This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this
material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this site.
Copyright 2006, The Johns Hopkins University and Benjamin Caballero. All rights reserved. Use of these materials
permitted only in accordance with license rights granted. Materials provided “AS IS”; no representations or
warranties provided. User assumes all responsibility for use, and all liability related thereto, and must independently
review all materials for accuracy and efficacy. May contain materials owned by others. User is responsible for
obtaining permissions for use from third parties as needed.
The Nutrition Transition
Benjamin Caballero, M.D., Ph.D.
Center for Human Nutrition
Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health
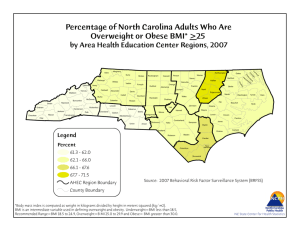
Annual increase in obesity rates in selected
countries (women)
3
% per year
2.5
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
US
Mexico
Brazil
Morocco Thailand
China
Popkin and Gordon-Larsen, 2004
Under- and overweight, 0-5 yr/old children
Underweight
30
25
20
15
Overweight
10
5
5
%
10
15
20
Is the world shifting from
undernutrition to overnutrition ?
Prevalence of stunting in < 5 yr/old children
2002
1995
1980
S Asia
SE Asia
SS Africa
Near E-N Africa
S America
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
Prevalence of stunting, %
SCC/SCN, UNICEF, 2004
World poverty, 1981-2001
% of people living with <US$2 per day
1981
1990
2001
South Asia
89.1
85.5
77.2
Sub-Saharan Africa
73.3
75.0
76.6
South E Asia & Oceania
84.8
69.9
47.4
Latin American & Caribbean
26.9
28.4
24.5
North Africa & Middle E
28.9
21.4
23.2
Europe & Central Asia
4.7
4.9
19.7
World Bank, 2004
The Nutrition Transition
Demographic trends
Food availability and cost
Lifestyle
Demographic trends
Urbanization
Increase in life expectancy
Reduction in infant mortality
World population growth, 15002100
2.5
Growth rate, %
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
-0.5
1500
1600
1700
1800
Year
1900
2000
2100
50
20
40
20
30
20
20
20
10
20
00
20
90
19
80
19
70
19
60
0-14
15-59
60+
19
50
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
-0.5
19
Growth rate, %
Age shifts in world population
Year
Zlotnik, UN Population Div.
Population over 59 years
Relative increase, 1950 =100
1200
1000
800
600
400
200
0
Europe
N. Amer.
1950
Asia
1985
Latin Am.
2025
Africa
Urban growth
Annual increase, 1990-2000
5
% increase
4
3
2
1
0
Africa
Asia
L.A.
Europe
N.A.
Projected population growth in the
developing world, 2000 - 2025
2000
2025
3.73
4
Pop. (billions)
3.5
3
2.92
3.09
2.5
1.99
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
Rural
Urban
United Nations, 1998
Urbanization and body mass index
Asia-Rural
Asia-Urban
Latin America
40
30
% 20
10
0
15
20
25
30
35
40
BMI
INCLEN, 1996
GROWTH OF VENEZUELAN CHILDREN
Weight/age
Percentiles
Rural (%)
Urban (%)
< 10th
27.69
17.99
10th > <90th
67.21
72.93
> 90th
5.09
9.06
Lopez Blanco et al, 1992
Dietary changes
Changes in food type, availability
and cost
Changes in eating behaviors
Food commodities –Global trends
FAOSTAT, 2002
Growth in processed food market by GNI
1996-2002
USDA ERS-Euromonitor, 2003 – World Bank country classification
Food cost: household budget share
50
47
40
%
29
30
20
12
10
0
Low (32)
Middle (41)
High (26)
Country income level
L=<15%, M=15-50%, H=>50% of U.S. median
USDA ERS WRS-01-1
