Sound

Primary Subject
Integrated Subjects
Grade Level(s)
Length of Unit
Research Sources
Unit Summary
Key Vocabulary
Sound
Science
Math, Reading, Writing, Social Studies
Second Grade
1 week
See attached lesson plans below for sound websites.
Students will explore how sound is produced. Students will identify the relationship between sound and the objects of the body that vibrate such as the eardrum and vocal chords. sound, vibrations, columns of air, eardrums, vocal chords, waves, energy, pitch
NC Essential Standards For
Science
Commor Core Standards for
Mathematics
Common Core Standards for
ELA & Literacy
Essential Questions
Materials & Resources
See attached Lesson Plans below
See attached Lesson Plans below
See attached Lesson Plans below
How is sound produced?
How do our ears allow us to hear sounds?
How can we produce different sounds?
Why is sound important?
Houghtin Mufflin Basal Reader (Moses Goes to a Concert)
A junior high/high school band to come and visit school.
Rice on aluminum foil on speaker/Slinky on a surface/Tuning Fork to show sound vibrations
Orff instruments
Noise Makers ( empty plastic pop bottle along with ingredients: popcorn kernels, dried peas, coins, etc.)
Garage Band to allow students to compose music.
Play Rock Band on Wii or Playstation game console.
Sound Flipcharts
MSP Sound Probes with Verniers
Activities/Procedures
• Essential Question
• Explore/Engage
• Explain
• Elaborate (Inquiry)
• Evaluate
Accommodations for
Differentiated Instruction
See attached Lesson Plans below
Computer use will be available to reduce the amount of writing.
Students will be paired with a buddy to assist with writing activities.
Students will be paired in varying ability groups to allow students to work together to share knowledge.
Cross Curricular
Integration
Created by
Supporting Documents
Math: Students will use measurement tools to measure how far away you can hear a sound. Tools include a ruler, yard stick, and meter stick.
Using the sound level meter graph students will draw a graph to show the sound patterns they made.
Reading: Students will read Moses Goes to a Concert . Teacher will read aloud Horton Hears a Who (watch Horton Hears a Who if allowed).
Students will read Magic School Bus: The Haunted Mansion . Students will discuss the stories.
Writing: Students go on a listening walk. Students write or draw the sounds they hear. Students will write a poem about sounds.
Social Studies - Students listen and identify various animal sounds. Students identify sounds in the immediate school envirnoment. In a learning center activity students will match the sound they hear to an animal. Students will play an interactive game on the computer matching sounds to pictures. Historical figures: Benjamin Franklin. The teacher will show pictures of Franklin’s musical invention.
Students will compare this instrument to the Orff instruments. Optional: Teacher will read aloud a short biography of Helen Keller. Teacher will teach a few simple words of sign language.
Music - Students will play high and low pitches on an orff instrument. Students will show different sounds for each season of the year. Students will create music sounds for each season based on using different instruments.
