Document 13478086
advertisement
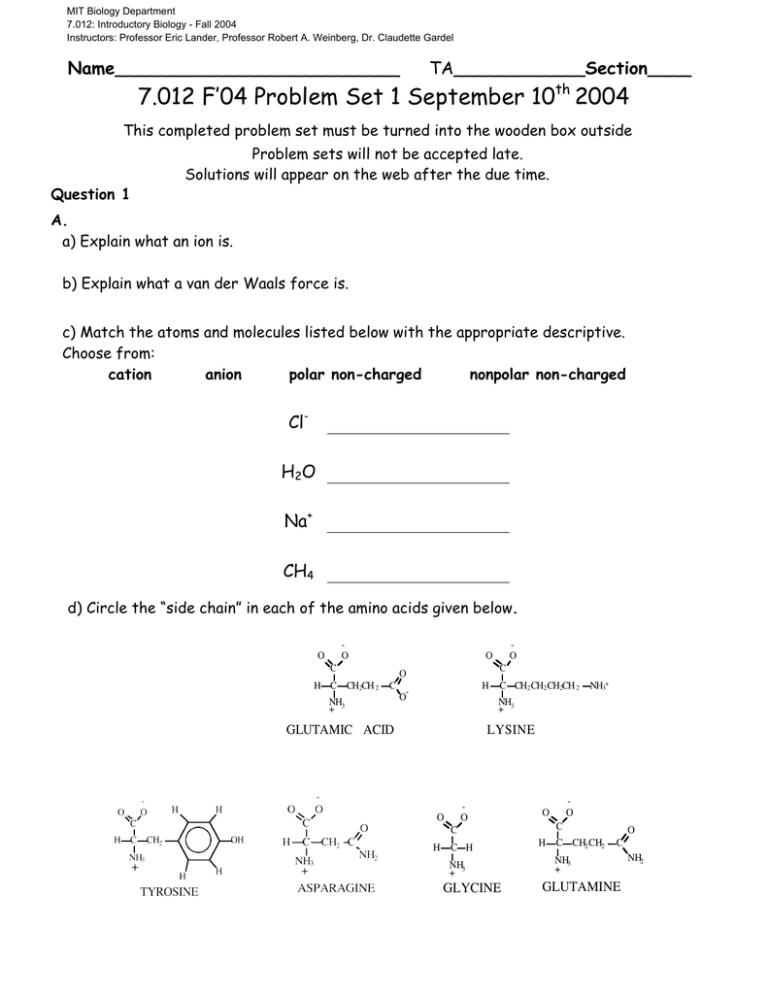
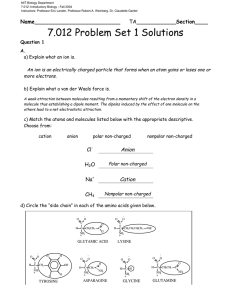
MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel Name__________________________ TA____________Section____ 7.012 F’04 Problem Set 1 September 10th 2004 This completed problem set must be turned into the wooden box outside Question 1 Problem sets will not be accepted late. Solutions will appear on the web after the due time. A. a) Explain what an ion is. b) Explain what a van der Waals force is. c) Match the atoms and molecules listed below with the appropriate descriptive. Choose from: cation anion polar non-charged nonpolar non-charged ClH2O Na+ CH4 d) Circle the “side chain” in each of the amino acids given below. O O C H C CH2CH 2 O O C O C NH + 3 H O- C CH2 CH2 CH2CH 2 NH3+ NH + 3 GLUTAMIC ACID LYSINE O O C C H C H NH3 + GLYCINE O O H C CH2 CH2 O C NH3 + GLUTAMINE NH2 e) Check the following terms to describe the side chains of the amino acids you circled above. Side Chain of… Glutamic Acid Charged Non Charged Polar Non Polar Hydrophobic Hydrophilic Lysine Tyrosine Asparagine Glycine Glutamine f) Explain why ethane (C2H6) is a non-polar molecule while ethanol (C2H5 - OH) is a polar molecule. (A diagram of each molecule may help.) B. a) What are two main differences between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells? b) Match the letter of the organelle on the left with the function or characteristic on the right. Complex or Organelle a. Mitochondria b. Nucleus c. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum d. Golgi Apparatus e. Lysosome f. Ribosome g. Chloroplast h. Nucleolus Function or Characteristic Site of lipid synthesis; where hydrophobic toxins‡ water soluable and thus excretable Digests macromolecules and degrades worn-out organelles Catalyzes protein synthesis Contains all genomic DNA in eukaryotic cell Uses sunlight to build sugar Where ribosomal RNA is made Prepares proteins for export from the cell Powerhouse of the cell; where the Krebs Cycle occurs 2 Question 2 One day in lab while studying your favorite enzyme, Votase, you discover the following potential interactions that could occur between this amazing enzyme and its substrate of choice. Gln O HO Asp C-O- Substrate Arg H3 N + NH3+ Lys H3C CH3 CH3 Ile Votase a) At each site between the chemical group on the substrate and the closest side chain of an amino acid on Votase determine if a favorable interaction is likely to take place. If a favorable interaction is likely to