Low Cost, General-Purpose High Speed JFET Amplifier AD825 Data Sheet
advertisement

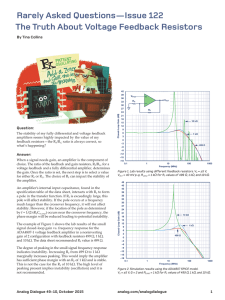
Low Cost, General-Purpose High Speed JFET Amplifier AD825 Data Sheet CONNECTION DIAGRAMS APPLICATIONS CCDs Low distortion filters Mixed gain stages Audio amplifiers Photo detector interfaces ADC input buffers DAC output buffers NC 1 NC 8 AD825 +VS TOP VIEW 6 OUTPUT (Not to Scale) 5 NC –VS 4 –IN 2 7 +IN 3 NC = NO CONNECT 00876-E-001 High speed 41 MHz, −3 dB bandwidth 125 V/µs slew rate 80 ns settling time Input bias current of 20 pA and noise current of 10 fA/√Hz Input voltage noise of 12 nV/√Hz Fully specified power supplies: ±5 V to ±15 V Low distortion: −76 dB at 1 MHz High output drive capability Drives unlimited capacitance load 50 mA min output current No phase reversal when input is at rail Available in 8-lead SOIC Figure 1. 8-Lead Plastic SOIC (R-8) Package NC 1 16 NC NC 2 15 NC NC 3 14 NC AD825 13 +VS –INPUT 4 TOP VIEW +INPUT 5 (Not to Scale) 12 OUTPUT 11 NC –VS 6 NC 7 10 NC NC 8 9 00876-E-002 FEATURES NC NC = NO CONNECT Figure 2. 16-Lead Plastic SOIC (RW-16) Package GENERAL DESCRIPTION The unique input stage has ultralow input bias current and input current noise. Signals that go to either rail on this high performance input do not cause phase reversals at the output. These features make the AD825 a good choice as a buffer for MUX outputs, creating minimal offset and gain errors. The AD825 is fully specified for operation with dual ±5 V and ±15 V supplies. This power supply flexibility, and the low supply current of 6.5 mA with excellent ac characteristics under all supply conditions, makes the AD825 well-suited for many demanding applications. Rev. G 10V 200ns 10V 00876-E-003 The AD825 is a superbly optimized operational amplifier for high speed, low cost, and dc parameters, making it ideally suited for a broad range of signal conditioning and data acquisition applications. The ac performance, gain, bandwidth, slew rate, and drive capability are all very stable over temperature. The AD825 also maintains stable gain under varying load conditions. Figure 3. Performance with Rail-to-Rail Input Signals Document Feedback Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners. One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. Tel: 781.329.4700 ©2014 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Technical Support www.analog.com AD825 Data Sheet TABLE OF CONTENTS Features .............................................................................................. 1 Typical Performance Characteristics ..............................................6 Applications ....................................................................................... 1 Driving Capacitive Loads .............................................................. 10 Connection Diagrams ...................................................................... 1 Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 10 General Description ......................................................................... 1 Input Consideration ................................................................... 10 Revision History ............................................................................... 2 Grounding and Bypassing ......................................................... 