PARTS OF SPEECH REVIEW ENG 7
advertisement

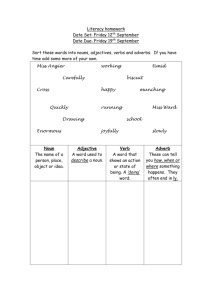
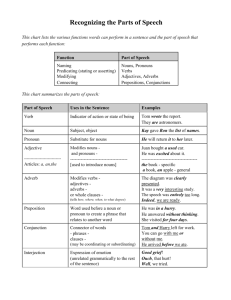
PARTS OF SPEECH REVIEW ENG 7 #1 THE NOUN Perhaps the words most frequently used are those that identify someone or something. These name words are called nouns. NOTES FOR NOTEBOOK: Definition – A noun is a word used to name 1) A person 2) A place 3) A thing 4) An idea taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 342 #1 NOUNS • Review Definition taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 342 COMMON AND PROPER NOUNS (ADD TO GRAMMAR NOTES) • There are two classes of nouns, proper nouns and common nouns. • A proper noun names a particular person, place, thing, or idea and is always capitalized. • A common noun names any one of a group of persons, places of things and is not capitalized. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 342 -343 COMMON AND PROPER NOUNS (ADD TO GRAMMAR NOTES) COMMON NOUNS (Any) PROPER NOUNS (Particular) scientist Carl Sagan, Sheldon Cooper female Beyonce, Michelle Obama, Heidi Klum city Cairo, St. Louis, Paris building World Trade Center, Buckingham Palace continent North America, Africa, Asia mountains Rockies, Alps, Blue Ridge Mountains day Monday, Thursday, Sunday taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 342 -343 COMPOUND NOUNS Two or more words may be used together as a single noun. EXAMPLES hair stylist Captain Brown Mexico City toothpick Merry-go- round taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 344 COMPOUND NOUNS The parts of a compound noun may be written as one word, as two or more words, or as a hyphenated word. Here are some other commonly used compound nouns. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 344 EXAMPLES volleyball newsstand news room cold front sister-in-law push-up Stratford-on-Avon COMPOUND NOUNS If you are in doubt as to how to write a compound noun, you should consult your dictionary. Some dictionaries may give two correct forms for a word; for example, you may find the word vice-president written both with and without a hyphen. As a rule, use the form the dictionary list first. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 344 #2 THE PRONOUN Definition: • A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun or of more than one noun. A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun or of more than one noun. • Definition: taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 345 #2 THE PRONOUN EXAMPLE • A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun or of more than one noun. Gloria stepped back from the picture and looked at it carefully. • Definition: taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 345 #2 THE PRONOUN EXAMPLES • A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun or of more than one noun. 1. Where is Lois? She said she would be here on time. 2. Our teacher and Mrs. Barnes said they would go to the meeting. • Definition: taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 345 #2 THE PRONOUN the antecedent • A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun or of more than one noun. “something going before.” • Definition: refers to the noun on which the pronoun depends for its meaning taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 345 EXAMPLES #2 THE PRONOUN • Definition: • A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun or of more than one noun. Jill opened her book and read from it. Janet took her dog to the veterinarian. The coach showed the players how they should throw the ball. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 346 #3 THE ADJECTIVE You may wish to describe, or make more definite, a noun or pronoun. You then MODIFY the word by using an adjective. An adjective modifies a noun or pronoun. To modify a word means to describe the word or to make its meaning more definite. An adjective modifies a noun or pronoun by answering these questions: What kind? Which one? How many? taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 349-350 #3 THE ADJECTIVE NOTICE HOW THE BOLDFACED ADJECTIVES THAT FOLLOW ANSWER THESE QUESTIONS ABOUT THE NOUNS MODIFIED. What kind? Which one? How many? gray sky old shoes clever dog low price that girl next day either way last chance five fingers many rivers fewer hours some problems taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 350 # PRONOUN OR ADJECTIVE? Notice that in the phrases in the previous slide, that, either, many, fewer, and some – Words that may also be used as pronouns – are adjectives, because they modify the nouns in the phrases rather than take the place of the nouns. The words my, your, his, her, its, our, and their are called pronouns; they are possessive forms of personal pronouns, showing ownership or relationship. Some people, however, prefer to think of these words as adjective because they tell Which one? about nouns: my sister, your book, our team, their tents. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 350 # NOUNS USED AS ADJECTIVES SOMETIMES YOU WILL FIND NOUNS USED AS ADJECTIVES. NOUNS crisp bacon blinding snow last December NOUNS USED AS ADJECTIVES Bacon sandwich Snow sculpture December sale taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 350 NOUNS USED AS ADJECTIVES SOMETIMES YOU WILL FIND NOUNS USED AS ADJECTIVES. December sale Notice in the example above that a proper noun, December, is used as an adjective. Look at how some other proper nouns are used as adjectives: PROPER NOUNS USED AS ADJECTIVES Texas chili Jackson concert Maine coast Sioux warrior Brazil nut Picasso painting taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 350 # ARTICLES The most frequently used adjectives are a, an and the. The words are called articles. A and an are indefinite article; they refer to one of a general group. EXAMPLES A girl won. An elephant escaped. This is an honor. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 351 ARTICLES A is used before words beginning with a consonant sound. An is used before words beginning with a vowel sound. This is an honor. Notice in the example above that an is used before a noun beginning with the consonant h, because the h in honor is not pronounced. Honor is pronounced as if it begins with a vowel. Remember that the SOUND of the noun, not the spelling, determines which indefinite article will be used. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 351 ARTICLES The is a definite article. It indicates that the noun refers to someone or something in particular. EXAMPLES The girl won. The elephant escaped. The honor goes to her. