5-27 electrically as it is stirred by a paddle-wheel at constant... 5-39
advertisement
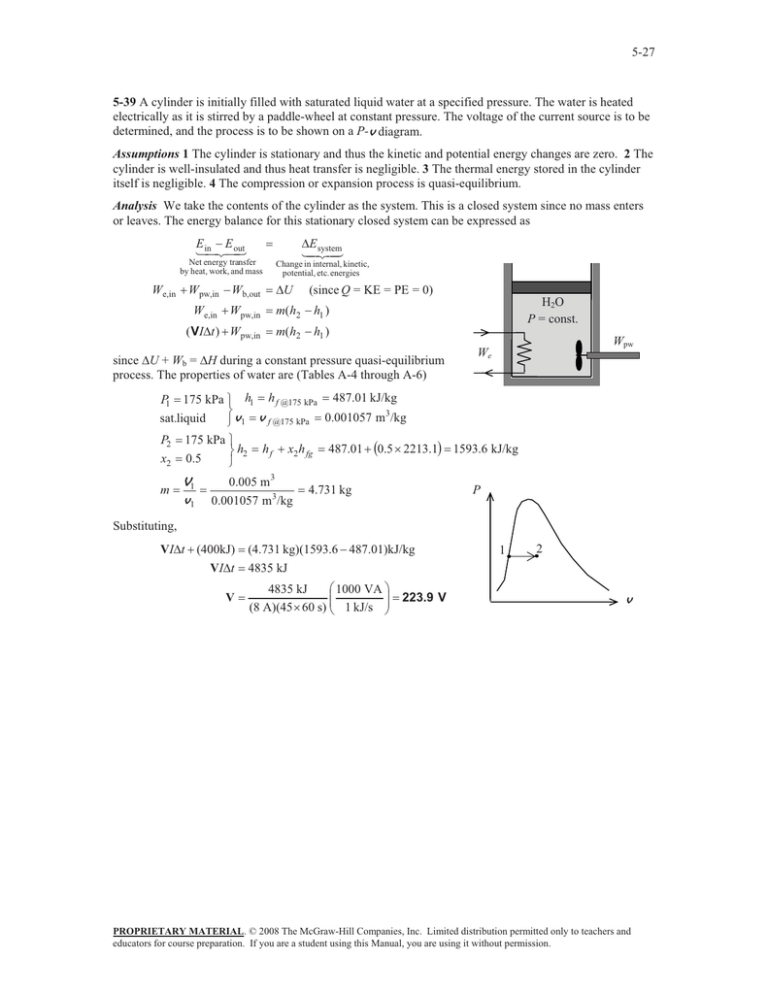
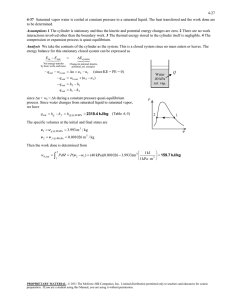
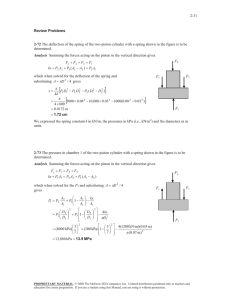
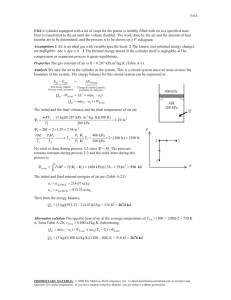
5-27 5-39 A cylinder is initially filled with saturated liquid water at a specified pressure. The water is heated electrically as it is stirred by a paddle-wheel at constant pressure. The voltage of the current source is to be determined, and the process is to be shown on a P-v diagram. Assumptions 1 The cylinder is stationary and thus the kinetic and potential energy changes are zero. 2 The cylinder is well-insulated and thus heat transfer is negligible. 3 The thermal energy stored in the cylinder itself is negligible. 4 The compression or expansion process is quasi-equilibrium. Analysis We take the contents of the cylinder as the system. This is a closed system since no mass enters or leaves. The energy balance for this stationary closed system can be expressed as E E in out Net energy transfer by heat, work, and mass We,in W pw,in W b,out 'E system Change in internal, kinetic, potential, etc. energies 'U (since Q = KE = PE = 0) We,in W pw,in m(h2 h1 ) ( VI't ) W pw,in m(h2 h1 ) H 2O P = const. since 'U + Wb = 'H during a constant pressure quasi-equilibrium process. The properties of water are (Tables A-4 through A-6) Wpw We 175 kPa ½ h1 h f @175 kPa 487.01 kJ/kg ¾ 3 sat.liquid ¿ v1 v f @175 kPa 0.001057 m /kg P2 175 kPa ½ ¾ h2 h f x2 h fg 487.01 0.5 u 2213.1 1593.6 kJ/kg x2 0.5 ¿ P1 m V1 v1 0.005 m3 0.001057 m3/kg P 4.731 kg Substituting, VI't (400kJ) VI't V (4.731 kg)(1593.6 487.01)kJ/kg 4835 kJ § 1000 VA · 4835 kJ ¨ ¸ (8 A)(45 u 60 s) ¨© 1 kJ/s ¸¹ 223.9 V 1 2 v PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Limited distribution permitted only to teachers and educators for course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.