Ultrafiltration of Seawater Impacted by Algal Organic Matter
advertisement

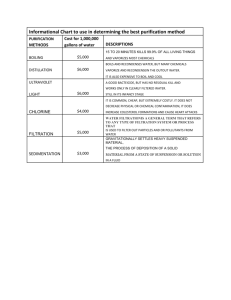
Ultrafiltration of Seawater Impacted by Algal Organic Matter Muhammad Tariq Khan*, Jean Philippe Croue*, Veronica G. Molina** and Nasir Moosa** *King Abdullah University of Science and Technology - Thuwal - Saudi Arabia **Dow Water and Process Solutions - Tarragona - Spain Water Desalination and Reuse Center King Abdullah University of Science & Technology (KAUST) Background 2 3 Source: K. B. Padmakumar et al., 2012 Occurence of HABs in Oman 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 source: A. Al Azri - HAB’s workshop Oman (Feb. 2012) Arabian Gulf Gulf Of Oman Red Tide Event (2008) 4 Trichodesmium sp. 5 Lepidodinium chlorophorum (Claquin et al., 2008) Chaetoceros affinis (Villacorte et al., 2013) Gonyaulax fragilis (Pompei et al, 2003) Gonyaulax hyalina (MacKenzie et al., 2002). 6 Materials and Methods 7 Main Goal Efficient use of UF membrane technology, especially during algal bloom events. Objectives of This Study Determination of Interactions between AOM and membrane? Reversible and Irreversible fouling. Role of membrane material characteristics: PVDF Vs PES. Impact of mode of Operation: Out/In VS In/Out 8 Hymenomonas sp. (HYM) Prymnesiophicae (≈ 8 μm), a Coccolithophores 10 µm cell Algae grown in F/2 Guillard Medium, prepared using 0.45 µm filtered Seawater 1.2 µm Filtered to remove the cells Optical Microscopic image of Hymenomonas sp. 9 40 200 Chlorophyll- a TOC 180 Increase in AOM 35 Stationary Phase Increase in Cells 160 140 25 120 20 100 80 15 60 TOC (mg C/L) Chlorophyll- a (ug/L) 30 10 40 5 20 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 Time (Days) 30 35 0 40 10 Feed, backwash and Chemical Inlets Flow Rate Controllers data acquisition 11 Comparison between Two Commercial UF Fibers While Using Hymenomonas sp. Culture Synthetic Seawater + AOM: HYM (1.2 µm Filtered) Membrane A Material: PVDF Pore Size: 20-25 nm Operation: O/I Membrane Performance Data Permeability Features and Fouling Indices Membrane Performance Data Membrane B Material: PES Pore Size: 25-30 nm Operation: I/O Rejection of Organics 12 Filtration Results 13 Average HIFI:8.5 (2.06) x10-4 m2 /L CEB after 10 Cycles CIFI: 1.19 X10-4m2 /L 14 Average HIFI:1.7 (0.64) x10-4 m2 /L CEB after 10 Cycles CIFI: 0.2 X10-4m2 /L 15 0.167 3.583 7 10.417 13.833 17.25 20.667 24.083 27.5 30.917 34.333 37.75 41.167 44.583 48 51.417 54.833 58.25 61.667 65.083 68.5 71.917 75.333 78.75 82.167 85.583 89 92.417 95.833 99.25 102.667 106.083 109.5 112.917 116.333 119.75 123.167 126.583 Signal Biopolymers 3.5 Feed Water 3 1st Filtration 2.5 5th Filtration 10th Filtration 2 11th Filtration 1.5 15th Filtration 20 th Filtration 1 21st Filtration 25th Filtration 0.5 30 th Filtration 0 Time (Minutes) 16 0.167 3.583 7 10.417 13.833 17.25 20.667 24.083 27.5 30.917 34.333 37.75 41.167 44.583 48 51.417 54.833 58.25 61.667 65.083 68.5 71.917 75.333 78.75 82.167 85.583 89 92.417 95.833 99.25 102.667 106.083 109.5 112.917 116.333 119.75 123.167 126.583 Signal Biopolymers 3.5 Feed Water 3 1st Filtration 2.5 5th Filtration 10th Filtration 2 11th Filtration 1.5 15th Filtration 20 th Filtration 1 21st Filtration 0.5 25th Filtration 30 th Filtration 0 Time (Minutes) 17 Membrane A Membrane B 18 Effect of Chlorination (CEB) on Organic Rejection For membrane A, decrease in rejection of organics, especially biopolymers. For membrane B, little change in organic rejection is observed Chorine Impact on membrane structural features? Or Impact of chlorine on organics accumulated on/in membrane structure? 19 Effect of Chlorination (CEB) on Organic Rejection For membrane A, decrease in rejection of organics, especially biopolymers. For membrane B, little change in organic rejection is observed Chorine Impact on membrane structural features? Or Impact of chlorine on organics accumulated on/in membrane structure? Recommendation It is suggested that after CEB fibers should be rinsed for longer period before getting the permeate to feed RO. 20 21