VOC’s
advertisement

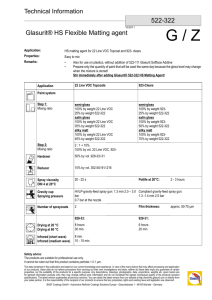
VOC’s Review of Signs and Symptoms People with allergies have hyperactive immune systems that think harmless things, such as pet dander, are dangerous. Their bodies react to try to fight off the danger. Allergies -itchy, stuffy nose, red eyes, coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, rash Asthma is a disease that causes inflammation and narrows the airways, making it difficult to breathe Asthma- coughing , wheezing, chest tightness, shortness of breath What are VOC’s? VOC’s are volatile organic compounds In short term exposure they can aggravate asthma and allergy symptoms Those with asthma may be even more susceptible to VOC’s Long term exposure can lead to an increased risk for cancer, liver damage, kidney damage, or nervous system damage Review Question 1 Which of these is not a risk from exposure to VOC’s? A) cancer B)liver damage C)kidney damage D) cystic fibrosis Where are they found in the home? Flooring Carpet Carpets can emit VOC’s when installed. The latex backing on carpet can also emit them. Vinyl flooring Made with PVC resin mixed with plasticizers and fungicides Wood flooring Stain on wood flooring contains VOC’s Where are they found in the home? Household Items Paint/Stain-Paints have heptane in them, which is like gasoline. Air fresheners- Contain naphthalene which can cause cancer or negative reproductive effects. Cosmetics-Acetone, alcohol, isopropyl alcohol can cause respiratory problems. Printers- Inks in printers can cause respiratory issues. Where are they found in the home? Chemicals and Fumes Space heaters Cleaning chemicals Wood burning stoves Fuel oil/gasoline-benzene, toluene Vehicle exhaust in an attached garage How can I tell if I have too much exposure? Frequent headaches or nausea Eye, nose, or throat irritation Skin reactions Difficulty breathing Vomiting Nose bleeds Dizziness Review Question 2 Which of these are signs of too much VOC exposure? A) headaches B) nose bleeds C)difficulty breathing D) all of the above How can I protect my family? Install new carpet only when necessary If you need new carpets, make sure installers use tack strips instead of adhesives Use water filters on faucets to reduce chances of VOC’s getting through to drinking water Do not dry clean clothes unless absolutely necessary How can I reduce exposure to VOC’s? Make sure your house is vented properly Keep humidity as low as possible. High humidity can increase VOC emissions. Perform renovations when your home is unoccupied or in summer months when ventilation is easier. What is a bake out? A bake out is used after construction or renovation. You should heat the house to a temperature around 100 F, then open all the windows , repeating the process for two or three days The idea is to emit all the VOC’s in a short period of time and get them out of the house rather than a small amount over a long period of time If you choose this option, you should not go back into the house for at least a week. Review Question 3 How long should you wait before going back into a house after a bake out? A)3 days B) One week C) One month D) 5 days What are low VOC alternatives? Cleaning products- Use BioKleen, Seventh Generation, or Earth Choice Switch to fabric shower curtains Paint with low VOC’s If possible use wool or cotton rugs instead of installing new carpeting Review Question 4 TRUE or FALSE Zero VOC paints are non-toxic. References Aerias. (2011). IAQ problems associated with different types of flooring. Retrieved from http://www.aerias.org/DesktopModules/ArticleDetail.aspx ?articleId=107 Cernasky, R. (2010). Low-VOC alternatives for the products that expose you to the greatest risk. Retrieved from http://planetgreen.discovery.com/home-garden/low-vocalternatives-products-that-expose-greatest-risk.html# Clement, C. (2005) What’s on your floor? Retrieved from http://www.alive.com/3131a6a2.php?subject_bread_cramb =110 References Minnesota department of health. (2011). Volitile organic compounds in your home. Retrieved from http://www.health.state.mn.us/divs/eh/indoorair/voc/ New York department of health. (2011). VOC’s in commonly used products. Retrieved from http://www.health.state.ny.us/environmental/indoors/ voc.htm Propex. (2005). VOC’s in the home. Retrieved from http://www.propex.com/C_f_env_voc.htm United States environmental protection agency. (2011). An introduction to indoor air quality. Retrieved from http://www.epa.gov/iaq/voc.html Quiz Answers 1) D 2)D 3)B 4)False