Lesson Plan
advertisement

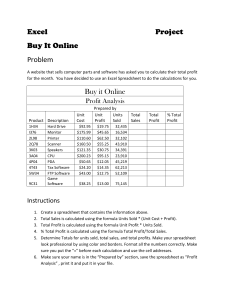
Lesson Plan Course Title: Principals of Technology Session Title: Phones To Go: Advanced Spreadsheet Functions Lesson Duration: Lesson length is subjective and will vary from instructor to instructor. Performance Objective: Upon completion of this assignment, the student will be able to use advanced spreadsheet features, formulate complex functions, and evaluate data. Specific Objectives: Define terms/vocabulary associated with the lesson Chart data in different ways Demonstrate an understanding of the Lookup function Create complex Conditional Statements Demonstrate how to sort data in a spreadsheet Demonstrate how to filter data lists Preparation TEKS Correlations: §130.272 Principles of Information Technology: (8) The student applies spreadsheet technology. The student is expected to (D) Create and analyze spreadsheets incorporating advanced features such as lookup tables, nested Conditional (IF) statements, subtotals, cell protection conditional formatting, charts, and graphs; (E) Edit a variety of spreadsheets by performing data management procedures using simple and multiple search parameters to locate, sort, search, and filter data. Interdisciplinary Correlations: English and Math disciplines Instructor/Trainer References: For additional help, use your favorite web browser to search for spreadsheet guides. Instructional Aids: HANDOUT: Advanced Spreadsheet Warm-Up Advanced Spreadsheet Functions Presentation IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: [Phones To Go Lesson] Plan Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. 1 HANDOUT: Advanced Spreadsheet Lesson Notes for the Presentation HANDOUT: Advanced Spreadsheet Lesson Notes (Key) for the Presentation HANDOUT: Conditional Statement Quiz HANDOUT: Phones To Go Case Study Phones To Go Case Study (Key) File: Advanced Spreadsheet Student Document File: Advanced Spreadsheet Teacher Document Grading Rubric Materials Needed: Spreadsheet software Instructional aids Equipment Needed: Projector for teacher computer Computer lab Learner Students should have already done some work in a spreadsheet software package and know the basics such as terminology, data entry, and formatting cells. Introduction MI Introduction (LSI Quadrant I): SAY, “Now that we know the basics about spreadsheets, we need to harness some of the more powerful features. Did you know that you can use spreadsheet software to make decisions? Did you know that you do not have to enter in data that changes over and over and over?” ASK, “Can you think of an example of a real world problem where things change depending on different things?” If students are having a hard time SAY, “An example might be this: for a different grade you make on your report card, your parents would give you a different reward. A’s would get $10.00, B’s would get $5.00, D’s would get you grounded.” Outline MI Outline (LSI Quadrant II): Teachers can use the Advanced Spreadsheet Warm-Up word search, Advanced Spreadsheet Presentation and Handout, Phones To Go Case Study, On Your Own Portion. I. Hand out the Advanced Spreadsheet WarmUp word search to the students. II. Hand out the Advanced Spreadsheet Lesson Notes handout, or advise students to take notes during the presentation. Instructor Notes: You can have the word search as homework the day before, or it can be used as a warm-up that class period. Students should either take notes or complete IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: [Phones To Go Lesson] Plan Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. 2 the handout during the presentation. IV. Show the presentation on the Advanced Spreadsheet Functions: a. Lookup tables b. Conditional statement functions c. Nested formulas d. Create different types of charts e. Sort data f. Filter data III. After the presentation, most students need help grasping the concept of conditional statements. Hand out and go over the Advanced Spreadsheet Lesson Notes handout. Students should try to complete the conditional statements for practice. Ask students to go up with their own conditional statement examples. Hand out the Phones To Go Case Study Lesson IV. For students who are SPED, or very slow typists, there is a preformatted file you can give them called Advanced Spreadsheet_Student Document. Walk students through pages 1-4. V. Students complete the Own Your Own portion V. Students will continue with the same employees from the case study to come up with The 2nd – 4th quarter sales Total employee sales Total store sales Bonus goals (Vertical Lookup table) Trainings (conditional statement) Sorting of data Filtering data Teacher file is included and called Advanced IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: (Advanced Spreadsheets) Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. Spreadsheet Teacher Document. Application MI Guided Practice (LSI Quadrant III): Advanced Spreadsheet Case Study: Phones To Go MI Independent Practice (LSI Quadrant III): The Own Your Own portion of the Phones To Go Case Study Rubric in students’ handout