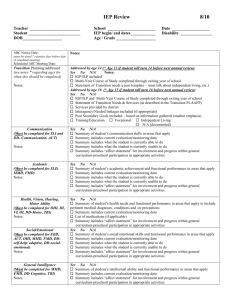
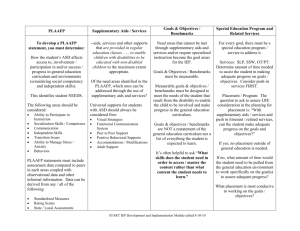
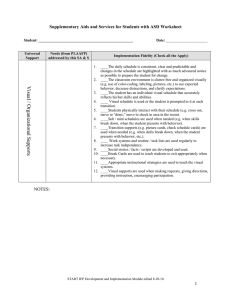
PLAAFP Reminders
advertisement
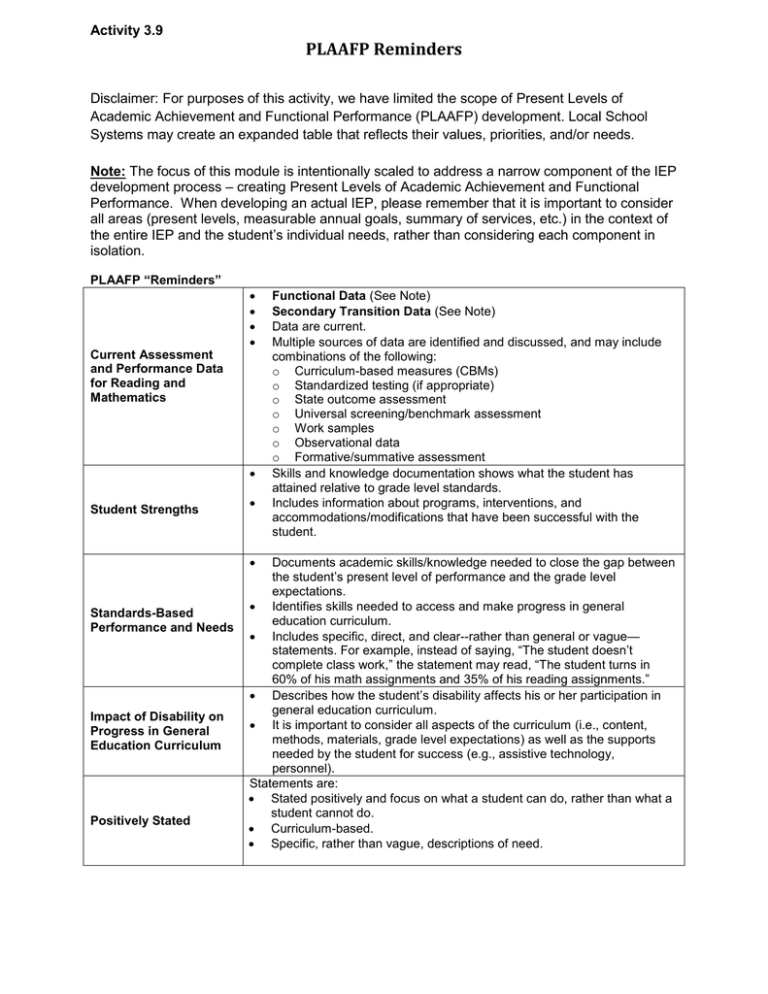
Activity 3.9 PLAAFP Reminders Disclaimer: For purposes of this activity, we have limited the scope of Present Levels of Academic Achievement and Functional Performance (PLAAFP) development. Local School Systems may create an expanded table that reflects their values, priorities, and/or needs. Note: The focus of this module is intentionally scaled to address a narrow component of the IEP development process – creating Present Levels of Academic Achievement and Functional Performance. When developing an actual IEP, please remember that it is important to consider all areas (present levels, measurable annual goals, summary of services, etc.) in the context of the entire IEP and the student’s individual needs, rather than considering each component in isolation. PLAAFP “Reminders” Current Assessment and Performance Data for Reading and Mathematics Student Strengths Standards-Based Performance and Needs Impact of Disability on Progress in General Education Curriculum Positively Stated Functional Data (See Note) Secondary Transition Data (See Note) Data are current. Multiple sources of data are identified and discussed, and may include combinations of the following: o Curriculum-based measures (CBMs) o Standardized testing (if appropriate) o State outcome assessment o Universal screening/benchmark assessment o Work samples o Observational data o Formative/summative assessment Skills and knowledge documentation shows what the student has attained relative to grade level standards. Includes information about programs, interventions, and accommodations/modifications that have been successful with the student. Documents academic skills/knowledge needed to close the gap between the student’s present level of performance and the grade level expectations. Identifies skills needed to access and make progress in general education curriculum. Includes specific, direct, and clear--rather than general or vague— statements. For example, instead of saying, “The student doesn’t complete class work,” the statement may read, “The student turns in 60% of his math assignments and 35% of his reading assignments.” Describes how the student’s disability affects his or her participation in general education curriculum. It is important to consider all aspects of the curriculum (i.e., content, methods, materials, grade level expectations) as well as the supports needed by the student for success (e.g., assistive technology, personnel). Statements are: Stated positively and focus on what a student can do, rather than what a student cannot do. Curriculum-based. Specific, rather than vague, descriptions of need.