Problem Set 7 (Rev B) Due Wednesday (5pm), April 11, 2012
advertisement
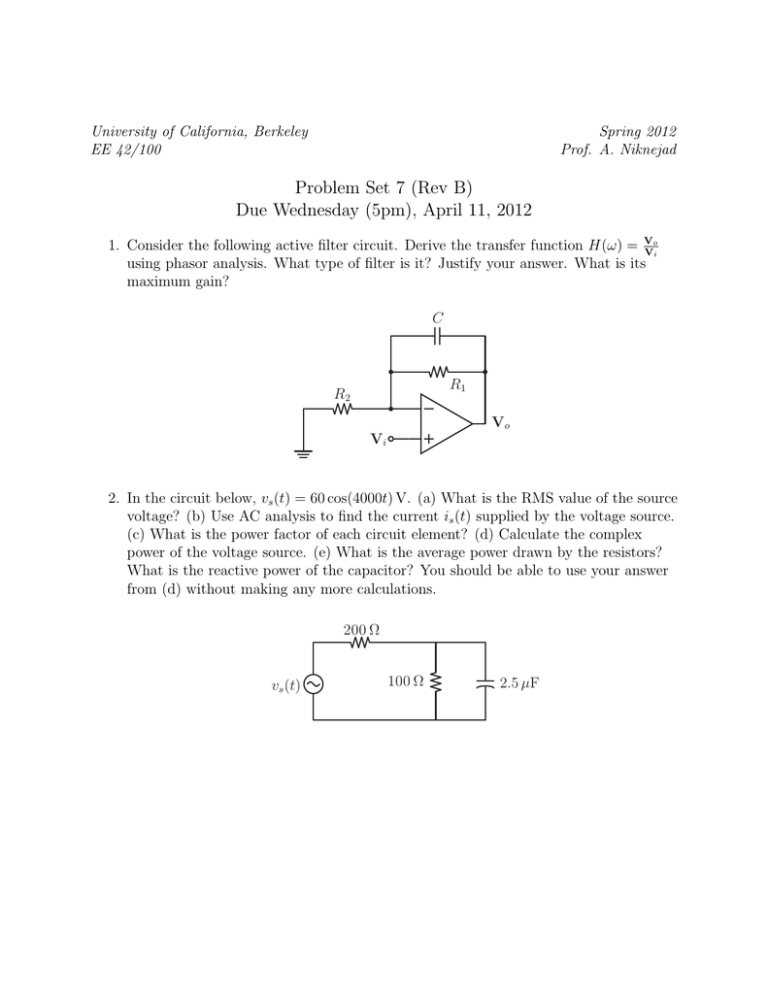
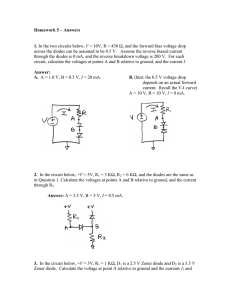
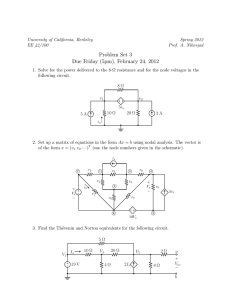
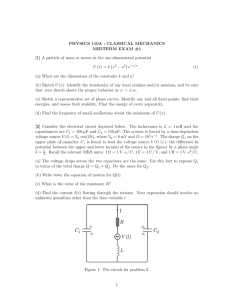
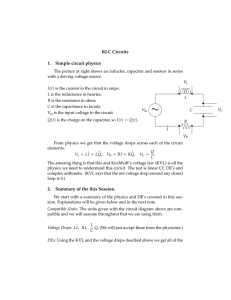
University of California, Berkeley EE 42/100 Spring 2012 Prof. A. Niknejad Problem Set 7 (Rev B) Due Wednesday (5pm), April 11, 2012 o 1. Consider the following active filter circuit. Derive the transfer function H(ω) = V Vi using phasor analysis. What type of filter is it? Justify your answer. What is its maximum gain? C R1 R2 Vo Vi 2. In the circuit below, vs (t) = 60 cos(4000t) V. (a) What is the RMS value of the source voltage? (b) Use AC analysis to find the current is (t) supplied by the voltage source. (c) What is the power factor of each circuit element? (d) Calculate the complex power of the voltage source. (e) What is the average power drawn by the resistors? What is the reactive power of the capacitor? You should be able to use your answer from (d) without making any more calculations. 200 Ω vs (t) 100 Ω 2.5 µF 3. Determine the average power delivered to the load RL in the circuit below, given that vin (t) = 0.5 cos(2000t) V. 0.1 µF 10 kΩ vin (t) 1 kΩ RL 1 kΩ 4. Use the maximum power transfer theorem to determine the load impedance ZL so that it will draw the maximum average power from the circuit. 2000I x + − j 4 kΩ 3 kΩ 6 kΩ 8 0 mA ZL Ix 5. Find the values of I and V in the circuit below, assuming that the diodes are all ideal. +20 V 200 Ω 200 Ω 200 Ω I +V− 2 200 Ω − 20 V 6. Sketch vo versus vin to scale for the circuit below, assuming that the diodes are ideal. The Zener diode has a breakdown voltage of 5 V. 1 kΩ 1 kΩ vin + 5V + vo − 7. Sketch the output waveform vo (t) for the circuit below, where vs (t) = 10 sin(t) V. Assume that the diodes are ideal and that the Zener diode has a breakdown voltage of 5 V. Also, RC is much larger than the period of the input voltage. C vs (t) R 5V 3 + vo(t) −