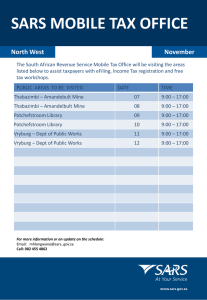
Document 13638342
advertisement

15.871 Syystem Dyynamics Recitation#1 1 A simp ple model that cap ptures the dyynamics of an infectious disease‐ SARS Historical data: SARSDATA.vdf ‐the the incidence (rate at which new cases were reported, measured in people/day) ‐ cumulative prevalence (cumulative number of cases reported, measured in people) for SARS in Taiwan 2 Step 1: Open A New Model 3 Step 2: Initial Settings 4 Step 3: Save As “SARS SARS_Tutorial_F12 Tutorial F12” 5 Step 4: Load SARSDATA.vdf 6 ‐‐‐‐Warning Warning‐‐‐‐ • We will ill compare our siimullati tion d data t to th the acttual/hist l/hi toriicall data in this file, so variable names need to match EXACTLY • SARSDATA has 2 variables, those names have to match: – New Reported Cases – Cumullati tive Reportted d Cases C 7 Step 5: Population Susceptible to SARS ( (stock) k) 8 Step 6: Population Infected with SARS ( (stock/level) k/l l) 9 Step 7: Infection Rate (flow/rate) First click in center of this stock Then click in center of this stock 10 Step 8: Infectivity (auxilary) 11 Step 9: Add Causal Arrow 12 Step 10: Right‐click on Arrow “handle” to Add dd Polarity l 13 Step 11: Contacts Between Infected and d Uninffected d Peoplle 14 Step 12: Complete the Rest off th he Model d l + Lab bell the h Loops 15 Use comment tool to add labels 16 Step 13: Specify Equations 17 Exogeneous and Endogeneous Variabl bles • Variables a ab es in SD S models ode s aaree classified c ass ed as either et e exogenous or endogenous: – Exogenous variables are defined independent of other variables of the model. • They are functions of time (i.e., Exogenous Variable = f(t)). • Of course the exogenous variables may be constants, in which case they are called parameters. – Endogenous variables are influenced by other variables in the system system • Endogenous Variable = f(x, y, z), where x, y, z are other variables in the model 18 Step 14: Define Infection Rate 19 Step 15: Define Population Susceptible to SARS 20 Step 16: Define Susceptible Contacts 21 Step 17: Define Contacts Between Inffected d and d Uninffected d Peoplle 22 Step 18: Define Probability of Contact with h Inffected d Person 23 Step 19: Define Total Population 24 Step 20: Define Contact Frequency 25 Step 21: Define Infectivity 26 Step 22: Define Population Infected with h SARS 27 Time Out and Run 28 Plotting Results 29 Optional: Permanent Graph Use: I//O Ob bject or Custom Graph h 30 Step 23: Add Variables in the Dataset 31 Step 24: Add Infection Rate ( a shadow (as h d variable) bl ) 32 Step 25: Add Causal Link and Polarity 33 Step 26: Define New Reported Cases 34 Step 27: Define Cumulative Reported Cases 35 Step 28: Units Check 36 Step 29: Error!!! 37 Step 30: Redefine Contact Frequency 38 Step 31: Units Check – A. O. K. 39 Step 32: Rename Case – “Base” and Run 40 Step 33: Plot Cumulative Reported Cases 41 Step 34: Try Lowering Contact Frequency 42 Step 35: Change Run Name 43 Step 36: Displaying Multiple Runs 44 Step 37: Synthesim 45 Amazing!!! 46 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 15.871 Introduction to System Dynamics Fall 2013 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.