Macfarlane Research Group
advertisement

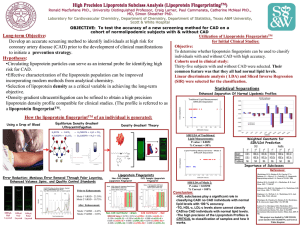
Macfarlane Research Group Ronald Macfarlane PhD., University Distinguished Professor, D’Vesharronne Moore, Craig Larner, Paul Cammarata Laboratory for Cardiovascular Chemistry, Department of Chemistry, Texas A&M University Lipoprotein Fingerprinting: A link between Analytical Chemistry And Healthcare for the Diagnosis of Coronary Heart Disease OBJECTIVE: To Develop a Combination of Chemical Methods for the Diagnosis of Early Onset of Cardiovascular Disease Difference in Apolipoprotein C1 Found for CVD Samples Vs Controls: High Performance Lipoprotein Profiling: Forming the Lipoprotein Fingerprint: Using a Drop of Blood Equilibrium Density Gradient Ultracentrifugation H4EDTA + CdCO3 MALDI Mass Spectrometry Control HDL-2 CVD HDL-2 Control HDL-3 CVD HDL-3 Density Gradient Theory → H2CdEDTA + H2O + CO2 H2CdEDTA + Cs2CO3 → Cs2CdEDTA + H2O + CO2 + Mass shift found for Apo C1 for all CVD patients in a small sample study. For these samples, the apoptosis values were also found to be 50% higher. In contrast, the Control patients had normal Apo C1 with lower apoptosis values. This indicates a possible connection between the Apo C1 and the development of CHD. Further Testing of Lipoprotein Fingerprint Samples: Chemical and Immunoaffinity Cell Culture Studies Integrated Intensities from the Lipoprotein Fingerprint Lipoprotein Finger Print Sample TRL LDL-1 LDL-2 LDL-3 LDL-4 LDL5 HDL-2b HDL-2a HDL-3a HDL-3b HDL-3c Serum added to Substance A and shaken to form lipoprotein bound complex and spun to obtain supernatant Isoelectric Focusing - + - Supernatant consists of serum depleted of lipoprotein or protein of interest Stripping buffer is added to beads to elute Lipoprotein or protein of interest and spun to obtain supernatant Supernatant consists of isolated lipoprotein or protein of interest Capillary Electrophoresis + Delipidated Denatured Proteins IPG Gel Children’s Study CVD Separation 7770 & 1532C CVD Library Study (90 Patients) - pH=7 + Enhanced Separation Of Normal Lipodemic Profiles Statistical Separations pH=4 Focused Proteins pH=4 pH=7 7770 and 2.5 1532C Control CVD Study CVD (1) vs Control (2) 2 1.5 CVD 1 Control 0.5 0 -2.5 -2 -1.5 -1 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 LDA Separation Value P-value = 0.14352 % Correct = 100% P-value = 0.23306 % Correct = 100% P-value = 0.03804 % Correct = 85.6% 2 2.5 Recent and Future Publications: 1. P.V. Bondarenko, Z.N. Farwig, C.J. McNeal, R.D. Macfarlane, MALDI- and ESI-MS of the HDL apolipoproteins; new isoforms of apoA-I, A-II, Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Process 219 (2002) 671–680 2. J.D. Johnson, N.J. Bell, E.L. Donahue, R.D. Macfarlane, Metal ion complexes of EDTA as solutes for density gradient ultracentrifugation: influence of metal ions, Anal. Chem. 77 (2005) 7054–7061 3. Henriquez, R.R. et al. World Intellectual Property Organization (2009) Characterization of Biological Samples. Patent # WO/2009/152437 4. D. Moore et al. Isoforms of apolipoprotein C-I with Individuals with Coronary Artery Disease. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 404 (2011) 1034–1038 5. Larner, C., Macfarlane, R.D. High Performance Lipoprotein Profiling. Anal. Chem. (To Be Published) 6. Larner, C., Cammarata, P., Ortega, E., Macfarlane, R.D. Use of Lipoprotein Fingerprints and Statistics to Classify Any Subjects for Coronary Artery Disease . Anal. Chem. (To Be Published) 7. Cammarata, P., Larner, C., Macfarlane, R.D. Lipoprotein Fingerprint: A New Approach to Classifying Normal Lipidemic Subjects for Coronary Artery Disease. Anal. Chem. (To Be Published) 8. Cammarata, P., Macfarlane, R.D. An Accurate and Precise Fraction Collector for Preparative Lipoprotein Density Profiling. Anal. Chem. (To Be Published)