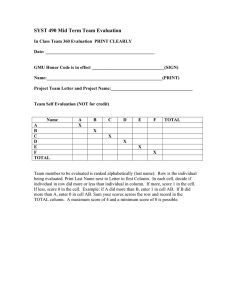
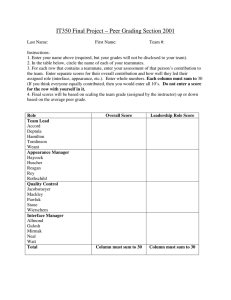
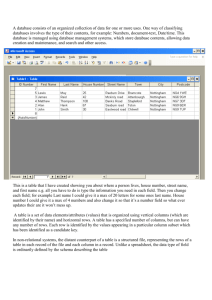
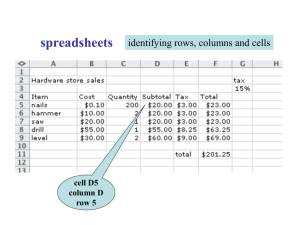
A table allows information to be arranged in
advertisement

A table allows information to be arranged in horizontal rows and vertical columns. A table appears as a single grid structure with black gridlines. A cell is the intersection of a row and column. Organizing text and numerical data in a table helps the reader to understand the information. Graphics, charts, clipart, pictures and other tables can be inserted into a table. The user can create a blank table and insert information or convert existing information into a table. The first row in a table is considered the header row. This row identifies the type of information in each column. The first column on the left in a table can sometimes be considered the header column which identifies the information in each row. To insert a blank table into a document, go to the Insert tab on the ribbon, and click on the down arrow. The table button allows the user to drag the mouse pointer across a blank grid to select the number of rows and columns the table will have. The following illustrates this. The above illustrates that the table will have two columns and five rows available thus creating a 2 x 5 table to insert data. After clicking the mouse the following blank table will appear in the text. The two columns are of equal width. There are also end-of cell markers and end-of-row markers. These are non-printing characters. End of Cell Marker End of Row Marker The student will now create a table with two columns and five rows. The contextual tab “Table Tools” appears when the insertion point is placed within the table. The following illustrates the contextual tab. There are 98 different styles in the styles library. As you select different options in the Table Style Options such as Total Row or Banded Rows, the table format changes. The Layout Tab is divided into the groups: Table, Rows and Columns, Merge, Cell Size, Alignment and Data. The Table Tools contextual tab has two tabs— Design tab and the Layout tab. The Design tab as three groups—Table Styles Option, Table Styles, and Draw Borders. The Table Styles Option group is illustrated in the following: The TABLE group allows the user to Select the table, or a cell, column, or row. The View Gridlines option allows the user to view the gridlines. The Properties option will open a table properties dialog box which allows the user to change the table properties including rows, columns, and cells. The ROWS & COLUMNS group includes Delete which allows the user to delete cells, columns, rows, or tables. It also allows the user to insert columns and rows. The MERGE group allows the user to merge cells, split cells, and split tables. As the user selects an option from the Table Style Options group, the Table Styles group to the right gives a live preview of the option selected. The CELL SIZE group allows the user to change the cell widths, lengths or automatically fit the data in the cell. The ALIGNMENT group allows the user to align the text within a cell such as top left, top center, top right. The text direction button is located in this group. The DATA option allows the user to sort the data, convert a table to text and to insert formulas in a table. Enter the following data into the blank table. Notice that as you key information the end of cell marker moves to the right in order to accommodate the data. To move from one cell to the next cell, press the tab key. Schools MLC High School West Middle East Middle Southside Elementary Population 1500 850 650 298 The header row should be in bold because: 1. It distinguishes the header row from the rest of the table. 2. It allows Word to recognize the header row when using table commands. There are three ways in which to select a column or row. 1. Click inside a cell in the column or row and on the Layout contextual tab Table group, Select option, choose cell, row, table, etc. 2. Move the mouse to the left of the row and a right pointing arrow appears— click the mouse. To select a column, move the pointer to the top of the column and a black arrow appears and then click the mouse. 3. The lease efficient way is to select the cell as you would select a word or phrase. However, you may have trouble if the end of cell or end of row marker is not selected. This way may produce unpredictable results. The following illustration shows the table after bolding the header row. Schools MLC High School West Middle East Middle Southside Elementary Population 1500 850 650 298 Sorting a table means to rearrange the table contents in some type of order such as alphabetical, numerical, or chronological order. We will sort the school name by alphabetical order. 1. Select the column. 