Examining the Impact of Evidence-Based Interventions on Pennsylvania Delinquency Placement Rates
advertisement

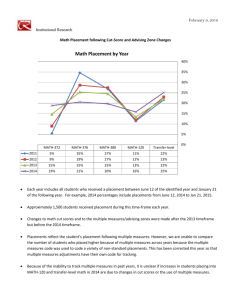
Examining the Impact of Evidence-Based Interventions on Pennsylvania Delinquency Placement Rates Julia E. Moore & Brian K. Bumbarger The EPISCenter, Prevention Research Center, Penn State University Background: The PA EBP Initiative PENNSYLVANIA’S EVIDENCE-BASED PROGRAMS (EBP) INITIATIVE Goal 1: Examine delinquency placement rates from 1999 to 2008 •Funded by the PA Commission on Crime and Delinquency (PCCD) to disseminate evidence-based delinquency & violence prevention programs •Since 1998, grants have been awarded to 120+ PA communities to fund nearly 200 replications of EBPs throughout the state Placement Trend Data: 1999-2008 Overall Sustainability Rate Goal 2: Compare placement rates in counties providing FFT, MST, or MTFC to those that have not Placement Rate (Placements as % of Dispositions) Counties With vs. Without EBIs 8,000 7,000 The goal of the PA EBP initiative is to make more efficient use of state & federal resources by directing them to strategies that are most likely to impact delinquency. 10.0% 9.5% 9.0% 8.5% 8.0% 7.5% 7.0% 6.5% 6.0% 5.5% 5.0% 6,000 5,000 4,000 3,000 HOW DOES IT WORK? 2,000 •Utilizing the Communities That Care model, community coalitions conduct a local risk and resource assessment to identify and prioritize risk and protective factors, then select EBPs to address these identified targets 1,000 •PCCD provides 4 years of funding, with a 25% local match in Year 3 and 50% match in Year 4, to implement the selected EBP •Grantee must demonstrate ongoing relationship with local collaborative board and collect outcome and implementation data to use for impact assessment and quality improvement 2005 0 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 Note: Red line indicates change in the way delinquency dispositions were measured. Placements as Percentage of Delinquency Dispositions 2007 Implementing MST, FFT, MTFC 2008 The total number of delinquency dispositions has increased slightly over the past decade, in 2000 there were 41,898 delinquency dispositions, compared to 43,754 in 2008, a 4.4% increase. 2006 No Program 2005 Mean (SD) 0.081 (0.047) With Program 0.066 (0.043) 2008 Not Implementing Any 2006 2007 N 53 Mean (SD) 0.091 (0.063) N 46 Mean (SD) 0.081 (0.047) N 30 2008 Mean (SD) N 0.077 (0.041) 24 14 0.067 (0.049) 21 0.069 (0.048) 37 0.075 (0.041) 43 Conclusions and Recommendations A TEST-BED FOR TYPE 2 TRANSLATIONAL RESEARCH 16.0% •In 2001, PCCD formed a partnership with Penn State’s Prevention Research Center to provide technical assistance to grantees and study the process of program dissemination, leading to the creation of the Evidence-based Prevention and Intervention Support Center (EPISCenter) in 2008 14.0% Overall Conclusions 12.0% • Delinquency dispositions are increasing, but both the number of new placements and the rate of placement have gone down significantly. Policy-Driven Research PROGRAMS FOR CHILDREN AT-RISK OF DELINQUENCY DISPOSITIONS AND PLACEMENTS • Functional Family Therapy - an empirically grounded family intervention program for dysfunctional and at-risk youth aged 11-18 and their families, including youth with problems such as conduct disorder, violent acting-out, and substance abuse • Multisystemic Therapy - an intensive family and community-based treatment that addresses the multiple determinants of serious antisocial behavior in chronic, violent, or substance abusing male or female juvenile offenders, ages 12 to 17, at high risk of out-of-home placement • Mulitdimentional Treatment Foster Care - a cost-effective alternative to group or residential treatment, incarceration, and hospitalization for adolescents who have problems with chronic antisocial behavior, emotional disturbance, and delinquency 10.0% 8.0% • A small number of counties account for a disproportionate percentage of placements, although this disparity has been decreasing. 6.0% 4.0% • Counties implementing FFT, MST or MTFC have lower placement rates, which could have large policy implications as a 1% reduction in placements state-wide could save the state approximately $1 million. 2.0% 0.0% 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 The number of delinquency placements has decreased from 4,384 in 2000 to 3,454 in 2008, a 24.3% decrease. Change in Dispositions and Placements (2000-2008) 10% 5% 0% -5% 4.40% Dispositions Placements -24.30% -10% -15% A 1% reduction in placements state-wide could save the state approximately $1 million -20% -25% -30% • Policymakers were interested in whether these programs were reducing delinquency dispositions and placements in Pennsylvania. Overall there was a 4.4% increase in delinquency dispositions, yet a 24.3% decrease in delinquency placements. Recommendations for Policymakers • Although these programs are intended for youth at risk of placement, there is a (sometimes conflicting) need to maintain a certain level of program placements, which leads programs to seek referrals through a variety of sources. • DPW could direct that youth who would otherwise be committed to out of home placement be given priority consideration for these programs. • Many youth who are not at “imminent” risk of placement might still end up being placed eventually in the absence of effective preventive programming. • There is a potential “floor effect” with placement rates, below which the system may be also be seen as inefficient. It is not reasonable to expect NO youth to be placed. • This project revealed gaps in the available data to monitor placements and referrals. The EPISCenter has recently established a reporting process for these (MST, FFT, MTFC) programs to submit quarterly data on referral sources and program impact on placements. The EPISCenter is a project of the Prevention Research Center, College of Health and Human Development, Penn State University, and is funded by the Pennsylvania Commission on Crime and Delinquency and the Pennsylvania Department of Public Welfare as a component of the Resource Center for Evidence-Based Prevention and Intervention Programs and Practices.