SAY, “Students, now you need to apply all that we have learned. It is time for you to use these same employee names, but now you get to be the boss. You come up with the sales for all the employees for the rest of the year. You get to decide what the bonuses are and what trainings those people will need to go to, and filter the data to see whatever employees you think the head office would like to see.” Summary MI Review (LSI Quadrants I and IV): Conduct a brief Q & A to review concepts and then ask if students have any further questions. Evaluation MI Informal Assessment (LSI Quadrant III): The teacher will monitor student progress during independent practice/application and provide independent reteach/redirection as needed. Conditional Statement Quiz MI Formal Assessment (LSI Quadrant III, IV): Phones To Go Case Study: On Your Own Portion. Rubric is included in the handouts for the students. Extension MI Extension/Enrichment (LSI Quadrant IV): Upon completion of the Phones To Go Case Study, students may create their own case study problem. Students may exchange case studies with their classmates. IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: (Advanced Spreadsheets) Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. Icon MI Verbal/ Linguistic Logical/ Mathematical Visual/Spatial Musical/ Rhythmic Bodily/ Kinesthetic Intrapersonal Interpersonal Naturalist Existentialist Teaching Strategies Personal Development Strategies Lecture, discussion, journal writing, cooperative learning, word origins Reading, highlighting, outlining, teaching others, reciting information Problem solving, number games, critical thinking, classifying and organizing, Socratic questioning Mind-mapping, reflective time, graphic organizers, color-coding systems, drawings, designs, video, DVD, charts, maps Use music, compose songs or raps, use musical language or metaphors Organizing material logically, explaining things sequentially, finding patterns, developing systems, outlining, charting, graphing, analyzing information Developing graphic organizers, mindmapping, charting, graphing, organizing with color, mental imagery (drawing in the mind’s eye) Use manipulatives, hand signals, pantomime, real life situations, puzzles and board games, activities, roleplaying, action problems Reflective teaching, interviews, reflective listening, KWL charts Cooperative learning, roleplaying, group brainstorming, cross-cultural interactions Natural objects as manipulatives and as background for learning Socratic questions, real life situations, global problems/questions Creating rhythms out of words, creating rhythms with instruments, playing an instrument, putting words to existing songs Moving while learning, pacing while reciting, acting out scripts of material, designing games, moving fingers under words while reading Reflecting on personal meaning of information, studying in quiet settings, imagining experiments, visualizing information, journaling Studying in a group, discussing information, using flash cards with other, teaching others Connecting with nature, forming study groups with like-minded people Considering personal relationship to larger context IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: (Advanced Spreadsheets) Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. Advanced Spreadsheet Lesson Notes: Conditional Statement Functions: If you ever need a spreadsheet to make a __________________________, the Conditional Statement function can do that for you. This function can be broken down into parts and combined with other formulas. The parts of a Conditional Statement function are =IF(_______________________, what to do if _______________________, what to do if_________________________________) Conditional Statement Function Practice: If your family will throw a party for every class that you have higher than a 90 in, what would that conditional statement look like? Use the information in the picture to see if you can create your statement. =IF(________________________________, ______________________________, _________________________________) Conditional Count Function: The Conditional Count function will ______________________________ the number of cells in a range that meet certain criteria. For example, you may want to ________________________________ the number of people attending a birthday party so you will know how many party favors to get. Lookup Tables: Lookup Tables can look up _______________________________ in a table for you. This saves you from having to enter the same values repeatedly. For example, if your parents were to reward you for good grades in all your classes, you can have the spreadsheet software calculate what your reward would be by creating a single formula. Now you don’t have to enter in the reward amount for every grade. It can be done automatically for you. Lookup Functions: Both the ______________________ and ________________________ work the same way. IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: (Advanced Spreadsheets) Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. Vertical LOOKUP looks