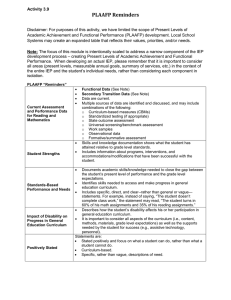
PLAAFP RUBRIC COMPANION 1. The PLAAFP includes data from multiple sources (evaluations, classroom data, accommodations and/or modifications, information from the family, and additional supports). A. Evaluations (such as FIE, STAAR, FBA, norm or criterion test results, etc.): i. The PLAAFP identifies and describes the disability condition that is reported in the FIE. ii. The PLAAFP includes how the student’s disability affects the student’s access to, participation in, and progress in the general education curriculum (for preschool students, how the disability affects the student’s participation in appropriate activities). B. Classroom data (such as anecdotal notes, checklists, inventories, rubrics, work samples, behavior reports, student interest surveys, etc.): i. The PLAAFP reports progress on the previous year’s IEP goals in measurable terms (criterion). ii. If there is a lack of progress noted from the previous year, the PLAAFP includes an explanation. C. Accommodations/Modifications: i. The PLAAFP includes specific statements about adaptations (conditions) that help the student access and make progress in the curriculum. ii. The PLAAFP includes quantifiable data to demonstrate justification for why the adaptations (conditions) are needed. D. Information from the family (such as student health, behavior in settings outside school, changes in home environment, outside services, community activities, student preferences and interests, etc.) E. Additional Supports (related services, speech therapy, assistive technology): i. The PLAAFP includes quantifiable data to demonstrate justification for why the supports are included in the IEP. Current performance in related services areas should be included. 2. The PLAAFP includes observable and measurable baseline data that identify the student’s strengths and critical areas of need. 3. The PLAAFP reflects the strengths and critical areas of need in the enrolled grade-level curriculum and in functional areas (such as communication, social skills, and self-help skills). A. For transition age students, the PLAAFP includes areas of education (post-secondary, continuing, adult), vocational/ employment, independent living, adult services, and/or community participation. Evaluations Xxx is a 3rd grade scholar at (school) in the RISE (self-contained) and general education classrooms. According to her most recent evaluation dated 10/11/2023, Xxx qualifies as a student with a Speech Impairment in the areas of expressive and pragmatic language. Evaluation is current. Evaluations are conducted every 3 years. Goal Progress Xxx is making steady progress with her goals. She met 4 of 4 goals. Xxx required moderate verbal/visual cues. Student’s strengths Xxx is motivated and participates in Speech Therapy activities with a smile. She has a lively personality and is a joy to work with. She enjoys interacting with others and sharing her experiences, feelings, and desires. She greets others appropriately and is very friendly. She appropriately responds to redirection in speech and follows classroom rules. She is polite and respectful. Xxx has strong receptive language skills when she understands the assignment. Xxx is able to self-correct when she realizes she has misarticulated or answered incorrectly. Xxx benefits from completed examples. Student’s critical areas of need Xxx’s expressive language is slightly below average. While she is able to use most parts of speech at an age-appropriate level, Xxx needs additional support with expressive semantics. Semantics look at meaning in language and the relationship between words. Semantic skills refer to the ability to understand and convey meaning in different types of words, phrases, narratives, signs, symbols and the meaning they give to the speaker and listener. Difficulties with semantic skills can lead to children not fully understanding what has been said or not fully making their ideas understood. Xxx can also grow in the area of pragmatics in respect to taking conversational turns appropriately, and using appropriate voice levels. Goals and accommodations are recommended to support deficits. Recommendations It is recommended that Xxx continue to receive Speech Therapy in the school setting to address Speech Impairment in the areas of expressive and pragmatic language.