C O N S U L T A N C... T E A M A 1 1
advertisement

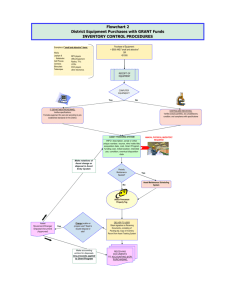
C O N S U LTA N C Y P R O P O S A L TEAM A1 1 Brief of Consultants 1. Faizan Qadri: Knowledge Management & Streamlining Business Processes Expert. 2. Richard Sharman: Supply Chain & Logistics Expert 3. Pauline Mmbaga: Facility Management Expert 4. Henry Ortiz Toloza: Facility & Space Management Expert 5. Parminder Singh: Health & Safety Expert 6. Modar Bakir: Human Resources Expert 2 Peter Drucker & British Government on Knowledge Management • In 1988 Peter Drucker wrote: “The typical business [of the future] will be knowledge-based, an organisation composed largely of specialists who direct and discipline their own performance through feedback from colleagues, customers and headquarters. For this reason it will be what I call an information-based organisation” (Economist 2009). • In the British government’s 1998 White Paper on the competitiveness of the nation, it said: “Our success depends on how well we exploit our most valuable assets: our knowledge, skills and creativity … they are at the heart of a modern knowledge-driven economy” (Economist 2009). 3 Our Understanding of the Brief Vision (Q3/2017) Five Years’ Plan The Current Status of the company (Q3/2012) Strategy No. 3 To be the first choice for clients where high quality meets affordability and set high standards in the UK and European Market Apply KM & AM Tangible Assets Intangible Assets Processes 4 Meet the criteria of the European Excellence Model WaveRiders GAP Analysis GAP Target Current Status Timeline Actions Responsibility 1 Expand distribution and logistics to Europe Supply chain in the UK Q4/2012 Outsourcing the distribution function in Europe and hiring a Logistic Manager (reporting directly to CEO) CEO, Production Director, Finance Director and Richard 2 Improve supplier base Multiple suppliers (10+) Q4/2012 Assess and review current supplier base and streamline CEO, Production Director and Richard 3 Allow a suitable environment for employees to perform core functions No facility director no awareness and concern on improving the value of the properties and No concern of the safety of the buildings Q4/2012 Hire Facility Director (reporting directly to CEO) 4 Increase inventory turnover Poor management of inventory Q4/2012 Implement Just In Time Production 5 Improve Safety Standards in plant and products No records Q4/2012 Hire Health & Safety Manager (Reporting directly to Facility Director for plant daily operation issues/ reporting directly to the CEO for company policy & road safety) 6 Vision/Mission and competency framework for the whole company No core values/competencies and shared vision Q1/2013 Setting up a Steering Committee chaired by the HR Director, the committee will be consisting of members from different levels and departments of the organisation 7 Setting up a new organizational structure/ job descriptions/HR Policies & Procedures/Employee Handbook /Orientation Program/ER/Recruitment & Retention Strategies The current organizational structure/ job descriptions while the rest are not available Q2/2013 HR Director, Henry and Pauline Production Director and Pauline HR Director and Parminder Board of Directors and Modar HR Director and Modar 5 Current Supply Chain of WaveRiders Material Suppliers UK Factory UK Warehouse Sales to Retailers Sales to End Users 6 Future Supply Chain Strategy Sales/Marketing UK After Sales UK Market Suppliers UK Factory UK Warehouse EU Market EU After Sales 7 Sales/Marketing Supplier Management Materials R&D Market Information Supplier Manufacturing Processes R&D Customer Feedback WaveRiders Materials Knowledge Marketing/Sales Forecast Competitive Advantage Supplier / Manufacturer Information Model Strategies: Improve Supplier Base through assessing and reviewing current supplier base and streamline in order to Improve Working Relationship and therefore bring new benefits. 8 Distribution in the EU Market • Outsourcing the distribution function in the EU Market. • Increase the Distribution Manager scope of work where he will be responsible of the distribution operation in the UK and supervising the outsourcing contract of distribution in the EU market. 9 Asset Life Cycle management • • • Measuring assets on a COST Vs. PROFIT basis Group assets into processes Consistently gather and log information and knowledge of the assets outputs and inputs on an accessible database. Output (profit) Raw Materials Useful Life Finished Goods Machines Initial Cost 10 Resale Value Running Costs/Maintenance Man hours required to operate Recommendations • New Asset Strategy – Use information from sources such as manufacturers/past experiences/forecasts/departmental requirements to assess and compare potential new assets to gain best balance of cost/capability and quality. (the head of the department that will use the asset should carry out these procedures) • Use financial measures such as Payback period and NPV to give financial insight. (finance department) 11 Recommendations • Current Asset Strategy – the manufacturing process and the storage process. • Log data, and keep records of performance and any costs incurred in the past. • Make operatives responsible for logging data and regular inspection to prevent problems escalating. • Have procedures in place to deal with the maintenance of assets so down time is reduced. • Constantly reassess the costs vs profit performance to map when parts of the processes need updating or replacing. 12 Facility & Property Management • Facility management is ‘an integrated approach to maintaining, improving and adapting the building of an organization in order to create an environment that strongly supports the primary objectives of that organization’ (Barrett and Baldry,2003). 