10 Specifications..................................................................................... 3 Second-Order Low-Pass Filter ................................................. 11 Absolute Maximum Ratings ............................................................ 5 Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 12 Pin Configurations ........................................................................... 5 Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 12 ESD Caution .................................................................................. 5 REVISION HISTORY 4/14—Rev. F to Rev. G 2/01—Data Sheet Changed from Rev. C to Rev. D Updated Outline Dimensions ....................................................... 12 Changes to Ordering Guide .......................................................... 12 Addition of 16-lead SOIC package (R-16) Connection Diagram ........................................................................4 Addition to Absolute Maximum Ratings .......................................4 Addition to Ordering Guide (R-16) ................................................4 Addition of 16-lead SOIC package (R-16) Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 11 10/04—Data Sheet Changed from Rev. E to Rev. F Changes to Figure 1 .......................................................................... 1 Changes to Figure 4 .......................................................................... 5 Changes to Figure 21 ........................................................................ 8 3/04—Data Sheet Changed from Rev. D to Rev. E Changes to Specifications ................................................................ 3 Addition of 16-Lead SOIC Pin Configuration ............................. 5 Changes to Figure 27 ........................................................................ 9 Updated Outline Dimensions ....................................................... 12 Updated Ordering Guide ............................................................... 12 Rev. G | Page 2 of 12 Data Sheet AD825 SPECIFICATIONS All limits are determined to be at least four standard deviations away from mean value. At TA = 25°C, VS = ±15 V, unless otherwise noted. Table 1. Parameter DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE Unity Gain Bandwidth Bandwidth for 0.1 dB Flatness −3 dB Bandwidth Slew Rate Settling Time to 0.1% to 0.1% Total Harmonic Distortion Differential Gain Error (RLOAD = 150 Ω) Differential Phase Error (RLOAD = 150 Ω) INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE Conditions Gain = +1 Gain = +1 RLOAD = 1 kΩ, G = +1 0 V to 10 V Step, AV = −1 0 V to 10 V Step, AV = −1 FC = 1 MHz, G = −1 NTSC Gain = +2 NTSC Gain = +2 VS Min ±15 V ±15 V ±15 V ±15 V ±15 V ±15 V ±15 V ±15 V 23 18 44 125 AD825A Typ 26 21 46 140 150 180 −77 1.3 2.1 ±15 V 1 ±15 V 10 15 40 20 700 30 TMIN TMAX ±15 V COMMON-MODE REJECTION INPUT VOLTAGE NOISE TMIN TMAX VOUT = ±10 V RLOAD = 1 kΩ VOUT = ±7.5 V RLOAD = 1 kΩ VOUT = ±7.5 V RLOAD = 150 kΩ (50 mA Output) VCM = ±10 f = 10 kHz ±15 V ±15 V INPUT CURRENT NOISE f = 10 kHz ±15 V INPUT COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE RANGE OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING Output Current Short-Circuit Current INPUT RESISTANCE INPUT CAPACITANCE OUTPUT RESISTANCE POWER SUPPLY Quiescent Current RLOAD = 1 kΩ RLOAD = 