up the ___________________________ lines in a table (like the one you just saw.) Horizontal LOOKUP looks up the _______________________ lines in a table. The function is broken down into parts: o _________________________________: What are you looking up? o _________________________________: Where is this lookup table located? o _________________________________: Which column has the answer? =_______________________________(Lookup Value, Table_Array, Col_Index_Number) =_______________________________________(Lookup Value, Table_Array, Col_Index_Number) Pie Charts: These show each slice as a part of the whole. A good use of a pie chart is to show the __________________________________of grades a teacher may give out. Line Charts: These charts are a great way to chart out data over ________________________. A good example would be charting stock prices over a period of time. Filter: Sometimes, when you have a huge amount of data, sorting is just not enough. Your spreadsheet software can _______________________________ and __________________________ data that you do not want to see. For example, if you have 10,000 names in a spreadsheet and you only want to see the people with the last name of Smith, you can _______________________ all the people who do not have the last name Smith. Continuing with the Smith example, if you were to see all the people with that last name in the state of Texas, the list would still be extremely long and more than you could manage. IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: (Advanced Spreadsheets) Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. Fortunately, with spreadsheet software you can _________________________ filters so that you would only see the people with the last name Smith who live in the Austin area. Now, we have a much more _______________________ list of information. IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: (Advanced Spreadsheets) Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. Advanced Spreadsheet Lesson Notes: KEY Conditional Statement Functions: If you ever need spreadsheet to make a _CHOICE_, the Conditional Statement function can do that for you. This function can be broken down into parts and combined with other formulas. The part of a conditional statement function are =IF(__LOGIC TEST_, what to do if __TRUE__, what to do if__FALSE__) Conditional Statement Function Practice: If your family will throw a party for every class that you have higher than a 90 in, what would that conditional statement look like? Use the information in the picture to see if you can create your statement. =IF(_2B>90__, __” PARTY”_, ___”NO PARTY”__) Conditional Count Function: The Conditional Count function will ___COUNT___ the number of cells in a range that meet certain criteria. For example, you may want to _COUNT__ the number of people attending a birthday party so you will know how many party favors to get. Lookup Tables: Lookup Tables can look up __VALUES____ in a table for you. This saves time from having to enter the same values repeatedly. For example, if your parents were to reward you for good grades in all your classes, you can have the spreadsheet software calculate what your reward would be by creating a single formula. Now you don’t have to enter in the reward amount for every grade. It can be done automatically for you. Lookup Functions: Both the __Vertical Lookup___ and ____Horizontal Lookup____ work the same way. Vertical LOOKUP looks up the ___VERTICAL___ lines in a table (like the one you just saw.) Horizontal LOOKUP looks up the_HORIZONTAL_lines in a table. The function is broken down into parts: o __LOOKUP VALUE___: What are you looking up? IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: (Advanced Spreadsheets) Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. o __TABLE ARRAY___: Where is this lookup table located? o __COLUMN INDEX NUMBER__: Which column has the answer? =_VLOOKUP___(Lookup Value, Table_Array, Col_Index_Number) =_HLOOKUP____(Lookup Value, Table_Array, Col_Index_Number) Pie Charts: These show each slice as a part of the whole. A good use of a pie chart is to show the __PERCENTAGE__ of grades a teacher may give out. Line Charts: These charts are a great way to chart out data over __TIME___. A good example would be charting stock prices over a period of time. Filter: Sometimes, when you have a huge amount of data, sorting is just not enough. Your spreadsheet software can __FILTER__ and ___HIDE__ data that you do not want to see. For example, if you have 10,000 names in a spreadsheet and you only want to see the people with the last name of Smith, you can _HIDE__ all the people who do not have the last name Smith. Continuing with the Smith example, if you were to see all the people with that last name in the state of Texas, the list would be extremely long and more than you could manage. Fortunately, with spreadsheet software, you can _ADD__ filters so that you would only see the people with the last name Smith who live in the Austin area. Now, we have a much more ___MANAGEABLE___ list of information. IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: (Advanced Spreadsheets) Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. PHONES TO GO CASE STUDY: STUDENT INSTRUCTIONS Upon completion of this project, you should be able to Format spreadsheets Use lookup tables Use and construct conditional statement functions, nested formulas, and subtotals Create and modify charts Sort and filter data SETTING UP YOUR SPREADSHEET 1. Create a new spreadsheet workbook with the name LastName_PhonesToGo. 