Parent Education Meeting February 16, 2016
advertisement

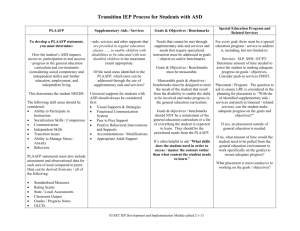
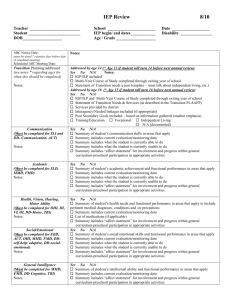
Parent Education Meeting February 16, 2016 Agenda • Understanding PLAAFPS • Understanding IEPs • State Assessment – STAAR, STAAR-A, and STAAR-ALT PLAAFP stands for... Present Level (PLAAFP) utilizes CURRENT data Academic Achievement (PLAAFP) focuses on what specific kinds of academic information and skills the student has mastered – such as reading at a certain grade level / rate, or performing certain mathematical calculations for example. Functional Performance (PLAAFP) refers to other areas of achievement that are not academic. It can include information about your child’s social skills, communication skills, and other activities of daily living (ADL). TEA Resource Region 20 IEP Goad Development Q & A Document revised 6/14/2015 Develop the PLAAFP • Strengths & Needs – What do we know about the student’s response to academic instruction? – What programs, accommodations and/or interventions have been successful? – What have we learned form previous IEPs and student data that can inform decision making? – Are there assessment data (i.e., state, district, classroom, formal) that can provide useful info about strengths & needs (patterns in data?)? Develop the PLAAFP • Factors related to disability – How does the disability affect participation and progress in the general curriculum? – What supports does the student need to learn and attain skills to progress in the general curriculum? – Is the student on track to achieve grade level proficiency within the year? PLAAFP is the basis on which the ARD Committee will write goals for the student’s Annual Review year. After reading the PLAAFP, we should know… 1. How the child’s disability affects the involvement & progress in the general education curriculum 2. Current Progress 3. Current accommodations & modifications 4. Student’s strengths / needs 5. Current supports the student used in the year 6. Baseline data TEA Resource • Region 20 IEP Goal Development Q & A Document revised 2015 Questions 1.15, 1.16, 1.17 & 1.18 • Measurable annual goals are developed from information contained in the PLAAFP • Separate goals will need to be written for each subject area where the PLAAFP indicates a critical need • The PLAAFP provides the baseline of where the student is performing. That information is then used to determine the progress that can be reasonable expected in 1 year PLAAFP Short Term Objectives Annual Goal Annual Goal OBJ. #3 OBJ. #2 OBJ. #1 PLAAFP STAAR ALT 2 participants MUST have at least 2 objectives per academic goal Success Ed has identified Five PLAAFP areas: • Physical • Behavior • Discipline • Functional • Academic PLAAFP Annual Goal 1. trace her name with assistance, 2. bath, eat & dress herself 3. likes nursery rhymes and country music 4. likes looking at picture books 5. match some colors and shapes 6. responds to verbal praise and OBJ. #2 reinforcers 7. repeats words/phrases OBJ. #1 PLAAFP Short Term Objectives OBJ. #3 Annual Goal: Kelly will solve mathematics problems using visual support 7 out of 10 times PLAAFPs in Success Ed • SE IEP Goals – Student Narrative • SE Manager – Physical – Behavior – Discipline – Functional…including • Transition • Vocational • communication skills – Academic PLAAFPs that give a good picture of the student follow these steps… Define how the student's disability affects their involvement and progress in the general curriculum Describe the student as of today and indicate amount of progress over the past year(s) Defines your data source – use both qualitative & quantitative Baseline data is measurable / observable / comparative Define how the student's disability affects their involvement and progress in the general curriculum This defines why they needed special education for the disability. Do not use disability / eligibility condition but how the disability affects them in the educational setting. How does this weakness get in the way of doing well in the general education curriculum (TEKS)? Describe the student as of today and indicate amount of progress over the past year(s) 1. What are the current accommodations / modifications in place? 