500 Ω 2 5 5 Rev. G | Page 3 of 12 MHz MHz MHz V/µs ns ns dB % 440 mV mV µV/°C pA pA pA pA pA pA ±15 V 70 76 dB 70 76 dB 68 71 74 80 12 dB dB ±15 V ±15 V ±15 V ±15 V ±15 V ±15 V ±15 V Open Loop TMIN to TMAX Unit Degrees 5 INPUT OFFSET CURRENT OPEN-LOOP GAIN 180 220 ±15 V TMIN to TMAX Offset Drift INPUT BIAS CURRENT Max ±15 V ±15 V nV/√Hz fA/√Hz 10 13 12.9 50 ±13.5 ±13.3 ±13.2 V V V mA mA Ω pF Ω 100 5 ×1011 6 8 6.5 7.2 7.5 mA mA AD825 Data Sheet All limits are determined to be at least four standard deviations away from mean value. At TA = 25°C, VS = ±5 V unless otherwise noted. Table 2. Parameter DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE Unity Gain Bandwidth Bandwidth for 0.1 dB Flatness −3 dB Bandwidth Slew Rate Settling Time to 0.1% to 0.01% Total Harmonic Distortion Differential Gain Error (RLOAD = 150 Ω) Differential Phase Error (RLOAD = 150 Ω) INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE Conditions Gain = +1 Gain = +1 RLOAD = 1 kΩ, G = −1 −2.5 V to +2.5 V −2.5 V to +2.5 V FC = 1 MHz, G = −1 NTSC Gain = +2 NTSC Gain = +2 VS Min ±5 V ±5 V ±5 V ±5 V ±5 V ±5 V ±5 V ±5 V 18 8 34 115 AD825A Typ 21 10 37 130 75 90 −76 1.2 1.4 ±5 V 1 ±5 V 10 10 30 15 600 25 TMIN TMAX INPUT OFFSET CURRENT ±5 V COMMON-MODE REJECTION INPUT VOLTAGE NOISE ±5 V ±5 V INPUT CURRENT NOISE f = 10 kHz ±5 V INPUT COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE RANGE OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING Output Current Short-Circuit Current INPUT RESISTANCE INPUT CAPACITANCE OUTPUT RESISTANCE POWER SUPPLY Quiescent Current POWER SUPPLY REJECTION Rev. G | Page 4 of 12 MHz MHz MHz V/µs ns ns dB % 280 mV mV µV/°C pA pA pA pA pA pA ±5 V 64 64 69 ±5 V ±5 V 66 66 80 12 dB dB dB nV/√Hz fA/√Hz 10 +3.2 +3.1 50 ± 3.5 ±3.4 ±3.2 V V V mA mA Ω pF Ω 80 5 ×1011 6 8 Open Loop TMIN to TMAX VS = ±5 V to ±15 V 2 5 5 ±5 V RLOAD = 500 Ω RLOAD = 150 Ω Unit Degrees 5 TMIN TMAX VOUT = ±2.5 RLOAD = 500 Ω RLOAD = 150 Ω VCM = ±2 V f = 10 kHz Offset Current Drift OPEN-LOOP GAIN 90 110 ±5 V TMIN to TMAX Offset Drift INPUT BIAS CURRENT Max ±5 V ±5 V 6.2 76 88 6.8 7.5 mA mA dB Data Sheet AD825 ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS PIN CONFIGURATIONS Table 3. Rating ±18 V NC 1 +VS TOP VIEW 6 OUTPUT (Not to Scale) 5 NC –VS 4 7 See Figure 6 ±VS ±VS See Figure 6 −65°C to +125°C −40°C to +85°C 300°C NC = NO CONNECT 00876-E-001 +IN 3 Figure 4. 8-Lead SOIC NC 1 16 NC NC 2 15 NC NC 3 –INPUT 4 14 NC AD825 13 +VS TOP VIEW +INPUT 5 (Not to Scale) 12 OUTPUT 11 NC –VS 6 Specification is for device in free air: 8-lead SOIC package: θJA = 155°C/W 16-lead SOIC package: θJA = 85°C/W Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. NC 7 10 NC NC 8 9 NC NC = NO CONNECT Figure 5. 16-Lead SOIC MAXIMUM POWER DISSIPATION (W) 2.5 TJ = 150°C 2.0 16-LEAD SOIC PACKAGE 1.5 1.0 0.5 8-LEAD SOIC PACKAGE 0 –50 –40 –30 –20 –10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (°C) Figure 6. Maximum Power Dissipation vs. Temperature ESD CAUTION Rev. G | Page 5 of 12 00876-E-004 1 NC 8 AD825 –IN 2 00876-E-002 Parameter Supply Voltage Internal Power Dissipation1 Small Outline (R) Input Voltage (Common Mode) Differential Input Voltage Output Short-Circuit Duration Storage Temperature Range (R-8, RW-16) Operating Temperature Range Lead Temperature Range (Soldering 10 sec) AD825 TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS 100 