Body tissues
advertisement

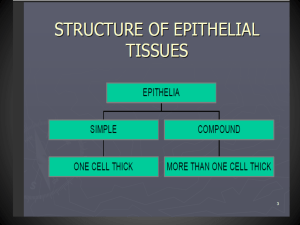
Body tissues Tissues: groups of cells closely associated that have a similar structure and perform a related function. The tissues of the human body include four major types:1.Epithelial tissues. 2.Connective tissues. 3.Muscle tissues. 4.Nervous tissues. 1.Epithelial tissues : Epithelium forms the coverings of surfaces of the body. As such, it serves many purposes, including protection, adsorption, excretion, secretion, filtration, and sensory reception. Epithelium Characteristic Cells fit closely together Tissue layer always has one free surface The lower surface is bound by a basement membrane Avascular (have no blood supply) Regenerate easily if well nourished Classification of Epithelium Number of cell layers Simple – one layer Stratified – more than one layer Shape of cells Squamous – flattened Cuboidal – cube-shaped Columnar – column-like Simple Epithelium a.Simple squamous :composed of single layer of flattened cells with disc-shaped central nuclei. Location Usually forms membranes, Lines ventral body cavities(serosae) Lines lungs and capillaries Kidney glomeruli b.Simple cuboidal : composed of Single layer of cube-like cells with large spherical centrale nuclei. Location Common in glands and their ducts Forms walls of kidney tubules Covers the ovaries c.Simple columnar: composed of tall cells,with round to oval nuclei . Location Often includes goblet cells, which produce mucus Lines digestive tract Gallbladder . d.pseudostratified : composed of Single layer, but some cells are shorter than others and Often looks like a double cell layer. Location Nonciliated type in efferent ductules of epididymis . Ciliated in trachea and bronchi. Stratified Epithelium a.Stratified squamous : Cells at the free edge are flattened Locations: Nonkeratinized type in Esophagus and vagina. Keratinized in epidermis of skin . b.Stratified cuboidal:composed of 2 or 3 layers of cuboidal cells. Location : Lining of larger ducts of mammary glands ,sweets glands ,salivary glands,and pancreas . c.Stratified columnar epithelium:found in vas deferens, part of the male urethra, parts of the pharynx (throat). It̕s function in protection and secretion d.Transitional epithelium: Can stretch, and Shape of cells depends upon The amount of stretching. Location Lines organs of the urinary system (bladder and urethra)