2. In your new spreadsheet file, enter in the following information: 3. We are going to use this information to explore some new formulas that we have just learned. SUM FORMULA 4. In cell 7E, we need to sum up all the sales from Larry Gutierrez for the first quarter. Use the sum function to do this. If you need help, enter =SUM(4E:6E) into cell 7E. 5. After you have entered this to get Larry’s total sales for the quarter, we need to copy this down to all the Phones To Go employees. IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: (Advanced Spreadsheets) Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. 6. To copy the formula down to all the store’s employees, point to the fill handle at the bottom-right of cell 7E, and drag that formula down so that it is in cells 7E through 7M. 7. Now create a sum formula so that we can total up the Total Store Sales for the first quarter. a. __________________________ Vertical LOOKUP TABLE 8. Now that we have our total sales for the employees, we need to determine if they can have a bonus. But we want to give out different bonuses for different sales goals. 9. In cells 12E: 13N, please enter the information shown to the right: 10. Since our table is laid out vertically, we are going to use the Vertical LOOKUP function to figure out who gets what bonus, but we need to enter it a certain way so that when we copy this formula, it does not move the location of our table. To do that, we need to list the “$” symbol in our formula so that it becomes an absolute cell reference. 11. In cell 8E, enter the following formula: =VLOOKUP(7E,$12$G:$13$N,2) COMPLEX CONDITIONAL STATEMENTS 12. Now that we have given our employees a bonus, we need them to attend training. However, we do not want every employee to attend the same one. Employees that did not make the $100 bonus need to attend a training called “Sales 101”, and employees that received a bonus of $180 or more need to attend the “How to be a Team Player” training. All other employees need to attend the training called “The Future Phones of Tomorrow”. 13. In order to make this kind of decision, we will have to use the conditional statement inside of another conditional statement. Let’s break this into parts: a. Sales 101 is a bonus of _____________________________ ? b. The Future Phones of Tomorrow is a bonus of _______________________? c. How to be a Team Player is a bonus of ______________________________? 14. Let’s try to merge a couple of these parts: a. IF(8E = 0, “_______________________________” (What training do we want them to go to?) b. IF(8E < 180, “____________________________” (What training do we want them to go to?) c. So the only training left is “__________________________________” 15. Let’s put it all together…. a. In cell 9O enter in =IF(8E<=0, "Sales 101", IF(8E<180, "The Future Phones of Tomorrow", "How to be a Team Player")) IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: (Advanced Spreadsheets) Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. CHART OUR FINDINGS 16. Phones To Go would like a chart of all the employees’ total sales and a chart of the number of staff members that need to attend each training. 17. Pie Chart a. In cells 10P through 13S, please enter the data as shown above. b. In cell 13Q, we will utilize the COUNTIF function. This function will count the number of cells in a range having certain criteria—or in this case, recommended training. c. In cell 13Q, enter the following formula: =COUNTIF($9$E:$9$M, "Sales 101") i. What do you think the formula should be for cells 13R and 13S? 1. 13R __________________________________________ 2. 13S __________________________________________ d. Enter in the formulas for 13R and 13S into your spreadsheet workbook. e. Let’s chart our results. Select cells 12Q to 13S. Look at the insert features available in your software and choose to insert a pie chart. 