take place, give the name for the strongest direct intermolecular interaction. Choose from ionic interaction, covalent bond, hydrogen bond, and van der Waals force. Amino Acid Will a favorable interaction take place? Circle one. Gln Yes/No Asp Yes/No Ile Yes/No Lys Yes/No Arg Yes/No If yes, Name the Strongest Interaction ionic interaction, covalent bond, hydrogen bond, or van der Waals force. 3 b) For all cases where a potential interaction seemed unfavorable, explain why. Question 3 a) In your continuing work with the enzyme votase you discover that the enzyme is also a transmembrane protein (part of the protein crosses the lipid bilayer of the cell). Circle the portion of the sequence below that you would expect to be the transmembrane region of the protein. +NH3 - glu - trp - asp - arg - his - asp - phe - glu - ser - gly – pro - thr - phe - ile - trp - leu - ile - trp - leu - val - ile - ala – val - leu - phe - leu - leu - ile - trp – ala - val - leu – arg - pro - gly - cys - ser - lys - ala - tyr - ala - lys -- val - cys - ala - gly - cys - ser - asp - lys - gly - glu - COOH b) Why will the section you circled be embedded in the membrane? c) Draw a schematic of the phospholipid bilayer. Label the lipid hydrocarbon chains, phosphate hydrophilic heads, and water. 4 Question 4 a) In the peptide below, circle the peptide bonds. What are the amino acids in this peptide? b) What is the name of the macromolecule below? ________________ c) What is the chemical difference between the pentose sugar in DNA and the pentose sugar in RNA? (See page 48 in text book.) 5 STRUCTURES OF AMINO ACIDS at pH 7.0 O O H C CH3 ALANINE (ala) H O O H N C H + C C CH2 NH3 + O N C H H H ISOLEUCINE (ile) HISTIDINE (his) O- O C CH2CH2 CH3 H NH3 + H OC H C C CH3 NH OH + 3 THREONINE (thr) C CH2 C CH2 C CH3 NH3 + CH3 O- H H C CH2 NH3+ O- O- O C H C CH2 OH NH3 + SERINE (ser) PROLINE (pro) H C H H H H O O NH3 + TRYPTOPHAN (trp) C CH2CH2CH2CH2 NH3 + H C CH2 CH2 H N CH2 H + H N C H H LYSINE (lys) O H O C H PHENYLALANINE (phe) O GLYCINE (gly) O C H C H NH3 + C NH3 + METHIONINE (met) O NH2 C S C LEUCINE (leu) H O- O C H H C C CH2CH3 NH3 CH3 + H H O O O C O GLUTAMINE (gln) O C H O- ASPARTIC ACID (asp) O NH3 + GLUTAMIC ACID (glu) CYSTEINE (cys) NH3 + OC CH2CH2 O- O C CH2 C NH2 C H C H ASPARAGINE (asn) O NH3 + NH3 + C CH2 C O C CH2CH2 C O NH3 + NH2 + C C CH2 SH H NH2 O- O C H C ARGININE (arg) O O C CH2CH2CH2 N O- O C H NH3 + NH3 + O O C C H O O H H C C H O O C CH2 OH NH3 + H TYROSINE (tyr) H H C C NH3 H + CH3 CH3 VALINE (val) 6