Chapter 1
advertisement

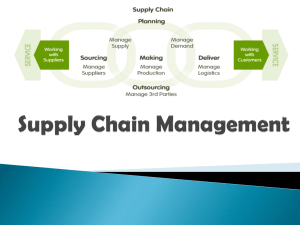
Chapter 14 Supply chain management Supply Chains Supply Chain The connected chain of all of the business entities, both internal and external to the company, that perform or support the logistics function 2 Supply Chains Supply Chain Management A management system that coordinates and integrates all of the activities performed by supply chain members into a seamless process, from the source to the point of consumption, resulting in enhanced customer and economic value 3 Benefits of Supply Chain Management Supply chain oriented companies commonly report: • Lower inventory, transportation, warehousing, and packaging costs • Greater supply chain flexibility • Improved customer service • Higher revenues • Increased profitability 10 Supply Chain Integration Relationship Integration Measurement Integration Technology and planning Integration Firm-to-Firm Social Interactions Operational Planning and Control Material and service supplier Integration Internal Operations Integration Customer Integration Customer Integration 5 Key Processes of Supply Chain Management 6 Customer Relationship Management Customer Relationship Management Process The prioritization of a firm’s marketing focus on different customer groups according to each group’s long-term value to the company or supply chain; designed to identify and build relationships with good customers. 7 Customer Service Management Customer Service Management Process A multi-company, unified response system to the customer whenever complaints, concerns, questions, or comments are voiced; designed to ensure that customer relationships remain strong. 8 Demand Management Demand Management Process The alignment of supply and demand throughout the supply chain to anticipate customer requirements at each level and create demand-related plans of action prior to actual customer purchasing behavior. 9 Order Fulfillment A supply chain Order Fulfillment management process that Process involves generating, filling, delivering, and providing on-the-spot service for customer orders. 10 Manufacturing Flow Management Manufacturing Flow Management Process A process that ensures that firms in the supply chain have the resources they need 11 Supplier Relationship Management Supplier Relationship Management Process A supply chain management process that supports manufacturing flow by identifying and maintaining relationships with highly valued suppliers 12 Product Development and Commercialization Product Development and Commercialization Process The group of activities that facilitates the joint development and marketing of new offerings among a group of supply chain partner firms. 13 Returns Management Returns Management Process A process that enables firms to manage volumes of returned product efficiently, while minimizing costs and maximizing the value of the returned assets to the firms in the supply chain. 14 Supply Chain Team Logistics Information System Logistical Components of the Supply Chain Sourcing & Procurement Production Scheduling Order Processing Inventory Control Warehouse & Materials Handling Transportation Sourcing and Procurement The Role of Purchasing: Plan purchasing strategies Develop specifications Select suppliers Negotiate price and service levels Reduce costs Production Scheduling Traditional Focus Customer Focus Push / Pull Strategy Push Pull Start of Production InventoryBased Customer-Order Based Manufacturing Mass Production Mass Customization Just-in-Time Manufacturing JIT A process that redefines and simplifies manufacturing by reducing inventory levels and delivering raw materials just when they are needed on the production line. Benefits of JIT Reduces raw material inventories Shortens lead times Creates better supplier relationships Reduces production and storeroom costs Reduces paperwork Order Processing Electronic Data Interchange Information technology that replaces paper documents that accompany business transactions with electronic transmission of the information. Order Processing Inventory Control System A method of developing and maintaining an adequate assortment of materials or products to meet a manufacturer’s or a customer’s demand. Order Processing Materials Requirement Planning (MRP) An inventory control system that manages the replenishment of raw materials, supplies, and components from the supplier to the manufacturer. Distribution Resource Planning (DRP) An inventory control system that manages the replenishment of goods from the manufacturer to the final consumer. Materials Handling Functions Receive goods into warehouse Identify, sort, and label goods Dispatch the goods to temporary storage Recall, select, or pick the goods for shipment Transportation Airways Water Pipelines Motor Carriers Railroads Transportation Mode Choice Cost Transit time Reliability Capability Accessibility Traceability 25