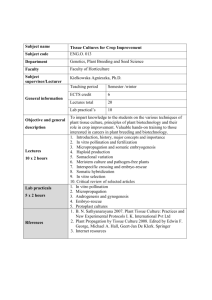
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this
material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this site.
Copyright 2015, The Johns Hopkins University and Michael Trush. All rights reserved. Use of these materials
permitted only in accordance with license rights granted. Materials provided “AS IS”; no representations or
warranties provided. User assumes all responsibility for use, and all liability related thereto, and must independently
review all materials for accuracy and efficacy. May contain materials owned by others. User is responsible for
obtaining permissions for use from third parties as needed.
Section E
In Vitro Toxicity Tests: Cellular Toxicity
The material in this video is subject to the copyright of the owners of the material and is being provided for educational purposes under
rules of fair use for registered students in this course only. No additional copies of the copyrighted work may be made or distributed.
Examples of Cell-Based In Vitro Assays
! Hepatocyte/liver slice cultures
- Metabolism, genotoxicity, cytotoxicity
! Fibroblast/cell line cultures
- Cytotoxicity
! Three-dimensional cell cultures
- Skin, eye irritation tests
3
Cellular Toxicity
Examples: In Vitro Methods which Replace Animal Use for Toxicity
Testing
In vitro assay
Whole animal
test replaced
Reduction in
animal use
EPIDERMTM skin corrosivity test—
Rabbits
reconstituted human skin
Total*
EPISKINTM corrosivity test
Rabbits
Total*
CorrositexR
Rabbits,
Rodents
Total*–in use by
DOT
Embryonic stem cell test
Rodents
Total*
In vitro 3T3 NRU phototoxicity
test
Rabbits,
Rodents
Total*
* Validated and recommended for regulatory use. See http://ecvam.jrc.it/index.htm, Web site for the European Center
for the Validation of Alternative Methods; See http://iccvam.niehs.nih.gov/, Web site for the U.S. Interagency
Coordinating Committee on the Validation of Alternative Methods.
4
Episkin®
! Episkin® was developed by IMEDEX and L’OREAL
- In vitro reconstructed human epithelium
Source: http://www.imedex.fr/Episkin.htm
5
Major Advantages of In Vitro Systems
! Reduced cost
! Reduction in animal use
! Greater experimental control over chemical
concentrations, environmental composition
! Uniform biological systems (cell lines)
! Ability to use human tissue/cells
! Potential for use in high-through-put screening assays
6
Major Disadvantages of In Vitro Systems
! Loss of organ structure and cell-cell interaction
! Loss of differentiated tissue/cell-specific function
! Short term
! Static regarding nutrient influx, metabolite accumulation
7
Toxicity Testing Challenges
! Universe of chemicals that require testing for potential
adverse health and environmental effects is enormous
- 87,000 chemicals candidates for screening for
endocrine disruption activity
- 30,000 chemicals in the REACH program
(Registration, Evaluation and Authorization of
Chemicals in the EU)
! Current assays take too long and are too costly in terms
of dollars and animals
8
Future Directions in Toxicity Testing
! NRC/NAS report on “Toxicity Testing in the 21st Century:
A Vision and a Strategy,” 2007
- New in vitro cell systems
- New high-through-put systems
- Dose-response and extrapolation modeling
! PBPK models
- Population-based and human exposure data
! ! Application of “omics” (genomics, transcriptomics,
proteomics, metabolomics) to identify biomarkers
New animal models; humane end points
- Transgenic animals
- Use of less sentient species
9
Future Directions in Toxicity Testing
10
Additional Challenges: Development and Use of
New Tests
! Research to uncover mechanism-based pathways to
toxicity
! Development of mechanism-based assays
! Sorting out value of correlative vs. mechanism-based
tests
! Validation
! Regulatory acceptance
! Harmonization
11