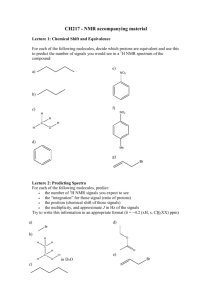
Version B melting point value of 68-69
advertisement

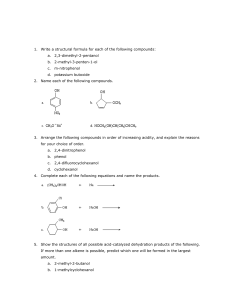
Version B 1. You carry out a reaction to synthesize 2,4-dinitrobenzaldehyde. It has a literature melting point value of 68-69oC, and the melting point of the material you recover was found to be 65-68oC. What statement best describes what should be concluded from this data? a. The data is consistent with the material being 2,4-dinitrobenzaldehyde containing a small amount of impurities. b. The data is consistent with the material being 2,4-dinitrobenzaldehyde containing approximately 50 % impurities. c. The data suggests the material is something other than 2,4-dinitrobenzaldehyde. d. The data proves the material is 2,4-dinitrobenzaldehyde with zero impurities. 2. Excess sebacoyl chloride in methylene chloride should be disposed of in which of the following? a. the sink with plenty of water. b. the organic solid non-halogenated waste container. c. the organic liquid non-halogenated waste container. d. the organic liquid halogenated waste container. 3. What is the limiting reagent in the following base catalyzed reaction if you begin with 2.05 mL of butanal and 2.15 mL of benzaldehyde? amt dens m.wt butanal benzaldehyde 5 M NaOH 2.05 mL 0.83 g/ml 72.1 g/mol 2.15 mL 1.04 g/ml 106.1 g/mol 4.0 mL 40 g/mol a. Butanal b. Benzaldehyde c. NaOH d. 2-ethyl-3-phenyl-propenal 2240L final, Version B, Page 1 of 15, Spring 2009 2-ethyl-3phenyl-propenal 0.897 g 234 g/mol Water 1.00 g/mL 18.00 g/mol 4. The overall tandem Diels-Alder reaction of cyclopentadiene (CP) and dimethylacetylene dicarboxylate (DMAD) proceeds as described in the below reaction schematic. What is the theoretical yield of the following reaction if you begin with 8.75 ml of cyclopentadiene and 10.30 mL of dimethylacetylene dicarboxylate? name Volume (mL) density (g/ml) mol. Wt. (g/mol) CP 8.75 DMAD 10.30 0.8021 1.1564 66.10 142.10 Product 274.30 a. 29.1 g b. 11.5 g c. 14.6 g d. 23.0 g 5. What splitting pattern will 3-pentanone show in the 1H NMR? a. two triplets and two doublets b. two quartets and two triplets c. one triplet and one doublet d. one quartet and one triplet 2240L final, Version B, Page 2 of 15, Spring 2009 6. Which of the compounds below could be responsible for this 1H NMR spectrum? 7. The 1H NMR below represents a compound with the molecular formula C9 H12. The peaks are identified, integrated and lettered below. Peak Peak Peak Peak A, B, C, D, 4 2 3 3 h , singlet, 7.21 ppm H, quartet, 2.65 ppm H, singlet, 2.33 ppm H, triplet, 1.22 ppm Which of the following compounds would give this spectrum? 2240L final, Version B, Page 3 of 15, Spring 2009 8. An unknown compound has 3 different peaks in the 1H NMR spectrum & 3 different peaks in the 13C NMR spectrum. Which of the following compound is the unknown? 9. The polymer made by the reaction of phthalic anhydride and ethylene glycol belongs to a class of polymers known as a. polyethylenes. b. polyesters. c. polystyrenes. d. polyamides. 10. Nylon-8,10 is made from which of the following combinations? a. An acyl chloride with 8 carbons and a diamine with 8 carbons. b. An acyl chloride with 10 carbons and a diamine with 8 carbons. c. An acyl chloride with 8 carbons and a diamine with 10 carbons. d. An acyl chloride with 10 carbons and a diamine with 6 carbons. 11. Which of these compounds CANNOT be used to make a polymer? O O || || a. HOCCH 2 CH2 CH2 CH2 COH O || b. HOCCH 2 CH2 CH2 CH2 NH2 c. H2 NCH 2 CH2 CH2 CH2 NH2 d. H2 NCH 2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 12. Which of the following procedure mistakes done during the synthesis of nylon is most likely to give a LOW yield of product? a. Dispensing the hexane-1,6-diamine solution into a wet beaker b. Pouring the sebacoyl chloride solution rapidly into the hexane-1,6-diamine solution c. Preparing the hexane-1,6-diamine solution without any NaOH in it d. Unwrapping the string of nylon from the graduated cylinder and weighing it immediately 2240L final, Version