General Geographic Information # of Languages Hundreds
advertisement
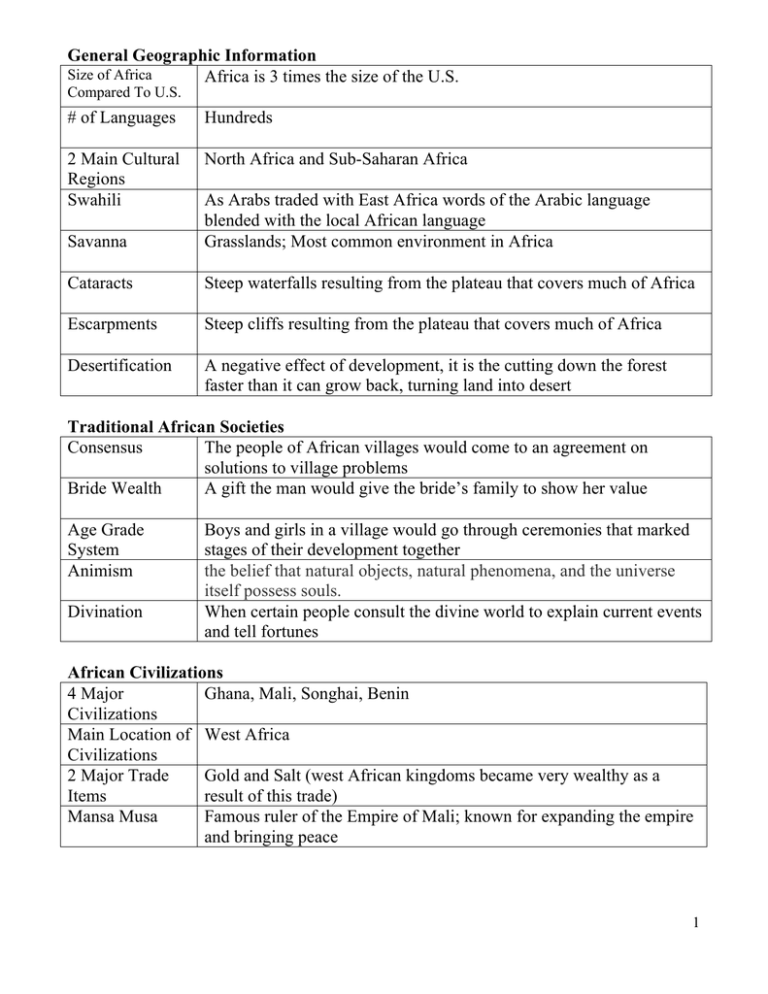
General Geographic Information Size of Africa Africa is 3 times the size of the U.S. Compared To U.S. # of Languages Hundreds 2 Main Cultural Regions Swahili North Africa and Sub-Saharan Africa Savanna As Arabs traded with East Africa words of the Arabic language blended with the local African language Grasslands; Most common environment in Africa Cataracts Steep waterfalls resulting from the plateau that covers much of Africa Escarpments Steep cliffs resulting from the plateau that covers much of Africa Desertification A negative effect of development, it is the cutting down the forest faster than it can grow back, turning land into desert Traditional African Societies Consensus The people of African villages would come to an agreement on solutions to village problems Bride Wealth A gift the man would give the bride’s family to show her value Age Grade System Animism Divination Boys and girls in a village would go through ceremonies that marked stages of their development together the belief that natural objects, natural phenomena, and the universe itself possess souls. When certain people consult the divine world to explain current events and tell fortunes African Civilizations 4 Major Ghana, Mali, Songhai, Benin Civilizations Main Location of West Africa Civilizations 2 Major Trade Gold and Salt (west African kingdoms became very wealthy as a Items result of this trade) Mansa Musa Famous ruler of the Empire of Mali; known for expanding the empire and bringing peace 1 Slave Trade European Motive for Exploring Africa Looking for new routes to India * Asia Why Europeans Wanted Slaves Middle Passage farming economy of the new colonies in the Americas; cheap labor to be profitable Journey of the slave ships from Africa to the Americas Triangular Trade Route How Europeans Got African Slaves Abolition Link between Europe (had guns), Africa (had slaves) and the Americas (had raw materials) Africans captured other Africans during battle and traded them for guns from the Europeans Movement to end slavery Nations Founded by Liberia (American) and Sierra Leone (British) Former Slaves Imperialism Europeans with Most Colonies Leopold II & the Congo Free State Berlin Conference African Nations Not Colonized Cecil Rhodes Independence Educated Elite British and French King of Belgium established a private colony in the Congo River Basin; He exploited the people and the resources for rubber European nations gathered together to draw the borders of the colonies of Africa; no Africans were invited to participate Ethiopia and Liberia British businessman that promoted imperialism in Africa; Rhodesia (now Zimbabwe) was named for him Pan-Africanism Africans able to attend secondary school were considered high in status, but often Africans could not get high level jobs Pride in one’s country; nationalism was not natural because thses countries did not exist before the Europeans arrived in Africa A movement to unify all Africans; it was not successful Negritude Movement that encouraged Africans to value their heritage 2 Decades Independence Achieved 1960s and 1970s Nationalism 2 Apartheid in South Africa Boers Descendants of the Dutch settlers in South Africa Colonial Power Britain Valuable Resources Diamonds & gold Apartheid Legal separation of the races in South Africa Afrikaners Homelands Descendants of the Dutch, French, and German settlers of South Africa; speak Afrikaans Part of apartheid, these laws required any person of color to produce special identification giving them permission to be where they were Areas outside the homeland that black South Africans were forced to live in and required to carry passes Areas assigned to ethnic groups of Africans to jeep them separated Sharpville Massacre Peaceful black protesters were attacked by the police; this gained attention of nations around the world Soweto Disturbance Peaceful African students protesting the forced use of Afrikaans in public schools; attacked by police Pass Laws Townships Desmond Tutu Black leader in the movement to fight apartheid; won the Nobel Peace Prize World Pressure Countries around the world participated in a trade embargo to try to to End Apartheid get South Africa to end apartheid F.W. de Klerk White president of South Africa that moved the government towards eliminating apartheid Nelson Mandela Black leader that worked to end apartheid; jailed for many years; when apartheid ended, elected first black leader of South Africa Nigeria Valuable Natural oil Resource Biafra Ibo of the southeast tried to secede from Nigeria, keeping control of the oil fields, & create Biafra, but the attempt was unsuccessful Government Moves back and forth from civilian to military run government over the Years 3 Zimbabwe Former Name Ethnic Issues Robert Mugabe Rhodesia The white minority declared independence and established Rhodesia; later there was a 2nd “independence” establishing a black-led gov. Leader of movement to establish an African run government (as opposed to a white minority led government) Genocide in Rwanda Genocide Effort to eliminate an entire race or ethnic group Definition Ethnic Groups Hutu (majority) and Tutsi (minority) Description of Conflict Role of U.S. & U.N. Tutsi were given better position under the Belgian colonial government; when Rwanda became independent, the Hutu majority sought retaliation for the past Barely did anything; UN sent peace keeping forces that were powerless; US wouldn’t admit it was a genocide Darfur Location Western Sudan Source of Conflict Land and ethnic/religious differences Janjaweed Arab militants that have been killing black farmers Role of Sudan’s Government Arab-dominated government has supported Arab militants Country Supporting Sudan China supports Sudan because of its oil AIDS in Africa Causes of Epidemic Cultural norms promote the spread of the disease Solutions for Epidemic Health education and aid 4