13 Recommended Strategies • Hiring a Facility Director: the main objective of this role is to ensure that an organisation has the most suitable working environment for its employees and their activities. Also, implementing cost cutting initiatives and Initiating projects which will enhance the image of the company. • Estimated Annual Salary: £60,000 CEO John Excellence Facility Director 14 Assets requiring management • Property Management: Design and Build Activities, Facility Services(Safety, Health and Environment), Space Management and Maintenance of Equipment • Inventory Management: Just-In-Time Production 15 Property Management Design and Build Facilities Current Situation • There is very little awareness and concern on improving the value of the properties and inaccessible property inventory Action Plan • Facility Director should outsource an external surveyor to conduct valuation on the plant at least every 3 years Anticipated Outcome • Reduced cost of wear and tear and reduced time wastage 16 Inventory Management Production Scheduling and Inventory Current Situation • Tied-up capital, inaccessible inventory audit Action Plan • Implement Just-In-Time production Anticipated Outcome • OTIF (On time in-full production, on time delivery and customer satisfaction ration to increase by 99%) 17 Current Situation to JIT S 18 RM WIP FG Space management Current situation: • There is not a fixed travel route for material and products transport from stock area to the dispatch area • There are not clear routes for loading vehicles, (forklifts) • The employees do not enough space to work comfortably Action plan • Optimize the space in the production area, creating fixed routes for the vehicles and create open plan offices. Anticipated outcome • Reducing the lead time • Improve communication between departments. 19 21 22 23 Maintenance Reactive policy 24 Proactive policy Health & Safety • What Environment? the surroundings in which an organization operates, including air, water, land, natural resources, flora, fauna, humans, and their interrelation. Clause 3.5 ISO 14001:2004(E) • Who’s Safety & Health? OH & S relates to the Conditions and factors that affect, or could affect, the health and safety of employees, or other workers (including temporary workers and contractor personnel), visitors, or any other person in the workplace. Clause 3.12 OHSAS 18001:2007 25 The Present at WaveRiders : • No Procedures for the safety and health of the employees • Fire fighting and no proper elimination of Safety concerned issues • No focused effort to prevent damage to the environment. 26 What needs to be done • Consider SHE as a strategic part of the overall business strategy. • Develop a system for SHE management. • Create a culture of health , safety and environmental awareness. • Create awareness regarding conservation of resources. 27 SHE Management - The way ahead (strategy) • Hire a SHE manger (reporting directly to Facility Director for plant daily operation issues/ dotted reported to the CEO for company policy & road safety). CEO John Excellence Facility Director SHE Manager • • 28 Incorporate a SHE Policy Train employees – create awareness SHE Management - The way ahead (strategy) • • • • • • • • • • • 29 Conduct – An Environmental aspect evaluation – A Hazard risk analysis Identify the most significant aspects. Make Safety management procedures (SMP) and environmental management procedures(EMP). Eliminate the aspects (Follow the PDCA methodology). Make Operational control Procedures (OCP). Have an emergency preparedness plan in place Maintain a legal register. Management Review Apply for ISO 14001 and IS 18001 certification. Start a near miss reporting and recording system. Start energy conservation and safety committees Knowledge management • Procedure manual (Environmental and Safety: • OCP • EMP & SMP • List of most significant aspects • Emergency preparedness plan • Legal register • Near miss reporting and analysis. 30 Timeframe for Implementation Timeframe for SHE implementation.xlsx 31 Estimated Budget for SHE • SHE manager • Training • Certification: £40,000 per annum £ 10,000 - £ 15,000 £ 3,000 – £3,500 per certification • Other costs depending upon the work to be carried out to make the work place more safe and environmental friendly. 32 Effective Asset Management through People Effectiveness In order to have an Effective Asset Management system within WaveRiders, we recommend you to apply the following three strategies (Lutchman 2006): • Organizational and People Effectiveness • Corporate Knowledge Retention • Performance Management (Balanced Scorecard) 33 Organizational Effectiveness Vision & Mission Tangible Assets Intangible Assets Processes Develop Organisational Structure Define Roles Responsibilities Competencies Framework Job Descriptions Staffing Numbers 34 Knowledge Management HR Policies & Procedures C&B Plans Recruitment Strategy Retention Strategy Succession Planning Strategy L&D Program Employee Assistance Program Employee Handbook Orientation Program SOPs Developing a High – performance Organization (Lutchman 2006) Performance Management Empowered Teams Continuous Improvement Organizational Development & Learning • • • • • • • • • • • • 35 Develop the core values/competencies framework for the company. job evaluation based on a Knowledge and Skills Framework. Validate Job Descriptions, Roles, technical and general skills. Introduce the competency skills framework to all posts. Identify individual learning and development needs against the