The CANTAB Intradimensional/Extradimensional Attentional Shift Procedure in Rhesus Monkeys:
advertisement
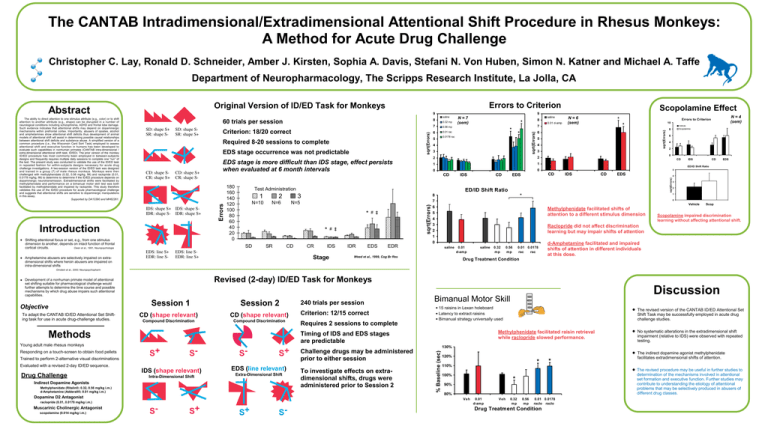
The CANTAB Intradimensional/Extradimensional Attentional Shift Procedure in Rhesus Monkeys: A Method for Acute Drug Challenge Christopher C. Lay, Ronald D. Schneider, Amber J. Kirsten, Sophia A. Davis, Stefani N. Von Huben, Simon N. Katner and Michael A. Taffe Department of Neuropharmacology, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA EDS stage occurrence was not predictable EDS: line S+ EDR: line S- EDS: line SEDR: line S+ 180 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 Test Administration 1 N=10 2 3 N=5 N=6 * * SD SR CD 7 0.56 mp 6 0.01 rac 5 CR # IDS Stage # IDR EDS EDR 8 * * * 0.0178 rac 4 3 7 0 0 EDS ED/ID Shift Ratio * N=4 (sem) Errors to Criterion 10 3 1 CD * 4 1 IDS 0.01 d-amp N=6 (sem) 5 2 CD saline 6 2 8 7 sqrt(Errors) CD: shape S+ CR: shape S- Errors CD: shape SCR: shape S+ EDS stage is more difficult than IDS stage, effect persists when evaluated at 6 month intervals 0.32 mp N=7 (sem) Vehicle Scopolamine 8 6 4 2 0 CD IDS CD EDS ED/ID Shift Ratio 5 CD IDS CD EDS 4 sqrt(Errors) Required 8-20 sessions to complete Introduction Amphetamine abusers are selectively impaired on extradimensional shifts where heroin abusers are impaired on intra-dimensional shifts Criterion: 18/20 correct sqrt(Errors) SD: shape SSR: shape S+ IDS: shape S+ IDS: shape SIDR: shape S- IDR: shape S+ Shifting attentional focus or set, e.g., from one stimulus dimension to another, depends on intact function of frontal cortical circuits. Owen et al., 1991, Neuropsychologia 8 60 trials per session SD: shape S+ SR: shape S- saline 9 Scopolamine Effect sqrt(Errors) 9 sqrt(Errors) Abstract The ability to direct attention to one stimulus attribute (e.g., color) or to shift attention to another attribute (e.g., shape) can be disrupted in a number of neurological conditions including schizophrenia, ADHD and frontal lobe damage. Such evidence indicates that attentional shifts may depend on dopaminergic mechanisms within prefrontal cortex. Importantly, abusers of opiates, alcohol and amphetamines show attentional shift deficits thus development of animal models of attentional shift will assist in determining possible causal relationships between attentional shift deficits and substance abuse. A simplified version of a common procedure (i.e., the Wisconsin Card Sort Task) employed to assess attentional shift and executive function in humans has been developed to evaluate such capabilities in nonhuman primates (CANTAB intra-dimensional / extra-dimensional attentional shift task; ID/ED). The prior version of the monkey ID/ED procedure has most commonly been employed in between-subjects designs and frequently requires multiple daily sessions to complete one run of the test. The present study was conducted to validate the use of the ID/ED task in repeated fashion for within-subjects designs necessary for acute drug challenge investigations. A two-session version of the ID/ED task was designed and trained in a group (7) of male rhesus monkeys. Monkeys were then challenged with methylphenidate (0.32, 0.56 mg/kg, IM) and raclopride (0.01, 0.0178 mg/kg, IM) to determine to determine if the ID/ED procedure depends on dopaminergic neurotransmission. Extradimensional