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 351 # ADJECTIVES IN SENTENCES In all of the examples you have seen so far, the adjective comes before the noun it modifies. This is its usual position in a sentence. Ms. Farrell tells all students that good workers will be given special privileges. A sweating, exhausted runner crossed the line. Sometimes, however, adjectives follow the word they modify. A dog, old and overweight, snored in the sun. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 351-352 ADJECTIVES IN SENTENCES Usually, the adjective comes before the noun it modifies. This is its usual position in a sentence. Sometimes, other words may separate an adjective from the noun or pronoun modified. Beverly was worried. She felt nervous about the play. Delighted by the news, he smiled broadly. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 351-352 # THE VERB A noun or a pronoun, no matter how many modifiers it may have, CANNOT make a sentence. The noun or pronoun must act in some way, or something must be said about it. The part of speech that performs this function is the VERB. Some verbs express action and some tell something about the subject. A VERB is a word that expresses action or otherwise helps make a statement. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 354 ACTION VERBS Words such as do, come, go, and write are action verbs. Sometimes action verbs express an action that cannot be seen: believe, remember, know, think, and understand. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 355 ROUND TABLE ACTION VERBS Students take turns writing on own paper then pass it on to teammates: 1. 2. 3. 4. • Take your notes out of your notebook. Write Action Verbs Teacher announces topic / gives “think time”. Each teammate writes his/her short answer to the topic on own paper then passes the paper on to the next teammate. 3. Writing continues until the teacher says stop. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 355 ROUND TABLE ACTION VERBS Topic: Action Verbs Try to include and underline at least five verbs that express an action that cannot be seen. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 355 # LINKING VERBS Read handout and be prepared for discussion. # taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 356-357 LINKING VERBS Complete Exercise 8 and 9. # taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 357-358 VERBS Complete Exercise 10. # taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 357-358 VERB PHRASES Re-read the handout, “Verb Phrases.” Complete Exercise 11 # taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 359 THE ADVERB We have learned that nouns and pronouns are modifies by adjectives. Verbs and adjectives have modifiers, too, and their modifiers are called ADVERBS. Adverbs also modify adverbs. Adverb – a word used to modify a verb, an adjective or another adverb. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 360 ADVERBS MODIFYING VERBS Sometimes an adverb modifies (makes more definite the meaning of) a verb. Look at the following adverbs in boldfaced type. What questions do they answer? We lived up there. She quickly agreed. May we go up tomorrow? I am completely happy. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 360 ADVERBS MODIFYING VERBS What questions do they answer? Where? When? How? To what extent (how long or how much)? WHERE? Please step up. I have the ticket here. WHEN? Water the plant weekly. We’ll see you later. HOW? The rain fell softly. Drive carefully. TO WHAT EXTENT? He hardly moved. Did she hesitate slightly? taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 360-361 ADVERBS MODIFYING VERBS Adverbs may precede or may follow the verbs they modify, and they sometimes interrupt the parts of a verb phrase. Adverbs may also introduce questions. EXAMPLE Where in the world did you ever find that pink and purple necktie? The adverb where modifies the verb phrase did find. Notice, too, the adverb ever, which interrupts the verb phrase also modifies it. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 360-361 ADVERBS MODIFYING VERBS Complete Exercise 12 for homework. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 360-361 # ADVERBS MODIFYING ADJECTIVES Sometimes an adverb modifies an adjective. EXAMPLES Beth did and exceptionally fine job. The adjective fine modifies the noun job. The adverb exceptionally modifies the adjective fine, telling how fine. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 361 ADVERBS MODIFYING ADJECTIVES Sometimes an adverb modifies an adjective. EXAMPLES The car had a slightly damaged fender. The adverb slightly modifies the adjective damaged, which in turn modifies the noun fender. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 362 ADVERBS MODIFYING ADJECTIVES The most frequently used adverbs are too, so, and very. In fact these words are overworked. Thy to avoid overusing them in speaking and particularly in writing; find more precise adverbs to take their place. Look at this list of adverbs. What do you notice that they have in common? Extremely entirely unusually dangerously especially Definitely completely surprisingly terribly dreadfully taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 362 ADVERBS MODIFYING ADJECTIVES The most frequently used adverbs are too, so, and very. In fact these words are overworked. Thy to avoid overusing them in speaking and particularly in writing; find more precise adverbs to take their place. Look at this list of adverbs. What do you notice that they have in common? Extremely entirely unusually dangerously especially Definitely completely surprisingly terribly dreadfully taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 362 ADVERBS MODIFYING ADJECTIVES Complete Exercise 13 and 14 as homework. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 362-363 # ADVERBS MODIFYING OTHER ADVERBS Sometimes an adverb modifies another adverb. Notice in the first column that each italicized adverb modifies a verb or an adjective. In the second column each added word in boldfaced type is an adverb that modifies the italicized adverb. EXAMPLES Calvin was never late. Calvin was almost never late. We’ll meet afterward. We’ll meet shortly afterward. She slept late. She slept too late. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 363 ADVERBS MODIFYING OTHER ADVERBS Complete Exercise 15 as homework. taken from Warriners English Composition and Grammar, Third Course, p. 363-364 #