T L A R
advertisement
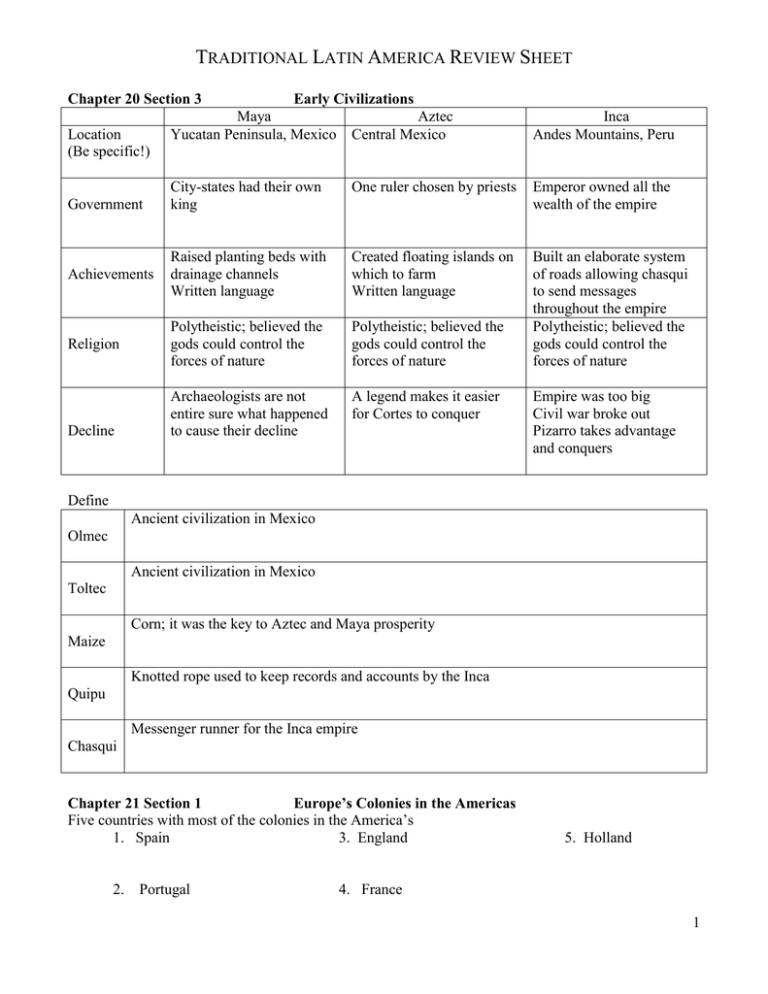
TRADITIONAL LATIN AMERICA REVIEW SHEET Chapter 20 Section 3 Early Civilizations Maya Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico Aztec Central Mexico Inca Andes Mountains, Peru City-states had their own king One ruler chosen by priests Emperor owned all the wealth of the empire Achievements Raised planting beds with drainage channels Written language Created floating islands on which to farm Written language Religion Polytheistic; believed the gods could control the forces of nature Polytheistic; believed the gods could control the forces of nature Built an elaborate system of roads allowing chasqui to send messages throughout the empire Polytheistic; believed the gods could control the forces of nature Archaeologists are not entire sure what happened to cause their decline A legend makes it easier for Cortes to conquer Location (Be specific!) Government Decline Empire was too big Civil war broke out Pizarro takes advantage and conquers Define Ancient civilization in Mexico Olmec Ancient civilization in Mexico Toltec Corn; it was the key to Aztec and Maya prosperity Maize Knotted rope used to keep records and accounts by the Inca Quipu Messenger runner for the Inca empire Chasqui Chapter 21 Section 1 Europe’s Colonies in the Americas Five countries with most of the colonies in the America’s 1. Spain 3. England 2. Portugal 5. Holland 4. France 1 Define/Identify Spanish conqueror that gained great riches from the Americas Conquistador Spanish conqueror that conquered the Aztec Cortés First explorer to cross Panama and go to the Pacific Ocean Balboa Explorer that sailed around Cape Horn Magellan Appointed by Spanish king to rule the colonies in the New World Viceroy Large, self-sufficient plantation that usually produced a cash crop Haciendas Council established by Spain to govern towns in colonies Cabildo Portuguese owners of large tracks of land in Brazil Donatario People, animals or plant life native to an area Indigenous Cash crop Encomienda system Crops that yield a high profit margin because they can only be grown in certain climates (ex. cotton, tobacco, coffee, sugar cane) Large land owners were supposed to take care of the people on their land and ask for taxes or labor in return. This leads to Spain abolishing slavery Explain Mercantilism Definition – Colonies make money for parent country by increasing exports Goal – make money 3 ways goal was achieved - Colonies supplied the parent country with raw materials - Colonies served as a market for finished products - Precious metals and jewels were mined 2 Explain Colombian Exchange The global exchange of people, ideas, and goods throughout the world Chapter 21 Section 2 Patterns of Life Identify and define classes in the colonial social structure from most powerful to least 1 Peninsulares – Born in Spain, these people were sent to the colonies to rule; They included viceroys, & high government/church officials 2 Creoles – Descendants of the Spanish settlers, they had the same rights as peninsulares, but were not appointed to high government positions = Mestizos – People of mixed Indian & European descent that eventually became the majority, they were shop owners, artisans, farmers & overseers Native Americans – The people native to the area, they worked on plantations owned by peninsulares & creoles, or they lived in villages raising crops on lands they had in common Free Blacks – Both Spain & Portugal allowed slaves to buy freedom, some freed in their master’s will. Most became farm workers & laborers; some became skilled tradesmen Slaves – Some Native Americans, but mostly African, Slaves were property, but could marry, own property, & buy their freedom (unlike British slaves) 3 4 5 6 What was the role of the Catholic Church? What role did it play? (Including missionaries/missions)? The Church controlled many aspects of colonial life (schools, health care, etc.) Additionally, the Church protected Native Americans from slavery, but required them to convert Chapter 22 Section 3 Liberator Winning Independence Country Haiti Toussaint L’Ouverture Gained Independence from… France Description of Struggle Rebels drove all foreigners out, but Napoleon wanted the rich sugar plantations back and took control; eventually Haiti pushed them out 3 Liberator Country Venezuela & Peru Gained Independence from… Spain Mexico Spain Brazil Portugal Simon Bolivar Miguel Hidalgo & Jose Morelos Pedro Description of Struggle It was a long and difficult struggle against the peninsulares and the rough terrain, but eventually Spain was pushed out As they pushed the Spanish out, took land and gave it to poor – Creoles not happy; Hidalgo captured, then Morelos captured; eventually won independence King of Portugal gave Brazil to son Pedro to make himself emperor; later, Brazil overthrew emperor and established republic What are the reasons the following groups wanted independence? Creoles Indians (Native Americans) Led many wars of independence because if the They wanted to get even for the Spanish taking Peninsulares left, they would be in charge their land Mestizos They hoped it would improve their status in society Slaves Hoped they would gain their freedom and slavery would be abolished Chapter 21 Section 4 The New Republics Identify Military strongmen who ruled as a dictator Caudillo A small elite group of people that possess the power in government Oligarchy What problems (obstacles) did Latin American countries face after independence? Geography, the old social structure, and a lack of experience with self-rule were a barrier to unity How did the goals of conservatives and liberals differ? Conservative Little change No freedom of speech and press Wealthy Liberal A lot of change Freedom of speech and press Poor How did foreign debt lead to economic imperialism in Latin America? Latin American countries borrowed money they could not pay back, which caused countries to take control of aspects of Latin American economies Foreign countries continued to have influence in Latin American countries 4