shifts were facilitated by methylphenidate and performance on a bimanual motor skill test was both facilitated by methylphenidate and impaired by raclopride. This study therefore validates the use of the ID/ED procedure for acute pharmacological challenge and suggests that attentional shifts are sensitive to dopaminergic manipulations in this assay. Supported by DA13390 and MH62261. Errors to Criterion Original Version of ID/ED Task for Monkeys * 3 2 1 0 6 5 Methylphenidate facilitated shifts of attention to a different stimulus dimension 4 3 2 Raclopride did not affect discrimination learning but may impair shifts of attention 1 0 saline Weed et al., 1999, Cog Br Res 0.01 d-amp saline 0.32 mp 0.56 mp 0.01 0.0178 rac rac Drug Treatment Condition Vehicle Scop Scopolamine impaired discrimination learning without affecting attentional shift. d-Amphetamine facilitated and impaired shifts of attention in different individuals at this dose. Ornstein et al., 2000; Neuropsychopharm Revised (2-day) ID/ED Task for Monkeys Development of a nonhuman primate model of attentional set shifting suitable for pharmacological challenge would further attempts to determine the time course and possible mechanisms by which drug abuse impairs such attentional capabilities. Session 1 To adapt the CANTAB ID/ED Attentional Set Shifting task for use in acute drug-challenge studies. CD (shape relevant) Compound Discrimination CD (shape relevant) Compound Discrimination Methods Young adult male rhesus monkeys Responding on a touch-screen to obtain food pellets Trained to perform 2-alternative visual discriminations Evaluated with a revised 2-day ID/ED sequence. Drug Challenge S+ S- IDS (shape relevant) Intra-Dimensional Shift S- S+ EDS (line relevant) Extra-Dimensional Shift Methylphenidate (Ritalin ; 0.32, 0.56 mg/kg i.m.) d-Amphetamine (Adderall ; 0.01 mg/kg i.m.) Dopamine D2 Antagonist Muscarinic Cholinergic Antagonist scopolamine (0.014 mg/kg i.m.) Criterion: 12/15 correct Requires 2 sessions to complete 15 raisins in Lexan holeboard Latency to extract raisins Bimanual strategy universally used Challenge drugs may be administered prior to either session To investigate effects on extradimensional shifts, drugs were administered prior to Session 2 + S + S S No systematic alterations in the extradimensional shift impairment (relative to IDS) were observed with repeated testing. 130% 120% * 110% 100% * 90% 80% 0.01 d-amp Veh 0.32 mp The indirect dopamine agonist methylphenidate facilitates extradimensional shifts of attention. The revised procedure may be useful in further studies to determination of the mechanisms involved in attentional set formation and executive function. Further studies may contribute to understanding the etiology of attentional problems that may be selectively produced in abusers of different drug classes. * Veh S The revised version of the CANTAB ID/ED Attentional Set Shift Task may be successfully employed in acute drug challenge studies. Methylphenidate facilitated raisin retrieval while raclopride slowed performance. Timing of IDS and EDS stages are predictable Indirect Dopamine Agonists raclopride (0.01, 0.0178 mg/kg i.m.) 240 trials per session Bimanual Motor Skill % Baseline (sec) Objective Session 2 Discussion 0.56 mp 0.01 0.0178 raclo raclo Drug Treatment Condition