20 15 5 RL = 150 10 OUTPUT IMPEDANCE () OUTPUT SWING (V) 10 RL = 1k 0 –5 –10 1 0.1 4 2 6 8 10 12 SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V) 14 16 18 0.01 100 15 10M 80 35 BANDWIDTH 30 UNITY GAIN BANDWIDTH (MHz) 10 VS = ±15V 5 VS = ±5V 0 –5 VS = ±15V –10 25 60 20 PHASE MARGIN 15 40 10 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 LOAD RESISTANCE () 800 900 1000 00876-E-006 5 0 –60 –40 –20 0 60 20 40 80 TEMPERATURE (°C) 100 120 00876-E-009 OUTPUT SWING (V) 1M Figure 10. Closed-Loop Output Impedance vs. Frequency Figure 7. Output Voltage Swing vs. Supply Voltage –15 10k 100k FREQUENCY (Hz) 1k 00876-E-008 0 PHASE MARGIN (°C) –20 00876-E-005 –15 20 140 Figure 11. Unity Gain Bandwidth and Phase Margin vs. Temperature Figure 8. Output Voltage Swing vs. Load Resistance 80 7.0 180 VS = ±15V OPEN-LOOP GAIN (dB) +85° 6.0 VS = ±5V 60 90 50 45 40 0 30 20 5.5 5.0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 SUPPLY VOLTAGE (±V) 16 18 20 0 1k Figure 9. Quiescent Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage for Various Temperatures 10k 100k 1M FREQUENCY (Hz) 10M 100M Figure 12. Open-Loop Gain and Phase Margin vs. Frequency Rev. F | Page 6 of 12 00876-E-010 10 00876-E-007 SUPPLY CURRENT (mA) 6.5 OPEN-LOOP PHASE (Degrees) 135 70 –40° +25° AD825 30 80 OPEN-LOOP GAIN (dB) 75 VS = ±15V 70 VS = ±5V 60 10 1k 10k LOAD RESISTANCE () 00876-E-011 65 20 RL = 150 10 0 10k Figure 13. Open-Loop Gain vs. Load Resistance 100k 1M FREQUENCY (Hz) 00876-E-014 OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V p-p) RL = 1k 10M Figure 16. Large Signal Frequency Response; G = +2 10 200 0 180 160 –10 –PSRR –30 +PSRR –40 –50 –60 140 0.01% 100 0.1% 60 –80 20 100k 1M FREQUENCY (Hz) 10M 00876-E-012 40 10k 0.1% 80 –70 –90 0.01% 120 0 10 8 6 4 2 0 –2 –4 OUTPUT SWING (0 to ±V) –6 –8 –10 00876-E-015 SETTLING TIME (ns) PSR (dB) –20 Figure 17. Output Swing and Error vs. Settling Time Figure 14. Power Supply Rejection vs. Frequency 130 –50 120 –55 110 –60 DISTORTION (dB) 100 90 80 VS = ±5V 70 60 SECOND –65 THIRD –70 –75 50 –80 30 10 100 1k 10k 100k FREQUENCY (Hz) 1M 10M –85 100k Figure 15. Common-Mode Rejection vs. Frequency 1M FREQUENCY (Hz) Figure 18. Harmonic Distortion vs. Frequency Rev. F | Page 7 of 12 10M 00876-E-016 40 00876-E-013 CMR (dB) VS = ±15V AD825 +VS 160 10F ±15V 0.01F ±5V 120 2 7 HP PULSE (LS) AD825 VIN OR 3 4 FUNCTION (SS) GENERATOR 50 100 80 –VS 6 VOUT TEKTRONIX P6204 FET PROBE TEKTRONIX 7A24 PREAMP 0.01F 00876-E-020 SLEW RATE (V/s) 140 RL 10F 60 Figure 22. Noninverting Amplifier Connection 40 0 –60 –40 –20 0 60 20 40 80 TEMPERATURE (°C) 100 120 00876-E-017 20 140 Figure 19. Slew Rate vs. Temperature 2 5V 1 100ns 0 –2 –3 –4 VOUT VIN VS 0.1dB FLATNESS ±5V 10MHz ±15V 21MHz –5 –6 –7 00876-E-021 GAIN (dB) –1 10k 100k 1M 10M FREQUENCY (Hz) 00876-E-018 5V –8 1k Figure 23. Noninverting Large Signal Pulse Response, RL = 1 kΩ Figure 20. Closed-Loop Gain vs. Frequency, Gain = +1 2 200mV 50ns 1 0 –2 –3 VIN 1k –4 1k VOUT –5 0.1dB FLATNESS ±5V 7.7MHz ±15V 9.8MHz –7 –8 1k 10k 100k 1M FREQUENCY (Hz) 200mV 10M 00876-E-022 VS –6 00876-E-019 GAIN (dB) –1 Figure 24. Noninverting Small Signal Pulse Response, RL = 1 kΩ Figure 21. Closed-Loop Gain vs. Frequency, Gain = −1 Rev. F | Page 8 of 12 AD825 00876-E-023 5V 5V Figure 25. Noninverting Large Signal Pulse Response, RL = 150 Ω Figure 28. Inverting Large Signal Pulse