Media: use studyjams.com, Bill Nye Science Guy Videos on Sound, Magic School Bus: The Haunted Mansion prybulann@rss.k12.nc.us
and knadeau@northhillschristian.com
Lesson Plan Unit (see below), Sound Flipcharts from http:// www.prometheanplanet.com/en-us/ , Horton Hears A Who trailor
(trailers.apple.com/trailers/fox/hortonhearsawho/ )
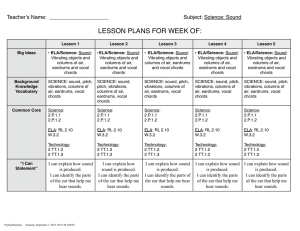
Teacher ʼ s Name: ____________________ Subject: Science: Sound
LESSON PLANS FOR WEEK OF:
Big Ideas
Background
Knowledge
Vocabulary
Common Core
“I Can
Statement”
Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Lesson 5
• ELA/Science: Sound:
Vibrating objects and columns of air, eardrums and vocal chords
• ELA/Science: Sound:
Vibrating objects and columns of air, eardrums and vocal chords
• ELA/Science: Sound:
Vibrating objects and columns of air, eardrums and vocal chords
• ELA/Science: Sound:
Vibrating objects and columns of air, eardrums and vocal chords
• ELA/Science: Sound:
Vibrating objects and columns of air, eardrums and vocal chords
SCIENCE: sound, pitch, vibrations, columns of air, eardrums, vocal chords
Science:
2.P.1.1
2.P.1.2
SCIENCE: sound, pitch, vibrations, columns of air, eardrums, vocal chords
Science:
2.P.1.1
2.P.1.2
SCIENCE: sound, pitch, vibrations, columns of air, eardrums, vocal chords
Science:
2.P.1.1
2.P.1.2
SCIENCE: sound, pitch, vibrations, columns of air, eardrums, vocal chords
SCIENCE: sound, pitch, vibrations, columns of air, eardrums, vocal chords
Science:
2.P.1.1
2.P.1.2
Science:
2.P.1.1
2.P.1.2
ELA: RL 2.10
W.3.2
ELA: RL 2.10
W.3.2
ELA: RL 2.10
W.3.2
ELA: RL 2.10
W.3.2
ELA: RL 2.10
W.3.2
Technology:
2 TT.1.2
2 TT.1.3
I can explain how sound is produced.
I can identify the parts of the ear that help me hear sounds.
Technology:
2 TT.1.2
2 TT.1.3
I can explain how sound is produced.
I can identify the parts of the ear that help me hear sounds.
Technology:
2 TT.1.2
2 TT.1.3
I can explain how sound is produced.
I can identify the parts of the ear that help me hear sounds.
Technology:
2 TT.1.2
2 TT.1.3
Technology:
2 TT.1.2
2 TT.1.3
I can explain how sound is produced.
I can identify the parts of the ear that help me hear sounds.
I can explain how sound is produced.
I can identify the parts of the ear that help me hear sounds.
Teacher ʼ s Name: ____________________ Subject: Science: Sound
PrybulaNicholas Saturday, September 7, 2013 10:31:39 AM ET
“I Will
Statement”
I will illustrate and describe how sound is produced.
I will explain which parts of the body produce and receive sound waves.
LESSON PLANS FOR WEEK OF:
I will illustrate and describe how sound is produced.
I will explain which parts of the body produce and receive sound waves.
I will illustrate and describe how sound is produced.
I will explain which parts of the body produce and receive sound waves.
I will illustrate and describe how sound is produced.
I will explain which parts of the body produce and receive sound waves.
I will illustrate and describe how sound is produced.
I will explain which parts of the body produce and receive sound waves.
PrybulaNicholas Saturday, September 7, 2013 10:31:39 AM ET
Teacher ʼ s Name: ____________________ Subject: Science: Sound
LESSON PLANS FOR WEEK OF:
Materials/Tools Websites: http:// resources.woodlandsjunior.kent.sch.uk/ revision/science/ sounds.html
http:// www.exploratorium.edu/ listen/online_try.php
http://dingo.care2.com/ cards/new/0422/Do-arain-deer.swf
http:// www.nyphilkids.org/ games/main.phtml?
http:// www.scholastic.com/ magicschoolbus/games/ sound/# http:// www.sciencekids.co.nz/ gamesactivities/ changingsounds.html
http://www.bbc.co.uk/ schools/magickey/ adventures/ soundmonster_game.shtml
Teacher ʼ s Name: ____________________ Subject: Science: Sound
PrybulaNicholas Saturday, September 7, 2013 10:31:39 AM ET
Introduction/ PBL: Your friend is
Hook/
Connections taking you to a music concert. You are excited to attend the concert; however you are deaf. How will you hear the sounds?
LESSON PLANS FOR WEEK OF:
PBL: Help the creatures of
Whoville. Horton needs your help to save Whoville. What can you do to make a high pitch that will save Whoville?