B, Page 4 of 15, Spring 2009 13. What functional group is most abundant in the product of the reaction between sebacoyl chloride and 1,6-hexanediamine? a. amine b. ester c. amide d. carboxylic acid 14. What was sodium hypochlorite used for in the oxidation of cyclohexanol? a. b. c. d. To reduce excess thiosulfate ion To oxidize cyclohexanol to cyclohexanone To make the reaction mixture acidic To reduced the solubility of cyclohexanone 15. Strong oxidizing agents such as chromic acid oxidize which of the following compounds to a ketone? a. b. OH OH c. d. OH OH 16. A peak is present in the IR spectrum of pure cyclohexanol but not cyclohexanone in which of the following frequency ranges? a. 1650-1800 cm–1 17. b. 2500-3000 cm–1 c. 3000-3100 cm–1 d. 3200-3600 cm–1 In the oxidation of cyclohexanol, which material is being reduced? a. cyclohexanol b. cyclohexanone c. sodium hypochlorite d. water 18. Commercial bleach usually contains 5.25% sodium hypochlorite, (0.750 M). How many moles of cyclohexanol could be converted into cyclohexanone with one half a liter of commercial bleach? a. 5.25 moles b. 0.375 moles c. 0.75 moles d. 2.63 moles 19. Using the following information, calculate the theoretical yield for the dehydration of 4.00 ml of cyclohexanol. Reagent Cyclohexanol Cyclohexene a. b. c. d. molecular mass (g/mole) 100.16 82.15 4.62 g 3.28 g 3.11 g 3.84 g 2240L final, Version B, Page 5 of 15, Spring 2009 density (g/ml) 0.948 0.811 20. Which of the following compounds cannot react with maleic anhydride in a DielsAlder reaction? b. a. c. d. 21. Which of the following is the major product of this reaction? + c. b. a. d. 22. You start a Diels-Alder reaction between maleic anhydride and anthracene with 2.0 moles of maleic anhydride and 4.0 moles of anthracene, and obtain 1.8 moles of the product. What is the percent yield? a. 45% b. 90% c. 25% d. 111% 23. Which alcohol is most likely to rearrange during an acid catalyzed dehydration? 24. Which of the following is reflux? a. Separating the product from impurities by distilling the product from the reaction mixture. b. Boiling the reaction mixture at a temperature that decomposes the impurities. c. Boiling the excess solvent off. d. Boiling the reaction mixture at a constant temperature and condensing the solvent vapors as they form keeping the solvent volume constant. 2240L final, Version B, Page 6 of 15, Spring 2009 25. Below is a GC trace which was made on a system with the following conditions. Flow = 60mL/min Inj.=Det= 120oC Column = 80oC= Carbowax 5 %, 4” x 1/8” Chart Speed = 0.50 cm/min Injection volume = 2 l What is the retention time of peak B? a. 13.0 minutes b. 11.0 minutes c. 22.0 minutes d. 26.0 minutes 26. Separation within our GC experiment occurred due to which characteristic? a. molecular weight of molecule. b. size of molecule c. boiling point of molecules. d. density of molecules. 27. Which of the following was the stationary phase used during the GC experiment? a. Carbowax ® b. helium c. Drierite d. toluene 28. If the sample size is increased from 2ul to 3ul, what will happen to the retention time of the compounds? a. retention time will increase b. retention time will decrease c. retention time will not change d. retention time will fluctuate. 2240L final, Version B, Page 7 of 15, Spring 2009 29. A mixture of following compounds were injected to a gas chromatograph (Carbowax 5 %, 4” x 1/8”Column) BP °C methylcyclohexane 101 pentane 36 octane 126 2,3-dimethyloctane 165 heptane 98 Which material has the shortest retention time? a. methylcyclohexane b. pentane c. 2,3-dimethyloctane d. octane 30. The major product of the dehydration of 2-methylcylohexanol is: 31. Which of the following is NOT true about Drierite? a. Drierite was used as a drying agent in the Dehydration of Cyclohexanol Experiment. b. Drierite used in lab was in the form of white granules. c. Drierite is anhydrous calcium iodate. d. Drierite was used as a pseudo-fractional distillation column packing in the Dehydration of Cyclohexanol experiment. 