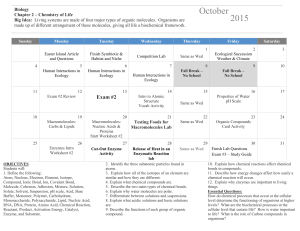
AP BIOLOGY – UNIT 1 Monday
advertisement
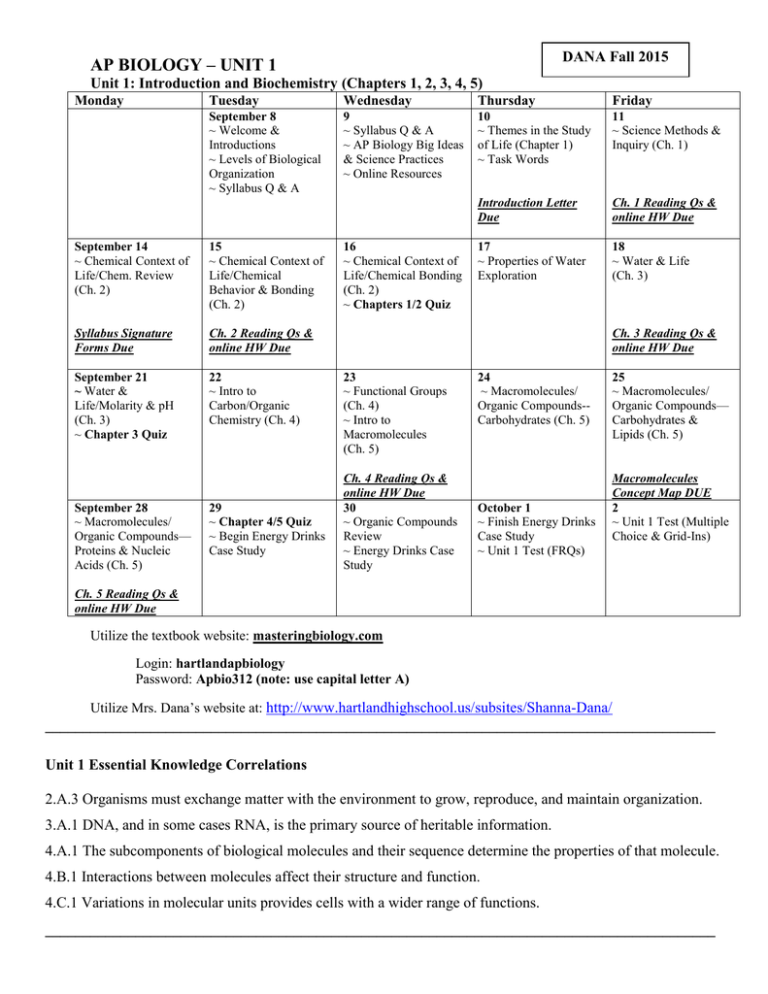
DANA Fall 2015 AP BIOLOGY – UNIT 1 Unit 1: Introduction and Biochemistry (Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5) Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday September 8 ~ Welcome & Introductions ~ Levels of Biological Organization ~ Syllabus Q & A 9 ~ Syllabus Q & A ~ AP Biology Big Ideas & Science Practices ~ Online Resources 10 11 ~ Themes in the Study ~ Science Methods & mnmn of Life (Chapter 1) Inquiry (Ch. 1) ~ Task Words September 14 ~ Chemical Context of Life/Chem. Review (Ch. 2) 15 ~ Chemical Context of Life/Chemical Behavior & Bonding (Ch. 2) Syllabus Signature Forms Due Ch. 2 Reading Qs & online HW Due September 21 ~ Water & Life/Molarity & pH (Ch. 3) ~ Chapter 3 Quiz 22 ~ Intro to Carbon/Organic Chemistry (Ch. 4) September 28 ~ Macromolecules/ Organic Compounds— Proteins & Nucleic Acids (Ch. 5) 29 ~ Chapter 4/5 Quiz ~ Begin Energy Drinks Case Study 16 ~ Chemical Context of Life/Chemical Bonding (Ch. 2) ~ Chapters 1/2 Quiz Friday Introduction Letter Due Ch. 1 Reading Qs & online HW Due 17 ~ Properties of Water Exploration 18 ~ Water & Life (Ch. 3) Ch. 3 Reading Qs & online HW Due 23 ~ Functional Groups (Ch. 4) ~ Intro to Macromolecules (Ch. 5) Ch. 4 Reading Qs & online HW Due 30 ~ Organic Compounds Review ~ Energy Drinks Case Study 24 ~ Macromolecules/ Organic Compounds-Carbohydrates (Ch. 5) October 1 ~ Finish Energy Drinks Case Study ~ Unit 1 Test (FRQs) 25 ~ Macromolecules/ Organic Compounds— Carbohydrates & Lipids (Ch. 5) Macromolecules Concept Map DUE 2 ~ Unit 1 Test (Multiple Choice & Grid-Ins) Ch. 5 Reading Qs & online HW Due Utilize the textbook website: masteringbiology.com Login: hartlandapbiology Password: Apbio312 (note: use capital letter A) Utilize Mrs. Dana’s website at: http://www.hartlandhighschool.us/subsites/Shanna-Dana/ _________________________________________________________________________________________ Unit 1 Essential Knowledge Correlations 2.A.3 Organisms must exchange matter with the environment to grow, reproduce, and maintain organization. 3.A.1 DNA, and in some cases RNA, is the primary source of heritable information. 4.A.1 The subcomponents of biological molecules and their sequence determine the properties of that molecule. 4.B.1 Interactions between molecules affect their structure and function. 