Stat 301 Lab 6: Due October 21 Fall 2013
advertisement

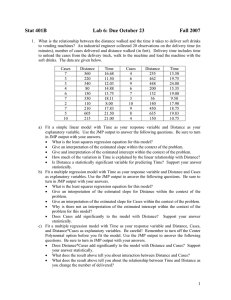
Stat 301 Lab 6: Due October 21 Fall 2013 1. What is the relationship between the distance walked and the time it takes to deliver soft drinks to vending machines? An industrial engineer collected 20 observations on the delivery time (in minutes), number of cases delivered and distance walked (in feet). Delivery time includes time to unload the cases from the delivery truck, walk to the machine and load the machine with the soft drinks. The data are given below. Cases 7 3 3 4 6 7 2 7 5 10 Distance 560 220 340 80 150 330 110 210 605 215 Time 16.68 11.50 12.03 14.88 13.75 18.11 8.00 17.83 21.50 21.00 Cases 4 6 9 6 7 3 10 9 8 4 Distance 255 462 448 200 132 36 140 450 635 150 Time 13.50 19.75 24.00 15.35 19.00 9.50 17.90 18.75 19.83 10.75 a) Fit a simple linear model with Time as your response variable and Distance as your explanatory variable. Use the JMP output to answer the following questions. Be sure to attach the JMP to your assignment. • • • • • • What is the least squares regression equation for this model? Predict the delivery time for 6 cases and 200 feet. Give an interpretation of the estimated slope within the context of the problem. Give and interpretation of the estimated intercept within the context of the problem. How much of the variation in Time is explained by the linear relationship with Distance? Is Distance a statistically significant variable for predicting Time? Support your answer statistically. b) Fit a multiple regression model with Time as your response variable and Distance and Cases as explanatory variables. Use the JMP output to answer the following questions. Be sure to attach the JMP to your assignment. • • • • • • What is the least squares regression equation for this model? Predict the delivery time for 6 cases and 200 feet. How does this compare to the prediction in a)? Give an interpretation of the estimated slope for Distance within the context of the problem. Give an interpretation of the estimated slope for Cases within the context of the problem. Why is there not an interpretation of the estimated intercept within the context of the problem for this model? Does Cases add significantly to the model with Distance? Support your answer statistically. 1 c) Fit a multiple regression model with Time as your response variable and Distance, Cases, and Distance*Cases as explanatory variables. Be careful! Remember to turn off the Center Polynomial option before you fit the model. Use the JMP output to answer the following questions. Be sure to attach the JMP to your assignment. • • • • • What is the least squares regression equation for this model? Predict the delivery time for 6 cases and 200 feet. How does this compare to the prediction in b)? Does Distance*Cases add significantly to the model with Distance and Cases? Support your answer statistically. What does the result above tell you about interaction between Distance and Cases? What does the result above tell you about the relationship between Time and Distance as you change the number of delivered? d) Fit a multiple regression model with Time as your response variable and Distance, Cases, and (Distance – Mean Distance)*(Cases – Mean Cases) i.e. leave the Center Polynomial option turned on. Use the JMP output to answer the following questions. Be sure to attach the JMP to your assignment. • • • • What is the least squares regression equation for this model? Predict the delivery time for 6 cases and 200 feet. How does this compare to the prediction in c)? Does (Distance – Mean Distance)*(Cases – Mean Cases) add significantly to the model with Distance and Cases? Support your answer statistically. How does this compare to your results in c) about the interaction between Distance and Cases? e) For the “best” model for these data, compute the residuals. Plot the residuals versus Distance. Plot the residuals versus Cases. Analyze the distribution of the residuals. Use the JMP output to answer the following questions. Be sure to attach the JMP to your assignment. • • What do the plots of residuals versus the explanatory variables tell you about the adequacy of the model you have chosen as “best”? What do they tell you about the equal standard deviation condition? Be sure to support your answers by referring to the plots. What does the analysis of the distribution of residuals tell you about the conditions of identically and normally distributed residuals? Be sure to support your answers by referring to the analysis. 2