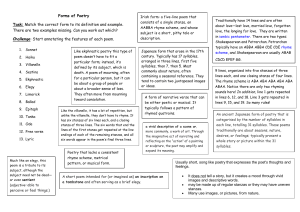
Poetry Notes p 572-574 Elements of Poetry: Poetry is a type of
advertisement

Poetry Notes p 572-574 Elements of Poetry: Poetry is a type of literature that uses the sounds, rhythms, and meanings of words to describe the world in striking and imaginative ways. Lines and Stanzas: Lines-poetry is divided into lines Stanzas-lines are organized into units of meanings or stanzas Stanza break- a blank line in a poem; Signals that one stanza has ended and a new stanza is beginning Refrains and repetition Refrain-a line or group of lines that is repeated at regular intervals in a poem Repetition- repeated lines, either identically or with variations Variations-repeating lines that change one or more words with each repetition Sound devices Rhythm-a beat created by the stressed and unstressed syllables in words of a poem Meter-a pattern of rhythm Feet-what a meter is measured in; units of stressed and unstressed syllables Rhyme-the repetition of vowel and consonant sounds at the ends of words Rhyme scheme-the rhymes follow a particular pattern Alliteration-repetition of consonant sounds in the beginnings of words, as in slippery slope Repetition-the use of any element of language-a sound, word, or phrase-more than once Onomatopoeia-the use of words that imitate sounds-splat hiss, and gurgle Analyzing Poetic Language Poetic language-is specific, imaginative, and rich with emotion Shade of Meaning Denotation-is the literal, dictionary definition of a word Connotation-consists of the ideas and feelings that the word brings to mind Poetry Notes p 572-574 Imagery-descriptions that appeal to the five senses to create vivid word pictures; Helps poets convey what they see, hear, smell, taste, or touch Figurative Language-language not meant to be taken literally Simile-uses the word like or as to compare two seemingly unlike things Metaphor-describes one thing as if it were something else Personification-gives human qualities to a nonhuman subject Analyzing Poetic Form and Structure Every form of poetry has its own structure Narrative-tells a story in verse; has elements similar to those in short stories such as plot and characters Haiku-a three-line Japanese form that describes something in nature; 5-7-5 syllables Free Verse-lack of structure; no regular meter, rhyme, fixed line length, or specific stanza pattern Lyric-expresses thoughts and feelings, often in highly musical verse Ballads-songlike poems that tell stories; often deal with adventure or romance Concrete-shaped to look like their subjects; creates a picture Limericks-humorous, rhyming five-line poems with a specific rhythm pattern and rhyme scheme