4.C.1 Variations in molecular units provides cells with a wider range of functions. _________________________________________________________________________________________ Word Roots (Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5) Chapter 1 bio- = life (biology: the scientific study of life; biosphere: all the environments on Earth that are inhabited by life; bioinformatics:using information technology to extract useful information from large sets of biological data) -ell = small (organelle: a small membrane-enclosed body with a specialized function found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells) eu- = true (eukaryotic cell: a cell that has a true nucleus) pro- = before; karyo- = nucleus (prokaryotic cell: a cell that has no nucleus) Chapter 2 an- = not (anion: a negatively charged ion) co- = together; -valent = strength (covalent bond: an attraction between atoms that share one or more pairs of outer-shell electrons) electro- = electricity (electronegativity: the tendency for an atom to pull electrons toward itself) iso- = equal (isotope: an element having the same number of protons and electrons but a different number of neutrons) neutr- = neither (neutron: a subatomic particle with a neutral electrical charge) pro- = before (proton: a subatomic particle with a single positive electrical charge) Chapter 3 kilo- = a thousand (kilocalorie: a thousand calories) hydro- = water; -philos = loving; -phobos = fearing (hydrophilic: having an affinity for water; hydrophobic: having an aversion to water) Chapter 4 hydro- = water (hydrocarbon: an organic molecule consisting only of carbon and hydrogen) iso- = equal (isomer: one of several organic compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and, therefore, different properties) enanti- = opposite (enantiomer: molecules that are mirror images of each other) carb- = coal (carboxyl group: a functional group present in organic acids, consisting of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and a hydroxyl group) sulf- = sulfur (sulfhydryl group: a functional group that consists of a sulfur atom bonded to an atom of hydrogen) thio- = sulfur (thiol: organic compounds containing sulfhydryl groups) Chapter 5 con- = together (condensation reaction: a reaction in which two molecules become covalently bonded to each other through the loss of a small molecule, usually water) di- = two (disaccharide: two monosaccharides joined glyco- = sweet (glycogen: a polysaccharide sugar used to store energy in animals) hydro- = water; -lyse = break (hydrolysis: breaking chemical bonds by adding water) macro- = large (macromolecule: a large molecule) meros- = part (polymer: a chain made from smaller organic molecules) mono- = single; -sacchar = sugar (monosaccharide: simplest type of sugar) poly- = many (polysaccharide: many monosaccharides joined together) tri- = three (triacylglycerol: three fatty acids linked to one glycerol molecule)