approved competency framework through carrying out TNA of current skills, knowledge and competencies (skills gap analysis). Develop a training program for all employees based on the TNA results. Assigning a training budget for the Sales team who are going to be involved in the EU market and for the SHE Manager. HR Team to achieve CIPD certification. Orientation program (Corporate and Departmental Induction). SOPs / best practices in coordination with the rest of the departments HR Policies & Procedures / Employee Handbook Employee Assistance Program / Redundancy Plans & Payments Job Rotation Establishing an E-learning portal for the company might not be suitable at the time being (EFQM 4e. Using information technology to support knowledge management). Recruitment & Retention • • • • • • • 36 To ensure that the attrition rate is at the minimum for the next five years (voluntary and involuntary resignations). Offer a variety of career packages and employment contracts (permanent, temporary, flexible ... Etc.) Building a professional reputation for the company (employer of choice). Recruitment processes must fulfill all legislative requirements and demonstrate fair and equitable treatment of all applicants. The HR department is committed to providing an efficient service to managers and applicants, and to ensuring that recruitment systems are reviewed as required to maintain a smooth process. Reward & Recognition policy. It is important to determine what causes staff to leave. To this end an exit procedure and guidelines is being developed and will be implemented in Q4 2012. The results will be analyzed to identify trends so that counter measures may be introduced where appropriate (employee branding). Staff Monthly meeting with BoD (staff involvement, enhancing two way communication). Performance Management - Balanced Scorecard Balanced Scorecard Objectives Increase Profitability Increase the efficiency of using the assets Increase the space use within the premises of the company Action Plan Measurement Target Initiative Budget ROCE 13% - - ROA 11.93% - - Hiring Facility Director £300k Lower the cost of maintenance and cleaning on a monthly basis Decrease the Dispatch time No of frequency and complaints from customers 2 Create fixed routes for materials and products, create clear routes for loading vehicles £30k Increase inventory turnover Percentage of stock outs 0 Implement Just In Time production - On-time in full production ration 99% Implement Just In Time production Percentage of perfect orders received 95% Assess and reduce suppliers - Number of staff reduced annually 1 Applying Redundancy £77k Percentage of on-time delivery to customers in Europe 98% Expand the distribution and logistic in EU £2k No. of accidents and near misses due to design and procedures 0 Hiring Health & Safety Manager, obtaining certifications and Training £217k Turnover of Sales Personnel 2% Take on new 3 Sales Rep £96k Percentage of employees active in improvement teams and team learning 90% Measurement of effectiveness and TNA - Number of job rotations each year per employee 2 Job rotations between and within departments, orientation programs and graduate schemes £90k TOTAL BUDGET £812k Increasing on time production Improve supplier base Reduce HR Team Identify New Distributor (s) in the EU market Improve Safety Standards in plant and products Recruit and Retain Qualified Sales Rep Increase value of learning (ROI) Increase knowledge sharing between employees and within departments 37 Summary Optimize the usage of the space of the premises Implement Just In Time Production Facility Management Supply Chain Review, Assess and Optimize Supplier Base Outsourcing Distribution function in EU market Hiring Facility Director Reduce Lead Time Increase and maintain the life of the physical assets of the company Effective Knowledge & Asset Management System Set up procedure manuals for safety and environmental management Obtain ISO 14001 and IS 18001 certification Organizational & People Effectiveness Health & Safety Human Resources Hiring Health & Safety Manager Performance Management WaveRiders’ Vision 38 Corporate Knowledge Retention To w a r d s E F Q M 4c: developing and implementing strategies for managing buildings, equipment and materials 4c: improve total life cycle performance 4c: optimising transportation usage 4c: Optimising material inventories 4c: minimizing impact on environment EFQM Model Partnership & Resources 4c: affect of organisation asset on health and safety 4e: identify information and knowledge req. 4e: providing appropriate access 4e: cultivating and protecting intellectual property 4e: generating innovative and creative thinking 4e: collecting and structuring information and knowledge 39 References • • • • • • • • 40 Economist (2009) knowledge management [online] available from http://www.economist.com/node/12960225 [24th April 2012] European Foundation for Quality Management (2009) EFQM Excellence Model, EFQM Publications. Lutchman, R. (2006) Sustainable Asset Management: Linking Assets, People, and Processes for Results. Pennsylvania: DEStech Publications, Inc. Shanthi, N. (2006) Knowledge Management for Business Strategy. Hyderabad: The ICFAI University Press. Fileding, K and Whicker, L (2012), ‘Planning and Control Systems: JIT, Logistics and Operations Management’, Supply Chain Lecture at the University of Warwick. Pain, S. W. (2010). Safety, Health, and Environmental Auditing. New York: CRC PRess. OHSAS 18001:2007. OHSAS project group ISO 14001:2004(E) Environmental management systems – General guidelines on principles, systems and Support techniques. T H A N K YO U Q&A 41