2. Select the Layout contextual tab. 3. Data group, select the Sort button. The following dialog box will open. Word has already filled in the necessary information: Sort by: Schools; Type: Text; Using: Paragraphs. Also the Ascending order is already selected. The user just needs to press OK. (If dates or numbers are sorted, the TYPE would change to numbers or dates.) Schools East Middle MLC High School Southside Elementary West Middle Population 650 1500 298 850 The above illustration shows the table after the sort was completed. Notice that because the header row is bolded, it was not affected by the sort. Remember: AS YOU SORT A TABLE ALL ITEMS IN A ROW MOVE TOGETHER. To insert a column in the table, click inside the last column and on the Table Tools contextual tab, select Layout, Rows & Columns, Insert Right. Now insert a new row at the bottom of the table. The following illustrates the new table. Schools East Middle MLC High School Southside Elementary West Middle To delete the contents of a table, row, column or cell, just select it and press the delete key. To delete the structure of a row, column, or the entire table including the contents, select it and on the Layout contextual tab, select delete and the following will open. This enables the user to delete cells, columns, row, and tables. Population 650 1500 298 850 Key in bold the header for the last column: Built and include the following dates in this order: 1985, 2009, 1954, and 1908. When deleting, the user must decide what needs to be deleted. The contents, the structure or both the contents and structure. There are four ways to enlarge the column width. 1. Drag the column’s right border to enlarge 2. Layout contextual tab, Cell Size and enter the cell width 3. Layout contextual tab, Cell size, and select AutoFit. 4. Double click on the column border to enlarge cell to automatically fit the data. To change the column height drag the row border to the desired height or use the contextual tab, Layout Tab, Cell Size Group to key in the row height. Schools East Middle MLC High School Southside Elementary West Middle Population Built 650 1500 1985 2009 298 1954 850 1908 To find the total population for all schools in the above table, position your cell pointer in the last row of the column. On the Layout contextual tab select the Data group. In the Data group, select Formula. The following dialog box will open. There are different functions that can be used in the formulas. They include but are not limited to: =MIN(ABOVE) Returns the minimum number =MAX(ABOVE) Returns the maximum number =COUNT(ABOVE) Returns the count =AVERAGE(ABOVE) Returns the average =SUM(ABOVE) Returns the total Word has built-in styles which allow the user to add color, borders, and shadings. Selecting a style can apply different formatting for the first column, last column, banded columns, header row, total row, and banded rows. Selecting the option banded rows or banded columns will produce a color for alternate rows or alternative columns. The following illustrates banded rows. A color is applied to alternate rows. The formula for adding the numbers in the column is displayed. =SUM(Above). Press OK and the following illustrates the change in the table. Schools Population Built East Middle 650 1985 MLC High 1500 2009 School Southside 298 1954 Elementary West Middle 850 1908 Total 3298 Population Just key in the words “Total Population” in the first column. Schools East Middle MLC High School Southside Elementary West Middle Population 650 1500 Built 1985 2009 298 1954 850 1908 Schools East Middle MLC High School Southside Elementary West Middle Population 650 1500 Built 1985 2009 298 1954 850 1908 The above illustrates banded columns. Copy and paste the table you created in the study guide three times in a blank document (delete the Total row). Make sure the header row is bolded and use each of the following formulas—one formula to one table (population column). Insert a blank row at the bottom of the table if necessary to insert the formula. 1st =SUM(ABOVE) Formula for the 1st table 1. =AVERGE(ABOVE) Formula for the 2nd table 2. =COUNT(ABOVE) Formula for the 3rd table Print making sure your name is on the document. Copy and paste the table three more times and apply the following table styles. 1st Table: 2nd Table: 3rd Table: Light Grid Accent 2 (3rd column 3rd row) Light Grid Accent 5 (6th column 3rd row) Dark List Accent 1 (4th row from the bottom, 2nd column. Print making sure your name is on the document. Copy and paste the table three more times deleting the formula row and apply the following sorts. 1. Sort the first table by date the school was built in ascending order. (Numerical sort) 2. Sort the second table by name in descending alphabetical order. (Alphabetical sort) 3. Sort the third table by population in ascending order. (Numerical sort) Print making sure your name is on the document. Creating a table is simply putting data in columns and rows or a grid of information. Not all information should be in a grid form, but some information is more easily understood if it is displayed as a grid. The many different table styles enhance the appearance of a table. Always keep in mind that “more” is not necessarily the best. This means the table should only be enhanced if it helps the reader understand the information more clearly. Word 2007 allows the user to sort information, enlarge or decrease column and/or cell width and height. It also allows the user to insert or delete columns and/or rows. Math functions are also available to the user. A contextual tab is available—TABLE TOOLS. This tab only appears when a cell, column, or table is selected. The two tabs available in Table Tools are Design and Layout.