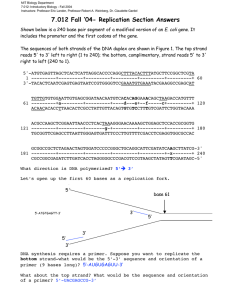
Biology 6.0 DNA/Protein Synthesis Structure of DNA:
advertisement

Biology 6.0 DNA/Protein Synthesis Structure of DNA: Monomer = __________________________ Composed of three parts: 1. 2. 3. Nitrogen Bases: A. Purines 1. 2. B. Pyrimidines 1. 2. Base Pairing Rules: 1. 2. Antiparallel Nature of the DNA – (why?) Replication of a DNA molecule Due to the fact that A always pairs with T and G always pairs with C. If one side of a DNA strand is given, the other side can be determined. Each strand of DNA is said to be _______________________ to the other strand. To simplify a diagram of DNA, only the sequence of nitrogen bases are labeled, since all nucleotides are composed of a phosphate group and deoxyribose. Draw an example below: Process of DNA replication 1. Separate the DNA strands using an enzyme known as helicase. 2. Addition of new nucleotides to the exposed single stranded DNA molecule using an enzyme DNA polymerase. DNA polymerase may only add nucleotides in a 5’ to 3’ direction. Leading Strand – Lagging Strand – Okazaki Fragment – Identify the leading and lagging strand…. Semi conservative Replication versus Structure of RNA Monomer = _______________________ Composed of: 1. 2. 3. Differences between DNA and RNA: 1. Conservative Replication 2. 3. Types of RNA: 1. 2. 3. Protein Synthesis – Two Steps: 1. 2. TRANSCRIPTION – The conversion of ________ to ________. RNA Polymerase – Codons – Translation – Conversion of ________ to ________. Structure of a tRNA molecule: Our simplified diagram Contributors to the Genetic Code: 1. Rosalind Franklin 2. James Watson and Francis Crick 3. Erwin Chargaff Prokaryotic Gene Regulation Operator Promoter Structural Genes OPERON Eukaryotic Gene Expression