flow rate of the refrigerant, the heating load, the COP... 11-49
advertisement

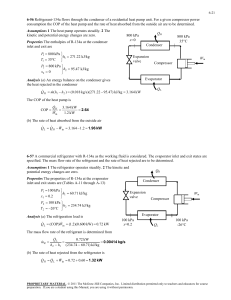
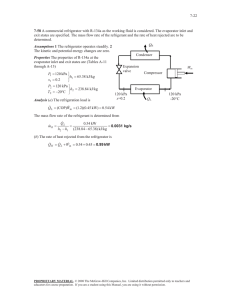
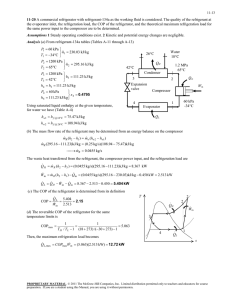
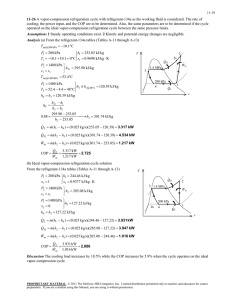
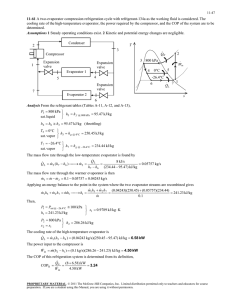
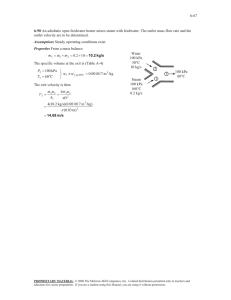
11-38 11-49 A geothermal heat pump is considered. The degrees of subcooling done on the refrigerant in the condenser, the mass flow rate of the refrigerant, the heating load, the COP of the heat pump, the minimum power input are to be determined. Assumptions 1 Steady operating conditions exist. 2 Kinetic and potential energy changes are negligible. Analysis (a) From the refrigerant-134a tables (Tables A-11 through A-13) T4 20C P4 572.1 kPa x 4 0.23 h4 121.24 kJ/kg h3 h4 Condenser 3 Expansion valve P1 572.1 kPa h1 261.59 kJ/kg x1 1 (sat. vap.) s1 0.9223 kJ/kg P2 1400 kPa h2 280.00 kJ/kg s 2 s1 From the steam tables (Table A-4) hw1 h f @ 50C 209.34 kJ/kg . QH 4 . Win Compressor 1 Evaporator sat. vap. 20C x=0.23 40C hw 2 h f @ 40C 167.53 kJ/kg The saturation temperature at the condenser pressure of 1400 kPa and the actual temperature at the condenser outlet are 2 1.4 MPa s2 = s1 Water 50C T · QH Tsat @ 1400 kPa 52.40C 2 1.4 MPa P3 1400 kPa T3 48.59C (from EES) h3 121.24 kJ/kg · Win 3 Then, the degrees of subcooling is 4s 4 Tsubcool Tsat T3 52.40 48.59 3.81C · QL 1 s (b) The rate of heat absorbed from the geothermal water in the evaporator is Q L m w (hw1 hw 2 ) (0.065 kg/s)(209.34 167.53)kJ/kg 2.718 kW This heat is absorbed by the refrigerant in the evaporator m R Q L 2.718 kW 0.01936 kg/s h1 h4 (261.59 121.24)kJ/kg (c) The power input to the compressor, the heating load and the COP are W in m R (h2 h1 ) Q out (0.01936 kg/s)(280.00 261.59)kJ/kg 0.6564 kW Q H m R (h2 h3 ) (0.01936 kg/s)(280.00 121.24)kJ/kg 3.074 kW COP Q H 3.074 kW 4.68 Win 0.6564 kW (d) The reversible COP of the cycle is COPrev 1 1 TL / TH 1 12.92 1 (25 273) /(50 273) The corresponding minimum power input is W in, min Q H 3.074 kW 0.238 kW COPrev 12.92 PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2011 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Limited distribution permitted only to teachers and educators for course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.