Food cost: income elasticity
80
73
70
58
60
50
% 40
29
30
20
10
0
Low (32)
Middle (41)
High (26)
Country income level
L=<15%, M=15-50%, H=>50% of U.S. median
USDA ERS WRS-01-1
China: dietary trends
Consumption of edible oils
55
50
45
40
35
30
g/day
25
20
15
10
5
0
1989
1997
Low
Middle
Income level
High
Lifestyle changes
Reduction in energy demands at work
Reduction in energy demands of daily
survival activities
Limited leisure physical activity
Television
% of employment
Trends in employment type in South Asian
transitional countries
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
Service
Manufacturing
Agriculture
1965
1975
1985
1995
Year
Popkin et al, 1998
The nutrition transition in China:
Prevalence of sedentary occupational activity
Men
90
80
Women
83
72
70
%
60
50
40
30
20
13
8
10
0
Urban
Rural
The added risk of early undernutrition
Birth weight and risk of diabetes and Syndrome X
IGT/NIDD
Syndrome X
50
40
30
%
20
10
0
< 2.5
< 2.95
< 3.4
< 3.86
< 4.3
> 4.3
Birth weight (kg)
Phipps et al, 1993
Effects of birthweight and adult BMI on prevalence of
the insulin resistance syndrome
The San Antonio Heart Study
25
20
%
15
3
10
2
5
1
BMI tertile
0
1
2
3
Birthweight tertile
Valdez et al, Diabetologia, 1994
China: trends in obesity
Population with BMI > 25
20
16
%
12
1989
1997
8
4
0
Low
Middle
High
Income level
Du et al, SSM 2004
Trends in diabetes in China
Adults
% prevalence
1994
2000
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
35-44
45-54
55-64
Age, years
China National Survey, InterAsia Study
China NTP: metabolic syndrome and BMI (urban and rural)
Men
25
Women
25
*
*
20
*
15
15
*
*
10
10
*
* Significantly higher than 1, p<0.05
>=26.5
24.5-26.4
22.5-24.4
20.5-22.4
18.5-20.4
<18.5
>=26.5
24.5-26.4
0
22.5-24.4
0
20.5-22.4
5
18.5-20.4
5
<18.5
Odds ratio
20
Age-adjusted urban-rural differences in lifestyle
factors: Energy intake
Men
Women
3000
kcal/day
2500
2000
2600
2500
2001
2059
1500
1000
500
0
Urban
Rural
Recent trends
In intermediate-income countries,
obesity is increasing more among the
poor
Obesity prevalence in rural populations
is approaching the rates of urban areas
Difference in prevalence of underweight and
obesity, low vs. high SES - Brazil
Difference in prevalence, %
8
1989
1997
6
4
2
0
-2
-4
-6
-8
Undernutrition
Obesity
Monteiro, AJPH 2004
Disease burden in the developing world
1990
2020
Acc
14%
Inj.
11%
CD
17%
Non-CD
47%
CD
42%
Non-CD
69%
Murray & Lopez, 1996
The big picture
BMI:
1.95
19
25
Height, m
1.85
1.75
1.65
1.55
40
50
60
70
80
Weight, kg
90
100
110
BMI:
1.95
19
25
Height, m
1.85
1.75
1975 ●
1.65
1785 ●
1705 ●
1870 ●
1.55
40
50
60
70
80
Weight, kg
90
100
110
Mean BMI in 27 yr-old U.S. males
25
BMI
24
23
22
21
1864
1894
1944
1961
1991
Costa & Fogel, 1997
Trends in BMI in China
Modeling from regional and national data
1960 → 1990
Upper SES
Lower SES
18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
% of men not working on the previous
month due to illness (excluding accidents) Bangladesh
50
40
%
30
20
10
0
<16
16-17
17-18
18-19
19-20
>20
BMI
Pryer, Eur J Clin Nutr, 1993
UN Millenium Development Goals
Eradicate extreme
poverty and hunger
Achieve universal
primary education
Promote gender
equality and empower
women
Reduce child mortality
Improve maternal
health
Combat HIV/AIDS,
malaria, and other
diseases
Ensure environmental
sustainability
Develop a global
partnership for
development