WALL 1310-10 Osteology: Fun with Roadkill Oct 18 Class Outline
advertisement

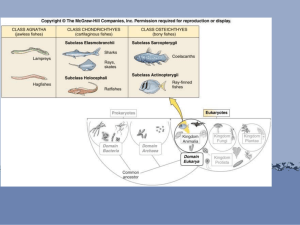
WALL 1310-10 Osteology: Fun with Roadkill Oct 18 Class Outline 1:30 Introduction to the Osteology Collection 1:35 Classification bases: structure development biogeography DNA sequencing schemes: Linnean taxonomy cladistic phylogeny evolutionary phylogeny Phylum Chordata notochord dorsal hollow nerve cord pharyngeal gill slits post-anal tail ultimobranchial/thyroid gland Subphylum Vertebrata vertebral backbone cephalization with three-region brain neural crest tissues semicircular canals nephritic kidneys 1:40 Practical vertebrate osteological taxonomy Class Agnatha – jawless fishes; no appendages, no cranium, no vertebrae (notochord only), single dorsal nostril Myxini – hagfish Cephalaspidomorpha/Petromyzontia – lampreys Class Chondrichthyes – cartilaginous fish; virtually no bone, patent notochord, oily liver for buoyancy, horizontal pectoral fins for planning, heterocercal tail, dorso-ventral flattening Elasmobranchii – sharks, skates, rays, sawfish; multiple exposed gill slits, open chondrocranium Holocephali – ratfish and rabbitfish; enclosed cartilaginous cranium, gill covers, six dental plates (teeth) Class Osteichthyes – bony fish; bony skeleton, no notochord in adult; partial consolidation of vertebrae; bony ribs, opercula cover gills, swim bladder for buoyancy Actinopterygii – ray-finned fish; fins supported on delicate bony rays Paleonischiformes – sturgeons, paddlefish, bichirs; largely cartilaginous skeleton Neopterygii – true bony fish; largely bony skeletons Chondrostei – gars Holostei – bowfins Teleostei – teleost fish Sarcopterygii – lobe-finned fish; fins supported by multiple basal and radial bones Crossopterygii – coelacanth Dipnoi – lungfish Class Amphibia – amphibians; first true tetrapods, pentadactylous (five fingers and toes), ventral lungs, aquatic larval form, three-chambered heart; no eyelids Urodela/Caudata – salamanders; short dorsal ribs; no ear hole Anura/Salientia – frogs and toads; no tail, elongated hind legs, external eardrum, modified pelvis with urostyle Mesobatrachia – primitive frogs Neobatrachia – modern frogs Apoda – caecilians; legless amphibians Class Reptilia – reptiles; amnoiotic eggs with leathery case; threechambered heart (except crocodylians); partially upright posture, consolidated vertebrae, elongated dorsal ribs Testudinata/Chelonia – turtles; anapsid skull, ribs form shell with carapace and plastron, pectoral and pelvic girdles inside ribcage Pleurodira – side-necked turtles; neck bends to side to withdraw head Cryptodira – bottom-necked turtles; neck bends ventrally to withdraw head Squamata – scaly skinned reptiles; diapsid skull, loss of legs in several groups Lacertilia – lizards Squamata – snakes Amphisbea – amphisbeans Rhyncocepala/Sphenodonta – tuataras Crocodylia – crocodiles, alligators, caimans, gavials; leathery skin, extended maternal care; ventral gastralia; socketted teeth; complete ribcage; four-chambered hearts; partially warm- blooded Class Aves – birds; four-chambered heart, modified diapsid skull with beak, loss of teeth, calcified amniotic eggs; extended parental care; hollow bones; feathers, complete homeothermy (warm-blooded); fused arch-shaped synsacrum; reduced tail; upright stance, enlarged brain Paleognathidae – ratite birds; flattened sternum rather than keel/carina Neognathidae – carinate birds; prominent keel/carina for flight; fused clavicles (furculum or wishbone) Galloanseres – fowl and waterfowl Neoaves – all other modern bird orders Class Mammalia – mammals; four-chambered heart, synapsid skull, complete homeothermy(warm-blooded, extended care of young, live birth of young (except monotremes); hair; milk production; upright stance; enlarged brain Protheriana – egg-laying mammals; common urogenital/anal opening (cloaca); lay leathery eggs Monotremata – platypus and echidnas (spiny anteaters) Metatheria/Marsupialia – pouched mammals; young born immature and develop in external pouch Ameridelphia – New World marsupials – 3 orders Australidelphia – Australian marsupials – 5 orders Eutheria – placental mammals: embryos/fetuses develop internally nourshed by placenta Xenarthra (S. American origin) Or. Pilosa – sloths and anteaters Or. Cingulata – armadillos Afrotheria (African orgin) Afroinsectiphila Or. Macroscelidea – sengi (elephant shrews) Or. Afroscoricida – golden moles and tenrecs Or. Tubulidentata – aardvarks Paenungulata Or. Proboscidea – elephants Or. Hyracoidea – hyraxes Or. Sirenia – manatees and dugongs Euarchotoglires (N. American/Eurasian origin) Glires Or. Lagomorpha – rabbits and pikas Or. Rodentia – rodents Euarchonta Or. Scandentia – tree shrews Or. Dermoptera – culogos (flying lemurs) Or. Primates – prosimians, monkeys, apes Laurasiatheria (N. American/Eurasian origin) Or. Eulypotyphla – shrews, moles, hedgehogs Or. Chiroptera – bats Or. Perrisodactyla – (odd-toed ungulates) horses, rhinos, tapirs Or. Cetartidactyla – (even-toed ungulates) cattle, deer, pigs, antelopes, cameloids, hippos, giraffes, toothed whales, baleen whales Or. Pholidota – pangolins (scaly anteaters) Or. Carnivora – dogs, cats, bears, weasels, raccoons, seals, sealions, walruses, hyenas, mongooses 2:25 Skeletal Articulation – appendicular skeleton Chimera/Crytozootic classification