18. Line Chart a. Select cells 1E to 2M; while holding down the control key on your keyboard, also select cells 7D to 7M. b. Choose the type of line chart that you like. There will options available in your spreadsheet software. c. Resize the chart so that all the information is present and nothing is unreadable. SORTING DATA 19. We need to sort the list of employees so that we can see them from the least amount of sales experience to the highest amount of sales experience. a. Select cells 1D to 9M. On the menu bar, choose the Data option, and then choose to sort the data. b. A dialog box may pop up depending on your software. Choose how to sort our data. Here, we will sort from smallest to largest. FILTER DATA 20. The Phones To Go manager would like to see a list of employees that have been at Phones To Go longer than 5 years and whose total first quarter’s sales are over $20,000. IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: (Advanced Spreadsheets) Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. a. Select cells 1D to 9M if they are not already selected from the previous step. Choose the Data option if available, and then click on the filter button. b. Row D should now have arrows next to every name in each cell. This is what we are going to use to help “filter” out the unwanted information. c. Click the arrow next to the Sales Age name in cell 3D. Since we only want to see the employees who have worked more than 5 years, we are going to choose the option Filter Numbers, and then choose the option of Greater Than. d. This will open a new dialog box. e. You will be able to enter the criteria for your search. Enter the number 5 to see the employees that have been with Phones To Go for more than 5 years. f. Now with the employees that we see, we need to do these steps again to see who has sold over $20,000. g. Click the arrow next to the Total Sales name in cell G4. We need to choose the option Filter Numbers again, and choose the option Greater Than again. h. This time, we need to enter 20000. You should see only 2 names that meet these criteria. i. List the 2 names that you see with the result of these filters: _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ 21. Now that we have filtered the data, we need to take off the filter to see our original information. (One of the great features about the filter option in spreadsheet software is that your information is still there and untouched. You just do not see it!) a. Most spreadsheet software allows you to clear your filters when you are finished, by selecting that option from a toolbar. Once you have cleared your filters, you will see your original data. ON YOUR OWN Now that you have the first quarter done, use separate sheets in your spreadsheet workbook to create information for the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th Sales Quarters. Use the same employee names, but make up your own data and bonus rates. Chart the same information for each page of the worksheet. Sort and filter the sales employees in several different ways. IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: (Advanced Spreadsheets) Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. PHONES TO GO CASE STUDY (Key) Upon completion of this project, you should be able to Format spreadsheets Use lookup tables Use and construct conditional statement functions, nested formulas, subtotals, Create and modify charts Sort and filter data SETTING UP YOUR SPREADSHEET 1. Create a new spreadsheet workbook with the name LastName_PhonesToGo. 2. In your new spreadsheet File, enter in the following information: 3. We are going to use this information to explore some new formulas that we have just learned. SUM FORMULA 4. In cell 7E, we need to sum up all the sales from Larry Gutierrez for the first quarter. Use the sum function to do this. If you need help, enter =SUM(4E:6E) into cell 7E. 5. After you have entered this to get Larry’s total sales for the quarter, we need to copy this down to all the Phones To Go employees. 6. To copy the formula down to all the store’s employees, point to the fill handle at the bottom-right of cell 7E, and drag that formula down so that it is in cells 7E through 7M. IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: (Advanced Spreadsheets) Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. 7. Now create a sum formula so that we can total up the Total Store Sales for the first quarter. a. =SUM(7E:7M) Vertical LOOKUP TABLE 8. Now that we have our total sales for the employees, we need to determine if they can have a bonus. But we want to give out different bonuses for different sales goals. 9. In cells 12E: 13N, please enter the information shown to the right: 10. Since our table is laid out vertically, we are going to use the Vertical LOOKUP function to figure out who gets what bonus, but we need to enter it a certain way so that when we copy this formula, it does not move the location of our table. To do that, we need to list the “$” symbol in our formula so that it becomes an absolute cell reference. 11. In cell 8E, enter the following formula: =VLOOKUP(7E,$12$G:$13$N,2) COMPLEX CONDITIONAL STATEMENTS 12. Now that we have given our employees a bonus, we need them to attend training. However, we do not want every employee to attend the same one. Employees that did not make the $100 bonus need to attend a training called “Sales 101”, and employees that received a bonus of $180 or more need to attend the “How to be a Team Player” training. All other employees need to attend the training called “The Future Phones of Tomorrow”. 13. In order to make this kind of decision, we will have to use the conditional statement inside of another conditional statement. Let’s Break this into parts: a. Sales 101 is a bonus of __________-0-___________________ ? b. The Future Phones of Tomorrow is a bonus of _________$100___________? c. How to be a Team Player is a bonus of ________$180_________________? 