Response, RL = 1 kΩ 50ns 200mV 00876-E-024 200mV 200mV 200mV Figure 26. Noninverting Small Signal Pulse Response, RL = 150 Ω Figure 29. Inverting Small Signal Pulse Response, RL = 1 kΩ 1k +VS 10F 0.01F HP PULSE VIN GENERATOR RIN 1k 7 2 AD825 6 3 VOUT TEKTRONIX P6204 FET PROBE TEKTRONIX 7A24 PREAMP 0.01F –VS RL 10F 00876-E-025 4 50 50ns Figure 27. Inverting Amplifier Connection Rev. F | Page 9 of 12 00876-E-027 5V 100ns 00876-E-026 100ns 5V AD825 Data Sheet DRIVING CAPACITIVE LOADS The internal compensation of the AD825, together with its high output current drive, permits excellent large signal performance while driving extremely high capacitive loads. NEG 1kΩ +VS VPOS 10µF POS 0.01µF HP PULSE VIN GENERATOR RIN 1kΩ 7 CF 2 AD825 6 3 VOUT TEKTRONIX P6204 FET PROBE VOUT TEKTRONIX 7A24 PREAMP –VS CL 00876-E-028 0.01µF 50Ω 10µF Figure 30. Inverting Amplifier Driving a Capacitive Load 5V VNEG Figure 32. Simplified Schematic 500ns 5V 00876-E-029 INPUT OUTPUT 00876-E-030 4 Figure 31. Inverting Amplifier Pulse Response While Driving a 400 pF Capacitive Load THEORY OF OPERATION The capacitor, CF, in the output stage, enables the AD825 to drive heavy capacitive loads. For light loads, the gain of the output buffer is close to unity, CF is bootstrapped, and not much happens. As the capacitive load is increased, the gain of the output buffer is decreased and the bandwidth of the amplifier is reduced through a portion of CF adding to the dominant pole. As the capacitive load is further increased, the amplifier’s bandwidth continues to drop, maintaining the stability of the AD825. INPUT CONSIDERATION The AD825 with its unique input stage ensures no phase reversal for signals as large as or even larger than the supply voltages. Also, layout considerations of the input transistors ensure functionality even with a large differential signal. The AD825 is a low cost, wideband, high performance FET input operational amplifier. With its unique input stage design, the AD825 ensures no phase reversal, even for inputs that exceed the power supply voltages, and its output stage is designed to drive heavy capacitive or resistive loads with small changes relative to no load conditions. The need for a low noise input stage calls for a larger FET transistor. One should consider the additional capacitance that is added to ensure stability. When filters are designed with the AD825, one needs to consider the input capacitance (5 pF to 6 pF) of the AD825 as part of the passive network. The AD825 (Figure 32) consists of common-drain, commonbase FET input stage driving a cascoded, common-base matched NPN gain stage. The output buffer stage uses emitter followers in a Class AB amplifier that can deliver large current to the load while maintaining low levels of distortion. The AD825 is a low input bias current FET amplifier. Its high frequency response makes it useful in applications, such as photodiode interfaces, filters, and audio circuits. When designing high frequency circuits, some special precautions are in order. Circuits must be built with short interconnects, and resistances should have low inductive paths to ground. Power supply leads should be bypassed to common as close as possible to the amplifier pins. Ceramic capacitors of 0.1 µF are recommended. GROUNDING AND BYPASSING Rev. G | Page 10 of 12 Data Sheet AD825 SECOND-ORDER LOW-PASS FILTER C1 24pF A second-order Butterworth low-pass filter can be implemented using the AD825 as shown in Figure 33. The extremely low bias currents of the AD825 allow the use of large resistor values and, consequently, small capacitor values without concern for developing large offset errors. Low current noise is another factor in permitting the use of large resistors without having to worry about the resultant voltage noise. 