2. Knowing data on student performance “with / without” certain specially designed instruction provides justification for why a particular acc / mod is included in the IEP 3. Helpful if an Accommodation Request Form (ARF) is needed for state testing Describe the student as of today and indicate amount of progress over the past year(s) • Accommodations change the how of learning • Modifications change the what of learning Accommodations ARE… ARE NOT… • Service or support that helps students access content and instruction • Changes to content or performance expectations • Allows student to accurately demonstrate what he/she knows • Major changes to standards • Alterations to the big idea or learning outcome (Nolet & McLaughlin, 2005) Modifications “Practices and procedures that change the nature of the task or target skill.” (TEA IEP Q & A 2013) ARE… Modifications • Changes to content or performance expectations • Thoughtfully planned and tightly aligned to enrolled grade-level standards • Used when “all” accommodations have been exhausted ARE NOT… • “Dumbing Down” the curriculum • Reducing a student’s opportunity to learn critical knowledge and skills • Teaching off grade level, resulting in greater gaps (Content courtesy of the IRIS Center, Peabody College, 2004) How do I know which it is? • It all depends on the standards… – What is the intent of the goal / standard? *what should student know and be able to do? *what ways must student demonstrate competency of the standard? – How does the teaching strategy / practice / procedure impact the integrity of the content standard? How do I know which it is? • The important concept is not what particular strategy is an accommodation but the purpose of that accommodation. It is something that offsets the impact of the disability without changing the content standard or performance expectation. • In contrast, a modification, whatever it may be, and it could be exactly the type of strategy or device that is mentioned under an accommodation, but in this case when it is applied, it actually changes or alters the content standard or the performance expectation. Margaret McLaughlin, Ph.D., Department of Special Education, University of Maryland, Courtesy of IRIS Center, Peabody College, 2004 Know the TEKS • Readiness Standards • Supporting Standards • Essence Statements “Shorten Assignments” • When might we recommend this? • When is it an accommodation? • When is it a modification? “Calculation Device” to help with Xs • 4th Grade Standard (4.4) Number, operation, and quantitative reasoning. The student multiplies and divides to solve meaningful problems involving whole numbers. The student is expected to: (D) Use multiplication to solve problems (no more than two digits times two digits without technology) • 8th Grade Standard (8.2) Number, operation, and qunatitative reasoning. The student selects and uses appropirate operations to solve problems and justify solutions. The student is expected to: (D) Use multiplication by a given constant factor (including unit rate) to represent and solve problems involving proportional relationships including conversions between measurement systems. Accommodation or Modification? Adaption Adding more white space to a test or assignment Providing a student with a list of five words to include in a chapter summary A student is to learn six new words when the standard state that 10 new words will be learned Allowing a student to respond orally to test questions rather than taking a written test The student uses an alternate curriculum rather than the general education curriculum for a specific subject level Acc Mod Accommodation or Modification? Adaption Adding more white space to a test or assignment Providing a student with a list of five words to include in a chapter summary A student is to learn six new words when the standard state that 10 new words will be learned Allowing a student to respond orally to test questions rather than taking a written test The student uses an alternate curriculum rather than the general education curriculum for a specific subject level Acc Mod State Assessments • STAAR • STAAR-A (Participation Requirements) • STAAR-ALT (Participation Requirements) STAAR & STAAR-A STAAR A is the same as STAAR in the following ways: • Same passing standards • Same time limits • Same assessed curriculum • Same test blueprint • Same progress measures STAAR vs. STAAR-A STAAR A is different than STAAR in the following ways: • STAAR A contains accommodated STAAR test questions and selections; however, • not necessarily the same ones as STAAR on the day of the test • No field test questions (this applies to EOC only since STAAR 3-8 have no field test • items in 2016) • Online administration • Embedded accommodations and accessibility features • Braille and Spanish versions of the assessment are not available