PrybulaNicholas Saturday, September 7, 2013 10:31:39 AM ET
Teacher ʼ s Name: ____________________ Subject: Science: Sound
Activities Pre-KWL: student will write what they Know,
Want to know, and
Learned about Sound before you teach it.
Read Moses Goes To A
Concert from Houghton
Mifflin Baal Reader.
Writing: Students go on a listening walk.
Students write or draw the sounds they hear and classify them into groups.
Compare/contrast
Helen Keller with
Moses Goes To A
Concert using a Venn
Diagram
Science Investigation
(from bottom of lesson plan)
LESSON PLANS FOR WEEK OF:
Teacher Demo: Rice on aluminum foil on speaker/
Slinky on a surface/
Tuning Fork to show sound vibrations
Show movie trailer of
Horton Hears a Who then read Horton Hears a Who
(watch Horton Hears a
Who if allowed) Use
MSP Sound Probe:
Vernier with Sound Level
Meter to show graphing of pitches.
A junior high/high school band to come and visit school.
Math: Measure how far away you can hear a wood block being dropped using a ruler, yard stick, and meter stick. read Magic School Bus:
The Haunted Mansion
Students will go to the computer lab and play sound games (websites are listed in materials and tools)
Use Garage Band to allow students to compose music that depicts themselves.
Students will create their own poetry sound notebook; use
Kidspiration rhyming words (under Reading tab) as a way to give ideas for poetry sound notebook.
Sound Review Flipchart
Science Investigation
(from bottom of lesson plan)
Students listen and identify various animal sounds. In a learning center activity students can match the sound they hear to an animal.
Use Sound Flipchart that explains more in-depth terminology.
Science Investigation
(from bottom of lesson plan)
Sound Energy Flipchart that focuses on the ears.
Post KWL: Pass back the pre-KWL for students to add onto their existing knowledge when the unit is over.
Students create noise makers
(empty plastic pop bottle and fill with one or more ingredients: popcorn kernels, dried peas, coins, etc.)
Play Rock Band on Wii or
Playstation game console.
*For extensions, students create a way to show sound waves*
Science Investigation
(from bottom of lesson plan)
Teacher ʼ s Name: ____________________ Subject: Science: Sound
PrybulaNicholas Saturday, September 7, 2013 10:31:39 AM ET
Closure/Review Science
Investigations are included at the bottom of this document: pick and choose what you feel comfortable teaching. These are to be done by students. Teacher model if applicable.
Pre-Assessment Pre-KWL
Students will turn this into the teacher.
LESSON PLANS FOR WEEK OF:
Science
Investigations are included at the bottom of this document: pick and choose what you feel comfortable teaching. These are to be done by students. Teacher model if applicable.
Science
Investigations are included at the bottom of this document: pick and choose what you feel comfortable teaching. These are to be done by students. Teacher model if applicable.
Science
Investigations are included at the bottom of this document: pick and choose what you feel comfortable teaching. These are to be done by students. Teacher model if applicable.
Post-
Assessment
Students turn and talk to their neighbor about what they learned in class.
Students will draw three ideas of how they can save
Whoville. Students will explain to a partner how their ideas will help
Whoville.
List Differentiated
Strategies: (groups)
Groups based on teacher grouping.
Students will write in their Science Journal about what they observed/learned during the investigation.
Students will evaluate themselves based on matching sounds to the season in which they occur.
Post KWL
Pass back their papers and have students add to their
KWL after this week.
Compare knowledge from Pre to Post
KWL.
PrybulaNicholas Saturday, September 7, 2013 10:31:39 AM ET
Teacher ʼ s Name: ____________________ Subject: Science: Sound
Higher Level
Thinking
Questions:
(analysis, evaluating and creating levels)
How can we communicate with someone who is deaf?
LESSON PLANS FOR WEEK OF:
How do we hear different sounds?
What affects how far a sound is heard?
What sounds do you associate to each season? How do the season ʼ s differ in the sounds you hear?
