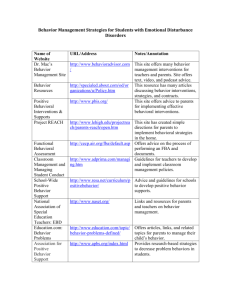
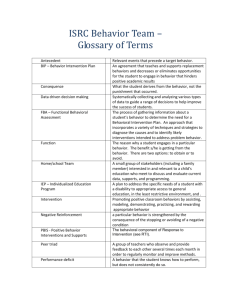
1 major issues in health promotion and disease prevention.

QCC HE 114 Syllabus:
Department: Health, Physical Education and Dance
Course: HE-114 Health Promotion and Disease Prevention
Prerequisite: HE 101 or 102
Hours & Credits: 3 hours/3 credits
Course Description: The purpose of this course is to provide an overview of the major issues in health promotion and disease prevention.
Students will be introduced to the major causes of premature mortality and morbidity and the behavioral and environmental contributions to illness and injury. Strategies for risk reduction and the development and implementation of interventions will be presented. Emphasis will be placed on understanding
the economic, political, and ethical considerations that may
impact the implementation and effectiveness of interventions.
Curricula For Which This Course Was Developed:
HE 114 is a free elective in the Department of Health,
Physical Education and Dance.
Educational Objectives
Educational Objective Brief description of course activities which help students to meet each of the educational objectives
Students will write summaries and reactions to newspaper articles on current topics in health promotion and disease prevention.
A.
Students will communicate effectively through reading, writing, listening, and speaking
B.
Students will use analytical reasoning to identify issues or problems and evaluate evidence in order to make informed decisions
C.
Students will integrate knowledge and skills in their major field and across disciplines
D.
Students will work collaboratively in diverse groups directed at accomplishing learning
objectives
Students will select a focus area for a health promotion intervention. Based on class lectures and outside readings, students will develop an intervention strategy for the target population they select.
Students will relate biology, psychology and sociology to the study of health promotion and disease prevention.
Students will present a group project on a health promotion intervention topic.
1
Curricular Objectives
A. Students will identify the leading causes of disease and death by age, gender, and national origin.
Students will identify disease trends and major causes of morbidity and mortality in the U.S.
Students will compare the health improvement priorities in the U.S. with that of other developed countries.
B. Students will describe the major behavioral and environmental risk factors for disease and injury.
Students will analyze the factors that have contributed to the escalating problems of obesity, mental illness, alcohol and other drug abuse, and tobacco use in the U.S.
Students will discuss the impact of the HIV/AIDS pandemic on public health activities.
C. Students will examine the social determinants of health.
Students will identify ways to create physical and social environments that promote good health.
Students will discuss the impact of socioeconomic conditions on quality- of-life, health risk factors, and health outcomes.
D. Students will describe health behavior models and theories of health behavior change.
Students will compare the major theoretical models of health behavior change.
Students will examine the value of theoretical models in providing direction for intervention development.
E. Students will examine public policy as it relates to health promotion and disease prevention implications.
Students will examine public health programs designed to reduce racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic health disparities in the U.S.
Students will examine public funding policies influencing health
F. Students will identify political and economic influences on health and disease in the U.S.
Students will examine the impact of governmental health reform bills on communitybased intervention programs.
Students will analyze healthcare spending in the U.S. And the debate over universal coverage.
G. Students will describe successful health intervention programs in the U.S.
Students will examine community-based public health initiatives designed to identify and improve behavioral and environmental factors influencing health.
Students will analyze the cost-effectiveness of community-based public health interventions
H. Students will describe the major social, cultural, economic, political, and environmental forces affecting the health of people around the world.
Students will analyze global health risks and health disparities and the various influencing factors.
Students will identify strategies to promote health globally.
2
Summary of Main Topics Covered in the Course
Major causes of morbidity and mortality in the U.S. and worldwide; Major risk factors for disease and injury; Social determinants of health; Health behavior models; Social, political, economic, and environmental factors influencing health; Design and maintenance of health promotion intervention programs
Required Texts/Readings
Required: Hubley, J., Copeman, J., & Woodall, J. (2013) Practical Health Promotion (2 nd
ed.)
Web Resources: www.healthy people.gov www.cdc.gov/healthyliving/ www.nytimes.com
Methods By Which Student Learning Will Be Evaluated
A.
Class Exams
B.
Final Exam
C.
Completion of assigned article summaries
D.
Group project/presentation
E.
Class Participation
Course Outline
Week 1 Course Outline; Levels of Disease Prevention
Week 2
Week 3
Week 4
Morbidity and Mortality Trends; Risk Factors
Global Health Issues
Health Care in the U.S.
Week 5
Week 6
Week 7
Week 8
Week 9
Week 10
Social Determinants of Health
Healthy People 2020; Health Behavior Models
Health Promotion Intervention; Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Obesity
Health Promotion Intervention; Substance Abuse and Tobacco Use
Health Promotion Interventions; Mental Health and Diabetes
Health Promotion Interventions; Reproductive and Sexual Health
Week 11
Week 12
Health Promotion Intervention; Heart Disease and Cancer
Presentations
3