Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: Treatment Approach and Outcomes The Drexel Experience
advertisement

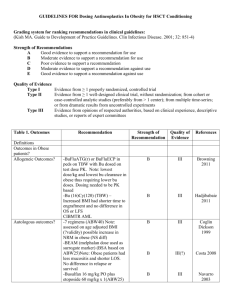
Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: Treatment Approach and Outcomes The Drexel Experience Sukhdeep Kaur1, Courtney Ackerman, Hareesha Chakunta, Michael Styler1, Division of Hematology and Oncology, Department of Medicine, Hahnemann University Hospital, Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia, PA INTRODUCTION RESULTS RESULTS CYTOREDUCTION THERAPY One hundred eighteen patients’ charts were reviewed and categorized based on treatment. Myeloproliferative neoplasms are a group of clonal disorders that arise from a transformation in a hematopoietic stem cell. When determining treatment strategies for these patients, one must consider long-term survival, morbidity from thrombotic complications, development of myelofibrosis or transformation into acute leukemia, and the effect of specific therapies on the incidence of leukemic transformation and on pregnancy. At Drexel University, a significant number of patients were treated with busulfan and were thought to have a more favorable clinical course and possibly increased survival in comparison to other agents. In our study we analyzed the outcomes of patients treated in the practice of I. Brodsky Associates diagnosed with essential thrombocytosis (ET), polycythemia vera (PCV), primary Myelofibrosis (PMF), and Myeloproliferative disorder NOS, who received a variety of treatment modalities, and compared their clinical courses to determine if there is a superior treatment. Percent survival 100 80 60 40 20 0 0 100 200 300 400 500 MONTHS P. VERA E. THROMBOCYTOSIS HYDROXYUREA 1 (7) HYDROXYUREA 2 (13) BUSULFAN 1 (19) BUSULFAN 2 (14) PATIENTS AND METHODS jGRAPH 1: Complications of groups based on treatment. This study is a retrospective cohort study in which we examined the medical records of patients treated for the diagnoses of ET, PCV and PMF at Hahnemann Hospital-Drexel University College of Medicine in the practice of I. Brodsky Associates from January 1960 to December 2013. The following variables were measured and compared (Table 1): Thrombotic events were most common in the Busulfan and Hydroxyurea combination group (56%). Second malignancy was diagnosed in 31% of patients treated with Hydroxyurea alone. Leukemic transformation occurred in 19% of patients treated with hydroxyurea alone. Hemorrhage occurred in 17% of patients in busulfan group. “Other” were considered to be transfusion dependent anemia, progression to myelofibrosis, and development of varices without bleeding. ESSENTIAL THROMBOCYTOSIS 100 E. P. Thrombocytosis Vera Total number of Pts 47 Primary Myelofibrosis 56 Myeloproliferative d/o NOS 8 Percent survival Baseline characteristics 7 Age (years) RANGE MEDIAN 41-97 40-97 70 75 37-85 35-96 63 67 Sex 80 60 40 20 0 Male 16 35 4 5 Female 31 22 4 2 0 ASPIRIN (9) 51 6 4 African American 9 6 1 2 Hispanic 0 0 1 0 Asian 1 0 0 1 Hemoglobin 13.2 17.7 11.3 11.1 Hematocrit 39.6 53.1 36.5 34.2 Platelet (thousand) 968 424 301 173 WBC 8.5 10.2 13.7 12.8 Labs at dx (median) jGRAPH 20 33 8 3 No 23 23 0 3 14 19 0 1 Hydroxyurea 13 7 3 3 Busulfan+Hydroxyurea 10 10 3 1 Aspirin/plavix only 9 14 2 0 Phlebotomy only JAK 2 Mutation documented Chromosome anomaly 2 7 1 2 HYDROXYUREA (13) 5 12 6 BUSULFAN (14) 2: Overall Survival by Treatment Group in Essential Thrombocytosis 100 80 60 20 0 100 200 300 400 500 MONTHS ASPIRIN (13) HYDROXYUREA (7) 0 REFERENCES BUSULFAN (19) PHLEBOTOMY (7) 1 3 Our retrospective study showed that busulfan used alone showed longest survival as well as having less complications. The significant amount of complications from thrombotic events noted in the dual treatment with busulfan and hydroxyurea occurred mostly prior to starting treatment with busulfan. Given longest median survival in this group, busulfan may provide the optimal disease control in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms, and thus most effectively reduce the risk of thrombosis. Moreover, increased risk of second malignancies, including transformation to acute leukemia, was not seen in the busulfan treated patients. This suggests that physicians should consider the use of busulfan in treating myeloproliferative neoplasms. 40 0 jGRAPH DISCUSSION PHLEBOTOMY (1) BUSULFAN/HYDROXYUREA (10) 9 500 POLYCYTHEMIA VERA Treatment Busulfan 400 Patients that were treated with a combination of Busulfan and Hydroxyurea had the longest survival of 398 months, while Busulfan alone had the longest survival of 455 months, Splenomegaly Yes 300 BUSULFAN/HYDROXYUREA (10) Percent survival 37 200 MONTHS Ethnicity Caucasian 100 3: Overall Survival by Treatment Group in Polycythemia Vera Patients that were treated with combination of Busulfan and Hydroxyurea had the longest survival of 492 months, while Busulfan alone had the longest survival of 457 months, 1. Zittoun R, the EORTC Leukemia and Haematosarcoma Cooperative Group. Busulfan versus 32P in polycytheaemia vera. Drugs Exp Clin Res 1986;12:283-6 2. Brodsky I. Busulphan treatment of polycythemia vera. Br J Haematol 1982;52 3. :1-6.