The first Law of thermodynamics
advertisement

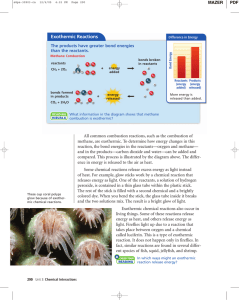
The first Law of thermodynamics Energy can neither be created nor destroyed, although it may be changed from one form into another. The total energy of an isolated system remains constant, although it may change form one form to another. Mathematical Derivation Suppose a system changes form state A to state B with the energy changes from UA to UB. The system, while undergoing change from state A to B, absorbs heat q from the surrounding and also performs some work W. On the other hand, the performance of work by the system tends to lower the energy of the system because performance of work requires expenditure of energy. Thermochemistry Chemical reactions are accompanied by evolution or absorption of heat. If a reaction is accompanied by the evolution of heat, it is called an exothermic reaction, and if it is accompanied by the absorption of heat, it is called an endothermic reaction. The science of thermochemistry is that branch of physical chemistry that deals with the thermal changes accompanying chemical and physical transformations. It deals with transformation of chemical energy into heat energy and vice versa. The energy change that occurs in a chemical reaction is largely due to a change in bond energy , that is change in potential energy that results from the breaking of bonds in the reactants and formation of new bonds in the products. Some thermochemical definitions are given here: Heat of reaction: the amount of heat evolved or absorbed during a chemical reaction is called the heat of reaction ( this is the difference between the heat contents (or enthalpies) of the products and the reactants; when molar quantities of the reactants indicated by the balance chemical equation, react completely, or mathematically, the heat of reaction, = Enthalpy of product – Enthalpy of reactant will be positive when heat content of the products is greater than heat content of reactants. Heat will be absorbed during the reaction and the reaction will be endothermic. will be negative when heat content of the reactants is greater than heat content of products. Heat will be evolved during the reaction and the reaction will be exothermic. Heat of combustion: heat of combustion of a compound or an element is the change in heat content when 1 mole of the substance is completely burnt in excess of oxygen because combustion reactions are always exothermic ,the heat of combustion is always negative. For example: CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l); = - 890.2 k J