1.414 2π f CUTOFF R1 C2 ( farads ) = 0.707 2r f CUTOFF R1 R1 = R2 = User Selected (Typically 10 kΩ to 100 kΩ ) A plot of the filter frequency response is shown in Figure 34; better than 40 dB of high frequency rejection is provided. C2 6pF C3 0.1µF VOUT AD825 00876-E-031 –5V Figure 33. Second-Order Butterworth Low-Pass Filter 0 –10 –20 –30 –40 –50 –60 –70 –80 10k 100k 1M FREQUENCY (Hz) 10M 100M 00876-E-032 C1 = R2 9.31kΩ C4 0.1µF HIGH FREQUENCY REJECTION (dB) With the values shown, the corner frequency will be 1 MHz. The equations for component selection are shown below. Note that the noninverting input (and the inverting input) has an input capacitance of 6 pF. As a result, the calculated value of C1 (12 pF) is reduced to 6 pF. VIN R1 9.31kΩ +5V Figure 34. Frequency Response of Second-Order Butterworth Filter Rev. G | Page 11 of 12 AD825 Data Sheet OUTLINE DIMENSIONS 5.00 (0.1968) 4.80 (0.1890) 8 4.00 (0.1574) 3.80 (0.1497) 5 1 6.20 (0.2441) 5.80 (0.2284) 4 1.27 (0.0500) BSC 0.25 (0.0098) 0.10 (0.0040) 1.75 (0.0688) 1.35 (0.0532) 0.51 (0.0201) 0.31 (0.0122) COPLANARITY 0.10 SEATING PLANE 0.50 (0.0196) 0.25 (0.0099) 45° 8° 0° 0.25 (0.0098) 0.17 (0.0067) 1.27 (0.0500) 0.40 (0.0157) 012407-A COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MS-012-AA CONTROLLING DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILLIMETERS; INCH DIMENSIONS (IN PARENTHESES) ARE ROUNDED-OFF MILLIMETER EQUIVALENTS FOR REFERENCE ONLY AND ARE NOT APPROPRIATE FOR USE IN DESIGN. Figure 35. 8-Lead Standard Small Outline Package [SOIC] Narrow Body (R-8) Dimensions shown in millimeters (inches) 10.50 (0.4134) 10.10 (0.3976) 9 16 7.60 (0.2992) 7.40 (0.2913) 8 1.27 (0.0500) BSC 0.30 (0.0118) 0.10 (0.0039) COPLANARITY 0.10 0.51 (0.0201) 0.31 (0.0122) 10.65 (0.4193) 10.00 (0.3937) 0.75 (0.0295) 45° 0.25 (0.0098) 2.65 (0.1043) 2.35 (0.0925) SEATING PLANE 8° 0° 0.33 (0.0130) 0.20 (0.0079) 1.27 (0.0500) 0.40 (0.0157) COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MS-013-AA CONTROLLING DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILLIMETERS; INCH DIMENSIONS (IN PARENTHESES) ARE ROUNDED-OFF MILLIMETER EQUIVALENTS FOR REFERENCE ONLY AND ARE NOT APPROPRIATE FOR USE IN DESIGN. 03-27-2007-B 1 Figure 36. 16-Lead Standard Small Outline Package [SOIC_W] Wide Body (RW-16) Dimensions shown in millimeters (inches) ORDERING GUIDE Model1 AD825ARZ AD825ARZ-REEL AD825ARZ-REEL7 AD825ARZ-16 AD825ARZ-16-REEL AD825ARZ-16-REEL7 AD825AR-EBZ AD825ACHIPS 1 Temperature Range −40°C to +85°C −40°C to +85°C −40°C to +85°C −40°C to +85°C −40°C to +85°C −40°C to +85°C Package Description 8-Lead SOIC_N 8-Lead SOIC_N, 13" Tape and Reel 8-Lead SOIC_N, 7" Tape and Reel 16-Lead SOIC_W 16-Lead SOIC_W, 13" Tape and Reel 16-Lead SOIC_W, 7" Tape and Reel Evaluation Board Die Z = RoHS Compliant Part. ©2014 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners. D00876-0-4/14(G) Rev. G | Page 12 of 12 Package Option R-8 R-8 R-8 RW-16 RW-16 RW-16