Sound Experiments
Do plastic and glass bottles make the same sound when you blow across the top and when you hit their sides?
Materials Needed
• different sized empty glass and plastic bottles
• water
• spoon
Instructions
1.
Begin with empty bottles. Try hitting them with the spoon.
2.
Blow across the tops of the empty bottles, like you're playing a flute, to see if they sound different.
3.
Now put different amounts of water in the bottles. Try hitting them and blowing across them again.
4.
What makes the bottles make different sounds?
http://pbskids.org/zoom/activities/sci/bottlehitandblow.html
Teacher ʼ s Name: ____________________ Subject: Science: Sound
LESSON PLANS FOR WEEK OF:
PrybulaNicholas Saturday, September 7, 2013 10:31:39 AM ET
Use a drinking straw and your noodle to make a musical kazoo-dle.
Materials Needed
• drinking straws
• scissors
Instructions
1.
First, flatten out one end of a straw. The easiest way to do this is to bite on it.
2.
With a pair of scissors, cut the flattened end of the straw in an upside-down "V" shape. This will act as a reed just like in a clarinet.
3.
Place the "V" end of the straw in your mouth so that the "V" end is just past the inside of you lips.
4.
Press on the "V" with your lips while blowing. This might take some practice. You may have to separate the "V" a bit.
5.
Here's another cool thing that you can do. Cut the straw and then blow on it. Hear how the pitch is higher?
http://pbskids.org/zoom/activities/sci/strawkazoo.html
PrybulaNicholas Saturday, September 7, 2013 10:31:39 AM ET
Teacher ʼ s Name: ____________________ Subject: Science: Sound
LESSON PLANS FOR WEEK OF:
Making Sounds With Rulers
Materials:
• 1 plastic ruler
• 1 heavy book
Find Out For Yourself
Explore ways to make sound with the ruler. Now try extending one end of the ruler over the edge of a table and plucking it. Listen carefully to what you hear. Which sounds come from the ruler hitting the table. Which comes from the ruler making the air move?
Try making the ruler vibrate so it does not hit the table. Hold the ruler down firmly with a book.
Think about the sounds the ruler might make when a long piece of it extends over the edge of the table and you pluck it. Do you think it might make high or low sounds? Write your predictions about the sound that will be produced by a long, medium and short piece of the ruler. Also write the reasons why you think this will happen.
Now think about how a long, medium, and short piece of the ruler will look when it extends over the edge of the table and you pluck it. How will each different length of the ruler vibrate when plucked? Write your predictions and reasons.
Work alone or with a partner to test your predictions.
What did you hear when you compared the sound produced by a long piece of the ruler with the sound of a short piece.
What did you see when you compared the vibrations of a long piece and a short piece of the ruler.
Ideas to Explore
Find object other than rulers that can be extended over the edge of the table and plucked to make sounds. Can you get the sound made by two different vibrating objects to match?
http://www.smm.org/sound/activity/ssl4.htm
PrybulaNicholas Saturday, September 7, 2013 10:31:39 AM ET
Teacher ʼ s Name: ____________________ Subject: Science: Sound
LESSON PLANS FOR WEEK OF:
Materials
• 6 balloons
• a partner
Activity
Sound Site: Activities: Vibrations Through Compacted Air
Ask your partner to stand half the distance across the room from you and whisper a sentence to you.
Blow up a balloon and tie the end. The air in the balloon is squeezed or compacted. Hold the balloon against your ear. Ask your partner to whisper a sentence to you again.
Trade places and repeat the experiment.
Did the balloon change the sound of your partner's whisper? How and why?
Does air or compacted air transmit sound better?
Science Notes
The air in the balloon is under greater pressure than the surrounding air. Since the air in the balloon is denser than the surrounding air, sound travels better through the balloon.
http://www.smm.org/sound/nocss/activity/3b.htm
PrybulaNicholas Saturday, September 7, 2013 10:31:39 AM ET