14. Let’s try to merge a couple of these parts: a. IF(8E = 0, “_____Sales 101______________” (What training do we want them to go to?) b. IF(8E < 180, “_Future Phones of Tomorrow__” (What training do we want them to go to?) c. So the only training left is “__How To Be A Team Player____” 15. Let’s put it all together…. a. In cell 9E, enter in =IF(8E=0, "Sales 101", IF(8E<180, "The Future Phones of Tomorrow", "How to be a Team Player")) IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: (Advanced Spreadsheets) Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. CHART OUR FINDINGS 16. Phones To Go would like a chart of all the employee’s total sales and a chart of the number of staff members that need to attend each training. 17. Pie Chart a. In cells 10P through 13S, please enter the following data as shown above. b. In cell 13Q, we will utilize the COUNTIF function. This function will count the number of cells in a range having certain criteria—or in this case, recommended training. c. In cell 13Q, enter the following formula: =COUNTIF($9$E:$9$M, "Sales 101") i. What do you think the formula should be for cells 13R and 13S? 1. 13R __=COUNTIF($9$E:$9$M, "The Future Of Phones Tomorrow") 2. 13S __=COUNTIF($9$E:$9$M, "How To Be A Team Player") d. Enter in the formulas for 13R and 13S into your spreadsheet workbook. e. Let’s chart our results. Select cells 12Q to 13S. Look at the insert features available in your software and choose to insert a pie chart. 18. Line Chart a. Select cells 1E to 2M; while holding down the control key on your keyboard, also select cells 7D to 7M. b. Choose the type of line chart that you like. There will options available in your spreadsheet software. c. Resize the chart so that all the information is present and nothing is unreadable. SORTING DATA 19. We need to sort the list of employees so that we can see them from the least amount of sales experience to the highest amount of sales experience. a. Select cells 1D to 9M. On the menu bar, choose the Data option, and then choose to sort the data. b. A dialog box may pop up depending on your software. Choose how to sort our data. Here, we will sort from smallest to largest. FILTER DATA 20. The Phones To Go manager would like to see a list of employees that have been at Phones To Go longer than 5 years and whose total first quarter’s sales are over $20,000. IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: (Advanced Spreadsheets) Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. a. Select cells 1D to 9M if they are not already selected from the previous step. Choose the Data option if available and then click on the filter button. b. Row D should now have arrows next to every name in each cell. This is what we are going to use to help “filter” out the unwanted information. c. Click the arrow next to the Sales Age name in Cell 3D. Since we only want to see the employees who have worked more than 5 years, we are going to choose the option Filter Numbers, and then choose the option of Greater Than. d. This will open a new dialog box. e. You will be able to enter the criteria for your search. Enter the number 5 to see the employees that have been with Phones To Go for more than 5 years. f. Now with the employees that we see, we need to do these steps again to see who has sold over $20,000. g. Click the arrow next to the Total Sales name in cell G4. We need to choose the option Filter Numbers again and choose the option Greater Than again. h. This time, we need to enter 20000. You should see only 2 names that meet these criteria. i. List the 2 names that you see with the result of these filters : __Juan Lopez___ __Jerry Shepard_ 21. Now that we have filtered the data, we need to take off the filter to see our original information. (One of the great features about the filter option in spreadsheet software is that your information is still there and untouched. You just do not see it!) a. Most spreadsheet software allows you to clear your filters when you are finished by selecting that option from a toolbar. Once you have cleared your filters, you will see your original data. ON YOUR OWN Now that you have the first quarter done, use separate sheets in your spreadsheet workbook to create information for the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th Sales Quarters. Use the same employee names, but make up your own data and bonus rates. Chart the same information for each page of the worksheet. Sort and Filter the sales employees in several different ways. IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: (Advanced Spreadsheets) Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. Graded Elements for On Your Own Portion of Phones To Go Case Study Total Points Sales employees listed with data Bonus table listed and used with Vertical LOOKUP function to determine sales employees’ bonuses Data sorted in some way, either by Sales Age, Last Name, or Total Sales Filter done to hide some sales employees Formulas used correctly Class