How Courses Support Program Outcomes
advertisement

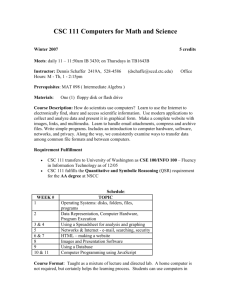
How Courses Support Program Outcomes Table 5 indicates how the courses in the program support each student learning outcome (SLO). A given course may provide a context in which skills that enforce an SLO are introduced (I), practiced (P) or assessed (A) for program evaluation purposes. Table 5. Courses Mapped to Supported Program Outcomes Course and Title Student Learning Outcome 1 2 3 4 5 6 CSC 100: Orientation to Computer Science I I I I CSC 121: Introduction to Computer Science I I I I I I CSC 133: Discrete Mathematical Structures I I I CSC 221: Introduction to Computer Science II P P I I P CSC 242: Digital Logic, Computer Organization and Assembly Language I I P CSC 320:Computer Animation P P P P P P CSC 332: Data Structures P P P P CSC 340: Scientific Computing P P P P CSC 342: Operating Systems P P P P P CSC 344: Computer Networks P P P P P CSC 360: Formal Languages and Computability I P P P CSC 370: Computer Graphics P CSC 385: Professional and Ethical Issues in Computer Science P P P A CSC 415: Artificial Intelligence P P P P CSC 421: Computer Gaming P P P CSC 422: Performance Evaluation of Computer Systems P P CSC 430: Digital Special Effects P P P CSC 434: Programming Languages A P CSC 437: Parallel Computing P P P CSC 442: Computer System Architecture P P P CSC 446: Grid Computing P P P CSC 450: Software Engineering A A A A A A CSC 453: Object‐Oriented Design and Analysis P P CSC 455: Database Management P A A A A P CSC 457: Compiler Construction P P CSC 475: Topics in Computer Science P P P P CSC 491: Directed Independent Study P P P P CSC 495: Seminar in Computer Science P P CSC 498: Internship in Computer Science P P A A A A CSC 499: Honors Work in Computer Science P P P P P P