System Support for Forensic Inference Ashish Gehani, Florent Kirchner, Natarajan Shankar SRI International
advertisement

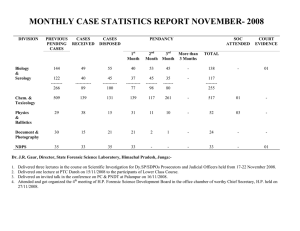
System Support for Forensic Inference Ashish Gehani, Florent Kirchner, Natarajan Shankar SRI International System Support for Forensic Inference – p. 1/17 Introduction Virtual conflict management Specify detailed policy Prevent disallowed actions Physical world differs Retrospective accountability Punishment deters crimes System Support for Forensic Inference – p. 2/17 Enforcement Choices Proactive security Must characterize a priori Supports pseudonymity Reactive security Adjudicate a posteriori Accounts for complex context, e.g. intent Monitoring distributed among population System Support for Forensic Inference – p. 3/17 Changing Approach Limits of proactive approach Institution-wide specification complex Characterizing attacks never ends Reactive security enablers Cryptographic digital identitities Trusted Platform Module Forensics matches reactive paradigm System Support for Forensic Inference – p. 4/17 Ex Post Facto Rules Policy creator’s burden is reduced Individual’s freedom is broader Legal semantics are interpretable Addresses false postive / negative tradeoff Intrusion detection systems System Support for Forensic Inference – p. 5/17 Evidence Standards 1923 - Frye case Based in scientific knowledge Assist the trier of fact 1993 - Daubert case Relevancy Reliability of collection process 1997 - Havner case If "foundational data underlying testimony are unreliable", considered "no evidence" System Support for Forensic Inference – p. 6/17 Evidence Selection Sarbanes-Oxley Act Publicly traded companies Information flow controls Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act Healthcare providers Data privacy protection Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act Financial firms, educational institutions Personal information safeguards System Support for Forensic Inference – p. 7/17 Forensic Analysis Reproducible by opposing counsel Framework must be agreed upon Commutativity of operations Invertibility implications Establishing chain of custody System Support for Forensic Inference – p. 8/17 Formal Framework Standardization Laws on digital evidence encoded in logic Automation Manage the proliferation of evidence Soundness Constructive proofs of conclusions Completeness Claims not inferred can be ruled out System Support for Forensic Inference – p. 9/17 CyberTrail CyberLogic Provides attestations ( :⊲) Predicates, certificates for trust queries Protocols are distributed logic programs Digital artifacts - Authority :⊲Statement Intuitionistic - ambiguity in real world System Support for Forensic Inference – p. 10/17 Case Study Intermediate granularity auditing User-space filesystem Facts that user can attest Future - automate reasoning Interface with λ-Prolog interpreter System Support for Forensic Inference – p. 11/17 Auditing Intercede on calls for: open(), close(), read(), write() File 2 Read open() close() File 1 Read open() close() Process execution Time close() open() File 3 Write System Support for Forensic Inference – p. 12/17 Facts Generated p is a process identifier e is process p’s owner f1 , f2 are files read by p f3 is a file written by p P rocess(p) Owner(e, p) F ile(f1 ) Input(p, f1 ) F ile(f2 ) Input(p, f2 ) F ile(f3 ) Output(p, f3 ) System Support for Forensic Inference – p. 13/17 Digital Artifacts Corresponding attestations: e :⊲ Owner(e, p) e :⊲ Input(p, f1 ) e :⊲ Input(p, f2 ) e :⊲ Output(p, f3 ) System Support for Forensic Inference – p. 14/17 Forensic Analysis List all users who modified f0 Authors(f0 ) := Output(p, f0 ) ∧ Owner(e, p) ∧ Input(p, f1 ) ∧ Authors(f1 ) Validate against digital artifacts Authors(f0 ) := Output(p, f0 ) ∧ Owner(e, p) ∧ Input(p, f1 ) ∧ Authors(f1 ) ∧ e :⊲ Output(p, f0 ) ∧ e :⊲ Owner(e, p) ∧ e :⊲ Input(p, f1 ) System Support for Forensic Inference – p. 15/17 More Forensic Analysis Check digital chain of custody from f0 to f1 Chain(f0 , f1 ) := Chain(f, f1 ) ∧ Output(p, f ) ∧ Input(p, f0 ) ∧ e :⊲ Output(p, f ) ∧ e :⊲ Input(p, f0 ) Find files derived from f0 Derivatives(f0 ) := Input(p, f0 ) ∧ Output(p, f1 ) ∧ Derivatives(f1 ) System Support for Forensic Inference – p. 16/17 Conclusion Acknowledgements IFIP Working Group 11.9 Digital forensics feedback National Science Foundation Grant OCI-0722068 Grant CNS-0644783 Internships available SRI’s Computer Science Laboratory URL: http://www.csl.sri.com/users/gehani/SPADE/ Email: ashish.gehani@sri.com Questions? System Support for Forensic Inference – p. 17/17