time used wisely Total 15 25 15 15 20 10 100 IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: (Advanced Spreadsheets) Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. Advanced Spreadsheets Warm-Up L V M E Y P Y C Q I J H L S Q O N S Q K U S U K D L M W B Z I Z X S Q R O N U W P T P G N I M Z Z X U T N R N E V K Y W K E A Q I Q Y I S L P A B N F T W Y O G T P R N U J U O I G N W Q J W A Z F L A Z R A Q F N R R T Q T Q E H C T U U C R R G I W O O R Y U H O E T T H X L N F Z U D P E A P L E S E P I Y J O Q D T Y R F U K L Y N K N S C U H B S A E D G D L Y S Y E C U N F Q Q E S C B O I D P Y P B N F K M L V U V O V U G N G T H G H Q Q D W X O N V N N W E M H N K R A L R I P I K K F A D R W K Y C T X F V G O H C E P U R X C G K I N W P O O N R I C W X AVERAGE BONUS TABLE CELL COLUMN CONDITION COPY DATA FALSE FILL A N O R M T S J Y I E B W A C I Y F C E Z T C E A G F H G E R V L K T K U B F Z B E S B G V I H D M D G E T Y O H N C O H L A Y Y W B F Z O O R W R D M S Z H L N Z M F K U L O H G J G O K N F K X X E C G Y K H V F O I J U G W M A H D I B Z K D U L Z A S B S U A O B M T J C M R Z X N P P S G J O Y M S I R A X L L I F P O I K S Q S T P J G H U W I U D J W W A W E R F K U A O R X P I I W O J X A T O M G P W L B U D A O H M V W U L A K L M D S B B S Z A N S U U Q G S Y A V Q K L M J Q O X Z J Y T I C O S F S U M A K N D D C S R N X V I C N I T M R L V B R Q M M X W M A Y H M M F B Z M J J L K K G Y B A L W Q P U K O O L V J R J J S V I T I E V B Y P U R X H X I Y A S D R V J O V Z F N H L K J O Y C B B O J C E O T H L X S U N H K N Q J A B Q G I F G N Z O L Y N C H C Z A K W T T M I O I H B V Y R Y J E L B A T S U N O B H Q U H F M FILTER FORMULAS FUNCTIONS HIGHEST LEFT CLICK LISTS LOGIC LOWEST PASTE S W U R H J G L Z C F J N E V U Z V K N D Z H F F H K P E S L A F N E L B H Z Z Z Z R R S P G X D H P T R U E E M I D G I B C N E I X E M O G A B B P H P W A S X K X E Q X E P G M X C Y J O Q L Q G E Y O Y O D R U T Z O N E T Z Y F T F P I Z Z B Z A F J Z A E V D T P N X J P B N Z Q H O J K G Z W M N X F F N I F V E Q K I P L K Y V T E F Y P L D P A O G C T D B C Z O Q R P O B H R A L U F M M O N I A C F R M Z P L T V F B T C B E T C Q G L X U Y I F S L P L F S C U A H F C Y O X L K H E W M V E I U O P C D F H M U S O U E A B E K F Q K T U Y L M Q J T W R E Z U E G N S I T Z B B T H I S N C S X U K B V K J A S L L Y X U H A X T T U D H O X W V X B Q I T T H W T X R Y S A S I J P S T W C Q M G M H P I E C H A R T A Q T S R W B O E Z D T A H Z G J Y Y X Z K N W E N Z T M W W B P W K Y V D O R X Q Z Z W F A P I T D N O J C M G G J I D I W N D T H L K T Z L S E M W Z J V M S B T N D T J U G P L H W K S O Z N W L W H U Y C Y H I J R X I T T H X M K A Q N W A U I N G A T N L O W E S T G A E V O A I Y Z I W T G V L C F A Z F L Y K C Q H D P PIE CHART ROW SORT SUBTOTAL SUM TRUE LOOKUP WORKSHEET IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: (Advanced Spreadsheets) Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. Conditional Statement Quiz Directions: Read each statement below and write out the appropriate conditional “IF” statement that will answer the scenario. 1. If cell 1A is greater than the value in cell 2A, then display “Winner” -- otherwise display “Try Again.” 2. If a book’s ID number (cell 13H) is over 20,000, display “Fiction” -- otherwise display “Non-Fiction.” 3. If an employee’s total sales (cell 25H) are over $5,000, his/her bonus is 10% of his/her sales. Otherwise display “No Bonus.” 4. If the average class grade (cells 4G to 34G) is greater than 70, display “Pizza Party” -- otherwise display “Try Again.” 5. Your Business Professionals of America advisor is trying to determine if you are eligible or not. If your grade (cell 5A) is greater than or equal to 70, display “Goes to Compete” -- otherwise, display “Ineligible.” IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: (Advanced Spreadsheets) Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. Conditional Statement Quiz: KEY Directions: Read each statement below and write out the appropriate “IF” statement that will answer the scenario. 1. If cell 1A is greater than the value in cell 2A, then display “Winner” -- otherwise display “Try Again.” =IF(1A>2A), “Winner”, “Try Again”) 2. If a book’s ID number (cell 13H) is over 20,000, display “Fiction” -- otherwise display “Non-Fiction.” =IF(13H>20000), “Fiction”, “Non-Fiction”) 3. If an employee’s total sales (cell 25H) are over $5,000, his/her bonus is 10% of his/her total sales. Otherwise display “No Bonus.” =IF(25H>5000, 25H*.10, “No Bonus”) 4. If the average class grade (cells 4G to 34G) is greater than 70, display “Pizza Party” -- otherwise display “Try Again.” =IF(AVERAGE(4G:34G) > 70, “Pizza Party”, “Try Again”) 5. Your Business Professionals of America advisor is trying to determine if you are eligible or not. If your grade (cell 5A) is greater than or equal to 70, display “Goes to Compete” -- otherwise, display “Ineligible.” =IF(5A > 70, “Goes to Compete”, “Ineligible”) IT: [Principals of Information Technology]: (Advanced Spreadsheets) Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved.