 days. • A day and a year on the moon is the same. • The same side of the moon, the “near side” always faces the Earth. The “far side” of the moon always faces away from the Earth. Phases of the Moon • The phase of the moon you see depends on how much of the sunlit side of the moon faces Earth. Eclipses • When the moon’s shadow hit Earth or Earth’s shadow hits the moon, an eclipse occurs. • An eclipse occurs when an object in space comes between the sun and a third object, and casts a shadow on that object. • There are 2 types of eclipses: – Solar – Lunar Solar Eclipse Lunar Eclipse Tides • What causes tides? • Tides are the daily rise and fall of Earth’s waters on its coastlines. When the tide comes in the tide rises until the water on the beach reaches the highest point. This is called HIGH TIDE. Then the tide will go out until it reaches the lowest part on the beach. This is called LOW TIDE. Tides happen regularly. Tides occur in all bodies of water, but they are most noticeable in the ocean and large lakes. Spring Tides • Twice a month the moon, Earth and sun are lined up (During the full and new moons). • Their combined gravitational pull produces the greatest range between the high and low tide, called a SPRING TIDE. Neap Tides • In between spring tides, at the first and third quarter of the moon, the sun and moon pull at right angles to each other. • This produces a NEAP TIDE, a tide with the least difference between low and high tide. • During a neap tide the sun pulls some of the water away from the bulge. This tends to “even out the water level reducing the difference between high and low tides. Tides • Tides are caused by the interaction of the Earth , the moon, and the sun. • This occurs by the force of gravity. • Gravity is the force exerted by an object that pulls other objects toward it. • As the distance between objects increase gravity decreases. The Effect of the Moon’s Gravity • The moon pulls on the side closest to it more strongly than it pulls on the center of the Earth. • This creates a bulge of water, called a tidal bulge, on the side of the Earth facing the moon (Letter A). • The water at point C is pulled toward the moon less strongly than Earth is as a whole. • This water is left behind to form a second bulge. • So you have tidal bulges at A and C and along coastlines in these areas you have high tides and the areas between the bulges are experiencing low tide. A D B • As the Earth rotates different places on the surface of the Earth pass through the areas of the tidal bulges and therefore experience the change in water levels. The Daily Tide Cycle • As the Earth rotates, once per day, people on or near the shore experience high and low tides as they pass through the tidal bulges. • In most areas high tide occurs about 12 hours and 25 minutes apart in each location. • As the Earth rotates eastern parts of the US pass through the area of the tidal bulge before points farther west. Therefore high tide occurs later the farther west you go along a coastline. • In some places there are 2 high tides and 2 low tides a day. • In other places, the range between the water level is less dramatic. One set of tides may be so minimal that there appears to be only one high tide and one low tide. • This is common along the coasts of Texas and Florida, due to the gradual slope of the ocean floor of the Gulf of Mexico. Factors that Affect Tide • High tide in California on a certain day is not necessarily the same height as the high tide in Oregon farther up the shore. • Landforms such as capes, peninsulas and islands interrupt the water’s movements. Monthly Tide Cycle • The suns gravity affects the tides as well as the moon even though it is much farther away. • Sometimes the moon and sun pull together on the Earth’s waters and at other times, they pull in different directions. • Changes in the position of the Earth, moon, and Sun affect the height of the tides during a month. Monthly Tide Tables Even with the many factors involved scientists are able to predict the tides accurately for various locations. Earth’s Moon The Moon • Ancient Greeks thought the moon was perfectly smooth. • It was not until 400 years ago that scientists were able to study the moon more closely. • In 1609 Galileo made his own telescope by putting two lenses together and observed the moon. • Galileo observed features on the moon called craters, highlands and maria. • Craters are small round pits caused by impacts. • Galileo inferred some areas on the moon were highlands or mountains. • The moon also had dark, flat areas, which Galileo called maria. – The latin word for sea. • Galileo thought that the maria might be oceans on the moon. • The maria are actually low, dry areas that were flooded with molten material billions of years ago. Moon Landing July 20, 1969 • Neil Armstrong landed on the moon; • “That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.” • He meant to say, “That’s one small step for a man..” • http://batesmotel.8m.com/ • Astronauts brought back samples to Earth. • Later Astronauts could stay on the moon for days instead of hours. • On the first trip to the moon astronauts brought back to Earth 382 kg of rocks to study. • Much of what scientists know about the moon came from the detailed study of these rocks. • Scientists have determined that the moon has cooled almost completely, unlike the Earth. • Apollo astronauts circled the moon and took pictures. • Astronauts realized the far side of the moon is rougher than the near side. • 1998 the Lunar Prospector mapped the entire moon from an altitude of only 100 km. The Lunar Prospector found evidence that there is frozen ice in the lunar soil near the poles.