Document 11710210
advertisement

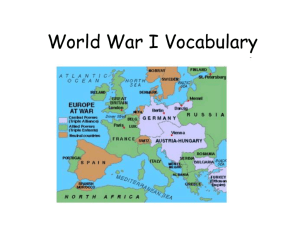
MAIN Causes of WWI 1.Militarism – the aggressive buildup of a nations armed forces. 2.Alliances – nations formed partnerships to help protect and defend themselves. 3.Imperialism – stronger nations began to take over weaker nations. 4.Nationalism – everybody thought their nation was the best. The First World War: What? •War involving nearly all the nations of the world When? •1914-1918 3 The First World War: Long term - Why? 1. Alliance system 2. Imperialist Competition 3. Stockpiling of Weapons Austria - Franz Ferdinand & daughter of Leopold Salvator. Upper right: Cardinal Nagle 4 Short term Assassination of Franz Ferdinand of the Austro-Hungarian Empire Alliances Form Triple Alliance: Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy formed it in 1882, but Italy left the Alliance in WWI. Triple Entente: France, Russia, and Britain formed it to counter the Triple Alliance. 5 Triple Alliance Central Powers Triple Entente Allies The First World War: Who? Central Powers: Germany Austria-Hungary Ottoman Empire Bulgaria 6 Allies: Russia France Great Britain Italy Japan United States (1917) Why did it take so long for America to get involved in the war? •America was isolationist “Why should I get involved in someone else’s problems” 7 Ask yourself: •Is isolationism really an option for a country as powerful as the United States? 9 Which side should the US pick? Central Powers: Allies: •11 million GermanAmericans •Irish-Americans hated Great Britain •Close cultural ties •Shared transatlantic cables (so censored stories) •Big business loaned much $ to allies US Exports to both sides: 10 What did it take to get the US involved? 1. Blockades •Britain blockaded (stopped) all German ships going to America •Germany announced a submarine war around Britain 11 What did it take to get the US involved? 1. Blockades •In May, 1915 Germany told Americans to stay off of British ships •They could/would sink them 12 What did it take to get the US involved? 1. Blockades •Lusitania torpedoed, sinking with 1200 passengers and crew (including 128 Americans) •Was eventually found to be carrying 4200 cases of ammunition 13 14 What did it take to get the US involved? 1. Blockades •The US sharply criticized Germany for their action •Germany agreed not to sink passenger ships without warning in the future 15 What did it take to get the US involved? 2. Unlimited Submarine Warfare •1917 Germany announced “unlimited submarine warfare” in the war zone Why? Otherwise their blockade would not be successful 16 What did it take to get the US involved? 3. Zimmerman Note •US intercepted a note from Germany to Mexico •It promised Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona back in return for an alliance 17 What did it take to get the US involved? •Zimmerman Note and the sinking of 4 unarmed American ships led to a declaration of war 18 SUMMARY OF CAUSES: http://www.history.com/topics/world-wari/world-war-i-history/videos/causes-of-worldwar-i 19 Examine the issue: •Should we tell the story of WWI with Germany as the “bad guy”? Explain. 20 How was the war looking for the allies? Not Good... •Trench Warfare caused the war to drag on with massive casualties. •Russia left the war after its communist Bolshevik revolution in 1917 •Made it a one front war for Germany - all its troops could concentrate on France 21 Convincing the American People Posters - Gee!! •How do you think this poster helped to convince the American people that the war was a good idea? 22 Convincing the American People Committee on Public Information •Created posters, movies, and other propaganda to portray the war effort as a cause worth supporting 23 •Sold Liberty Bonds to citizens; raised $70 billion for war. Convincing the American People Idealism: 2 Goals For War: 1. War to End All Wars 2. Making the World Safe for Democracy 24 What did the US do to help? Supplies: •US provided the food, money, and fresh troops needed to win the war 25 Life in America during the war: 26 • Food and fuel was rationed • “Victory Gardens” = grow your own food • Factories produced supplies for the war instead of consumer goods • National War Labor Board worked to prevent strikes that could hurt war effort = gave workers 8 hour work day and higher wages How did the War Affect the US? Women •Women filled factory jobs •May have led 19th Amendment after the war (Gave women the right to vote) African Americans •Black soldiers still served in Segregated Units 27 •“Great Migration” - thousands of African Americans moved North to work in factories 28 “Harlem Hellfighters” On the front lines for 6 months, longer than any other American unit during the war 29 The Draft Selective Service Act drafted 2.8 million men into WWI. Half of our army was conscripted. Some people refused to go against their will. They were prosecuted under the Espionage Act. Others spoke out against the draft and the war. They were prosecuted under the Sedition Act. Over 1,000 people jailed under these acts. 30 How did the War Affect the US? Enforcing Loyalty •Hatred of all things German •Ex. “Liberty Cabbage” •Espionage Act 1917 & Sedition Act of 1918 punished those against the war (many labor leaders) •Schenck v. US (1919) = free speech not protected during wartime if it poses a “clear and present danger” 31 Convincing the American People Idealism: Fourteen Points What? President Wilson’s Plan for after the war •Fourteen promises, including freedom of the seas & a League of Nations to work for peace 32 President Woodrow Wilson