Problem Set 1 Due Friday Sept. 19, 2014
advertisement

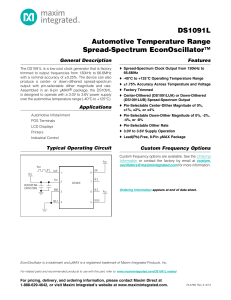
University of California, Berkeley EECS 242B Fall 2014 Prof. A. Niknejad Problem Set 1 Due Friday Sept. 19, 2014 For simulations, use the transistor model card from the PTM 65nm node (http://ptm.asu.edu/latest.html). In particular, use the BSIM4 model cards released on Feb. 22, 2006 (http://ptm.asu.edu/modelcard/2006/65nm_bulk.pm). Cµ Ri rx Cπ + vπ − gm vπ go 1. Given a simple transistor model with gate/base resistance Rx , input capacitance Cπ in series with rx (modeling NQS in a FET), feedback capacitance Cµ , and output resistance ro and transconductance gm , perform the following calculations: (a) Begin by neglecting Cµ and calculate the power gain and the fmax (or equivalently, the highest frequency when power gain > 1). (b) Calculate the maximum gain. Try to simply your calculations. You may want to consider the stability factor K or alternatively Mason’s Unilateral Gain U . (c) Derive fmax , or the maximum frequency of oscillation fmax . Under what √ conditions is fmax proportional to fT versus proportional to fT ? 2. Using the class provided transistor models, plot the GM SG /Gmax and Unilater gain U for the transistor versus frequency. Using a minimum channel length device, let W = 10µ and bias the transistor with VGS = VDD = 1.2V. (a) Sweep Vgs and plot fmax by taking the extrapolated U = 1 frequency point. (b) Compare the simulations to the hand calculated value of fmax . Use the mid-frequency two-port parameters to derive an equivalent circuit model of the previous problem and use your hand calculations to predict fmax . 3. Consider a multi-stage amplifier using inter-stage matching. Suppose a differential pair sized at W = 10µm is driving an output stage with W = 50µm. (a) Use a differential inter-stage LC matching network to provide optimal voltage swing on the gate of the second stage to provide maximum output power. What is the bandwidth of the match if we can tolerate 0.5 dB of gain variation due to the matching network? (b) Derive the transfer function of a transformer for inter-stage matching. Note that the transfer function has two poles which can be optimized to maximize the bandwidth. Design for maximum bandwidth and allow for 0.5 dB of gain variation due to the matching network. (c) Simulate your designs and compare. What are some of the benefits and drawbacks of the transformer coupled approach? 2