32. Which of the following is the proton NMR spectrum of the product from the dehydration of cyclohexanol? a. 3 2 PPM 1 2240L final, Version B, Page 8 of 15, Spring 2009 0 b. c. d. 4 6 4 3 5 2 PPM 4 3 3 PPM 2 PPM 1 2 0 1 1 0 0 33. What is the product from the aldol condensation of propanal? 2240L final, Version B, Page 9 of 15, Spring 2009 34. Which of the following cannot form an enolate? 35. Predict the structure which forms following this step: 36. Calculate the theoretical yield of the aldol condensation product when 1.00 mL of benzaldehyde was treated with 2.00 mL of acetaldehyde: O + H MW = 106.12 g density = 1.04 g/mL a. b. c. d. O H H NaOH heat CH3 MW = 44.1 g density = 0.780 g/mL O MW = 132.2 g 4.68 g 3.54 g 1.30 g 0.980 g 37. Which of these is a reactive intermediate in the mechanism of the reaction of benzaldehyde with acetone to give dibenzalacetone? 2240L final, Version B, Page 10 of 15, Spring 2009 38. Which of these compounds gives the SLOWEST reaction with HNO3/H2SO4? 39. Bromine is dangerous primarily because it is _______. a. a teratogen. b. a mutagen. c. carcinogenic. d. corrosive. 40. When aspirin is formed from the reaction of salicylic acid with acetic anhydride, what group acts as the nucleophile during the formation of the new backbone structure? a. b. c. d. the carboxylic acid the phenol the ester the anhydride 41. When aspirin is formed from the reaction of salicylic acid with acetic anhydride, what new functional group is formed? a. b. c. d. a carboxyl group a phenol an ester an anhydride 42. Which of these structures is Salicylic Acid? 2240L final, Version B, Page 11 of 15, Spring 2009 43. A student was unsuccessful in the micro synthesis of aspirin, and did not isolate any aspirin crystals at the end of the experiment. The student had carefully followed the directions until the end when 100 mL instead of 10 mL of deionized water was used to quench and work up the reaction. What likely caused the lack of product isolated? a. b. c. d. The excess water decomposed the aspirin. The excess water decomposed the acetic anhydride. The excess water quenched the phosphoric acid. The excess water kept the aspirin in solution. 44. Which of these compounds dissolves in water to give a solution that does not change the color of blue litmus paper? 45. Which of these compounds produces a green-blue solution when reacted with Jones reagent (chromic acid) but does not form a precipitate when reacted with 2,4dinitrophenylhydrazine? 46. Which of the following test reagents can be used to distinguish between phenol and cyclohexanol? a. b. c. d. DNP (2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine) Tollens’ test (Ag(NH3)2+) Ferric chloride test Bromine in carbon tetrachloride 47. Which of the compounds shown is a secondary alcohol? OH a. CH3 CHOH b. CH3 CH2 OCH3 c. CH3 CH2 CH2 OH d. CH3 2240L final, Version B, Page 12 of 15, Spring 2009 CH3 48. Following is a set of results from your qualitative analysis 2 experiment. Test Result Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO3) no bubbles formed Ferric Chloride Test clear yellow solution 2,4-DNP Test Thick yellow precipitate Tollens Test Black and silver precipitate Given this information where do you absolutely know a peak will be in the 1HNMR? a. 1-2ppm b. 2-4 ppm c. 6-7 ppm d. 9-12ppm 49. With the following set of information, determine the composition of your unknown. The IR is as following. The NMR with integrations is below. Peak A, 3.47ppm, relative size of 1, singlet Peak B, 1.63 ppm, relative size of 1, quartet Peak C, 1.17 ppm, relative size of 3, doublet. Peak D. 0.89 ppm, relative size of 9, singlet. 2240L final, Version B, Page 13 of 15, Spring 2009 Which is your compound? 2240L final, Version B, Page 14 of 15, Spring 2009 50. The identity of an unknown material is one of the below four compounds. Using the NMR and IR determine the identity of the unknown. a. 3, 3-dimethyl-2-butanol b. 3-methyl-1-butanol c. 2-butanol d. 2- hexanone 2240L final, Version B, Page 15 of 15, Spring 2009